Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment: Months-Long Building Contamination
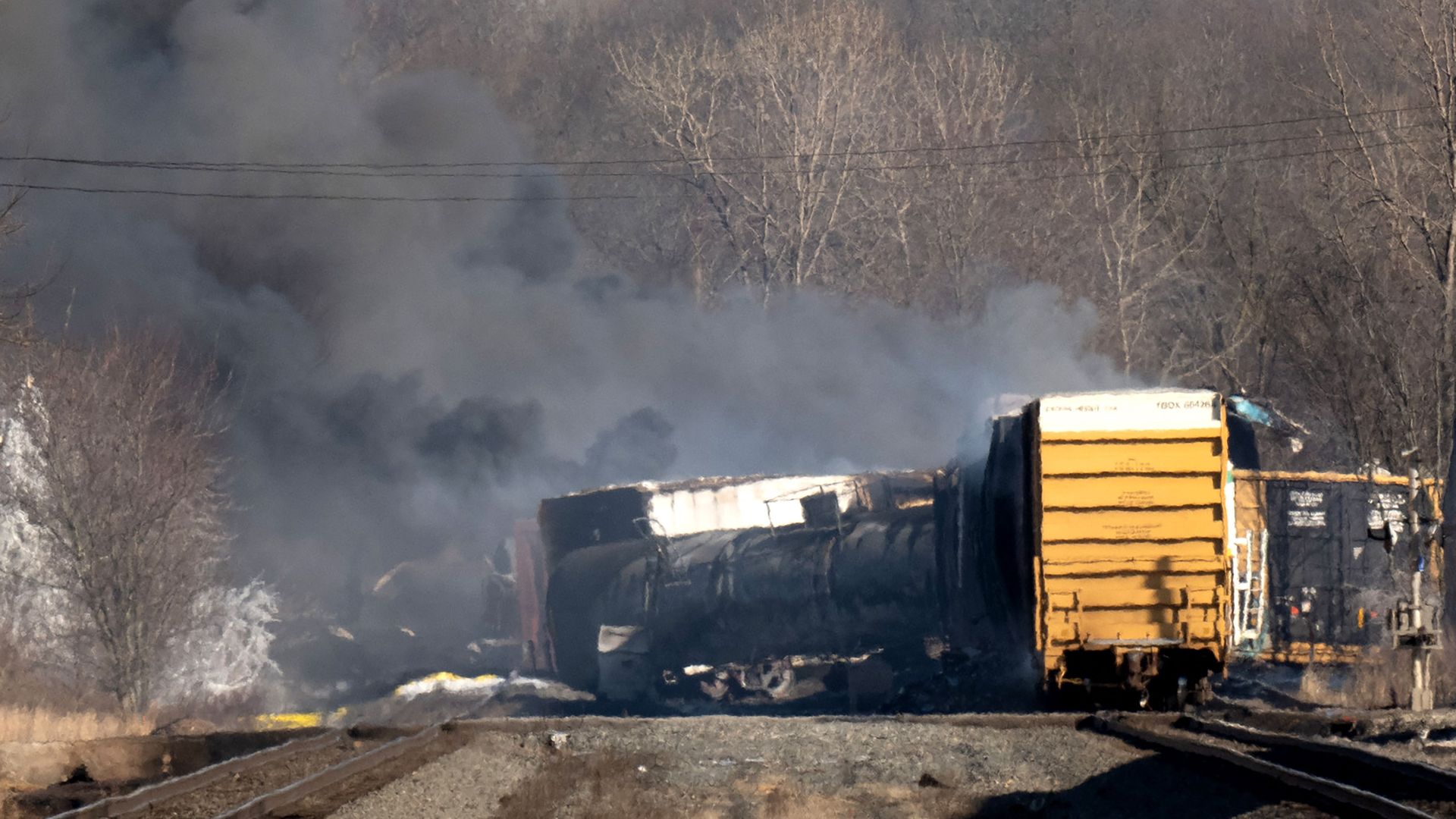

Table of Contents
Identifying the Toxic Chemicals Involved
The derailment resulted in the release of numerous hazardous materials, posing significant risks to both the environment and human health. Among the most concerning were vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen, and butyl acrylate, an irritant that can cause respiratory problems. Understanding the specific chemicals released is crucial to assessing the extent of the Ohio train derailment contamination.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) [link to CDC resource] and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) [link to EPA resource] provide detailed information on the health risks associated with these chemicals.
- Vinyl Chloride: Short-term effects include dizziness, headaches, and nausea. Long-term exposure is linked to an increased risk of liver cancer and other serious health problems. Its persistence in the environment adds to the long-term Ohio train derailment contamination concerns.
- Butyl Acrylate: Short-term exposure can cause skin and eye irritation, respiratory issues such as coughing and shortness of breath. Long-term effects are less well-understood but may involve chronic respiratory problems.
The presence of these and other chemicals necessitates a thorough assessment of the Ohio train derailment contamination across all affected areas.
Pathways of Building Contamination
The toxic chemicals released from the derailment infiltrated buildings through various pathways, leading to widespread building contamination. This contamination poses a significant, long-term health risk. Understanding these pathways is vital for effective remediation strategies.
- Airborne Contamination: Chemicals escaped into the air and infiltrated buildings through cracks, windows, and ventilation systems. This airborne spread contributed significantly to the Ohio train derailment contamination.
- Waterborne Contamination: Contaminated water sources, including groundwater and surface water, could have carried chemicals into buildings through water supplies, leading to water contamination.
- Soil Contamination: Soil contaminated with chemicals can leach into building foundations, contaminating indoor environments. This represents a significant aspect of the persistent Ohio train derailment contamination.
- Lingering Contamination in Building Materials: Chemicals may have adsorbed onto building materials, leading to persistent contamination that can release harmful substances over time. This highlights the complexities of dealing with Ohio train derailment contamination.
Assessing the Extent of Building Contamination
Accurately assessing the extent of building contamination from the Ohio train derailment presents significant challenges. The wide geographical area affected and the varied nature of the released chemicals complicate the process.
Several testing methods are employed to detect the presence of these chemicals:
- Air Quality Monitoring: Measures the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the air.
- Soil Sampling: Analyzes soil samples to determine the presence and concentration of contaminants.
- Water Analysis: Tests water samples for the presence of dissolved chemicals.
However, challenges remain:
- Lack of comprehensive testing in some areas: Ensuring thorough testing across all potentially affected areas is crucial to fully understand the extent of Ohio train derailment contamination.
- Variability in contamination levels: Contamination levels vary significantly depending on proximity to the derailment site and environmental factors.
- Long-term monitoring needs: Continuous monitoring is essential to track the persistence of contaminants and the long-term impact of the Ohio train derailment contamination.
Health Impacts of Prolonged Exposure
Prolonged exposure to the chemicals released during the Ohio train derailment poses significant health risks. Both short-term and long-term effects are cause for concern.
- Respiratory Illnesses: Increased risk of asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems due to inhalation of toxic chemicals.
- Neurological Problems: Potential for neurological damage, including cognitive impairment and other neurological disorders.
- Reproductive Health Concerns: Exposure to certain chemicals can negatively affect reproductive health.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Several of the released chemicals are known carcinogens, increasing the risk of various cancers. This underscores the severity of the Ohio train derailment contamination and its long-term consequences.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Remediating contaminated buildings requires a multifaceted approach. Various techniques are employed to remove or neutralize contaminants, ensuring the safety of residents and workers.
- Air Purification Systems: Employ high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove airborne contaminants.
- Water Filtration and Treatment: Install advanced filtration systems to remove contaminants from water supplies.
- Soil Remediation Techniques: Various methods, including bioremediation and excavation, are used to remove or neutralize soil contamination.
- Building Demolition: In cases of severe contamination, demolition may be necessary to prevent continued exposure to hazardous substances.
Proper safety procedures are paramount throughout the remediation process. This ensures the safety of both residents and remediation workers dealing with the lasting effects of Ohio train derailment contamination.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing the Ohio Train Derailment Contamination
The Ohio train derailment has resulted in widespread and persistent building contamination, posing significant long-term health and environmental risks. Understanding the types of toxic chemicals involved, the various pathways of contamination, and the potential health impacts is crucial for effective remediation. The long-term nature of this Ohio train derailment contamination necessitates continued monitoring, further research, and a commitment to effective remediation strategies. We need to remain vigilant about the ongoing situation, advocate for stronger safety regulations, and support the affected communities. Stay informed, seek reliable information from sources like the CDC and EPA, and demand accountability to prevent future incidents of Ohio train derailment contamination.

Featured Posts
-
 Unintended Consequences Evaluating The Price Of Trumps Economic Vision
Apr 22, 2025
Unintended Consequences Evaluating The Price Of Trumps Economic Vision
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Will The Next Pope Continue Franciss Reforms
Apr 22, 2025
Will The Next Pope Continue Franciss Reforms
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Fsu Announces New Plan For Resuming Classes After Campus Shooting Too Soon
Apr 22, 2025
Fsu Announces New Plan For Resuming Classes After Campus Shooting Too Soon
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Razer Blade 16 2025 Performance Review Ultra Settings Gaming And Productivity
Apr 22, 2025
Razer Blade 16 2025 Performance Review Ultra Settings Gaming And Productivity
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Details On The January 6th Allegations
Apr 22, 2025
Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Details On The January 6th Allegations
Apr 22, 2025
