Trump Tariffs And India's Solar Exports To Southeast Asia: A Detailed Analysis
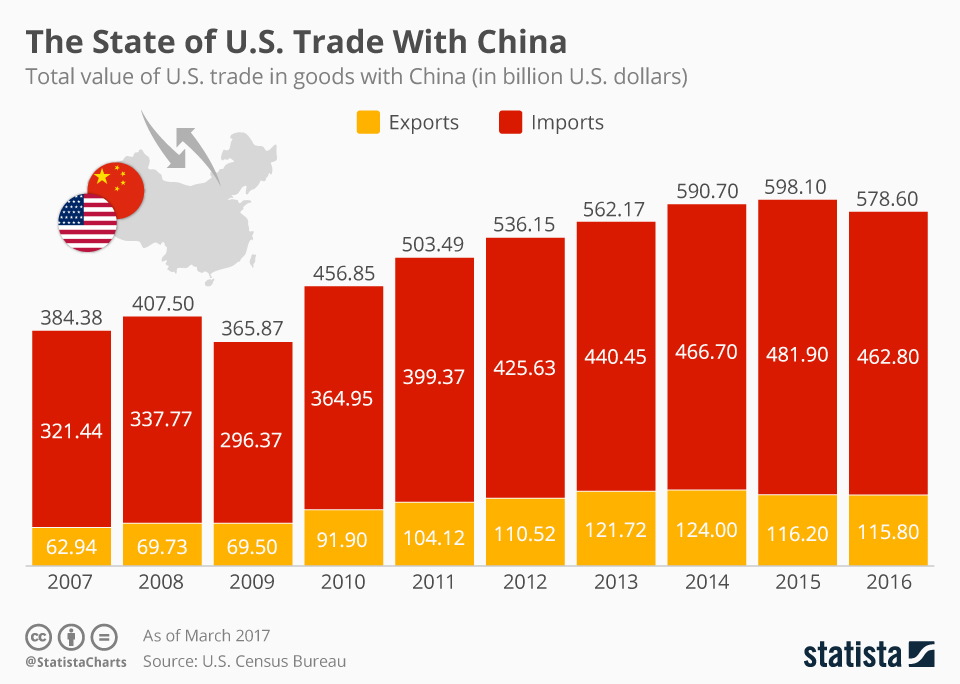
Table of Contents
The Impact of Trump Tariffs on the Global Solar Industry
Increased Costs for US Solar Projects
The Trump administration's tariffs on imported solar panels, primarily targeting Chinese manufacturers, significantly increased the cost of solar projects within the United States. This had a ripple effect throughout the global solar supply chain.
- Higher panel prices: Tariffs directly increased the price of solar panels, making solar energy less competitive compared to other energy sources.
- Project delays: Increased costs led to delays and cancellations of solar projects, hindering the growth of the US solar sector.
- Reduced competitiveness of solar energy: The higher prices reduced the attractiveness of solar energy, impacting its adoption rate and overall market growth in the US.
This situation forced a reassessment of global sourcing strategies, creating a pivotal moment for other solar panel producers, particularly those in India.
Shifting Global Solar Supply Chains
The tariffs spurred a significant shift in global solar panel sourcing. Countries like India, previously less prominent players, found themselves in a position to capitalize on the increased demand.
- Increased demand for Indian solar panels: With Chinese panels facing higher tariffs, buyers in the US and other markets actively sought alternative suppliers, leading to increased demand for Indian solar panels.
- Opportunities for Indian manufacturers: This surge in demand presented a considerable opportunity for Indian solar manufacturers to expand their market share and build stronger international partnerships.
Other countries, including Vietnam and Malaysia, also benefited from this reshuffling of the global solar supply chain, highlighting the interconnectedness of the renewable energy sector.
India's Position and Potential in the Southeast Asian Solar Market
India's Solar Manufacturing Capacity
India possesses both strengths and weaknesses concerning solar panel manufacturing. While it has demonstrated significant growth, challenges remain in achieving global competitiveness.
- Production capabilities: India has steadily increased its solar panel production capacity, driven by government initiatives and private investments.
- Technological advancements: India is actively investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of its solar panels.
- Cost competitiveness: While improving, achieving price parity with major manufacturers like those in China remains a crucial goal for Indian producers.
- Government support: Production-linked incentives and other government support programs are crucial in bolstering the domestic solar manufacturing sector.
Southeast Asia's Growing Solar Energy Demand
Southeast Asia presents a rapidly expanding market for solar energy, fueled by several key factors.
- Government policies promoting renewable energy: Many Southeast Asian nations have implemented policies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources, creating a favorable environment for solar energy projects.
- Increasing electricity demand: Rapid economic growth and rising populations are driving significant increases in electricity demand across the region.
- Falling solar panel prices (despite tariffs): While tariffs impacted prices in some markets, the overall trend of declining solar panel prices globally has made solar energy increasingly affordable in Southeast Asia.
Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia are experiencing particularly strong growth in solar energy adoption, offering significant opportunities for Indian exporters.
Navigating Trade Barriers and Challenges
Non-Tariff Barriers
Beyond the impact of Trump-era tariffs, Indian solar exporters face various non-tariff barriers in Southeast Asian markets.
- Logistics: Efficient and cost-effective logistics are critical, and challenges in transportation and infrastructure can hinder exports.
- Customs procedures: Complex customs procedures and regulations can create delays and increase costs for Indian exporters.
- Local content requirements: Some Southeast Asian countries may have local content requirements, favoring domestically produced components.
- Competition from Chinese manufacturers: Despite the tariffs, Chinese manufacturers remain major players in the global solar market and pose significant competition to Indian companies.
Strategies for Success
To overcome these challenges, Indian solar companies have adopted various strategies:
- Diversification of markets: Reducing reliance on any single market minimizes risk and ensures resilience against trade fluctuations.
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborations with local companies and distributors in Southeast Asia enhance market access and understanding.
- Investments in technology and infrastructure: Improving manufacturing efficiency and investing in modern technologies helps enhance competitiveness.
- Lobbying efforts: Advocating for favorable trade policies and agreements can help alleviate trade barriers.
The Future of India's Solar Exports to Southeast Asia
Long-Term Prospects
The long-term outlook for India's solar exports to Southeast Asia is promising, but subject to several evolving factors.
- Predictions for growth: Continued growth is expected in the Southeast Asian solar market, providing significant opportunities for Indian exporters.
- Market share: India's market share will depend on its ability to overcome trade barriers, enhance cost-competitiveness, and foster strong partnerships.
- Challenges and opportunities: Navigating geopolitical complexities and technological advancements will be crucial for sustained growth.
Policy Implications
Government policies in both India and Southeast Asia will significantly influence the future of this trade relationship.
- Trade agreements: Favorable trade agreements can facilitate increased trade and investment between India and Southeast Asian nations.
- Incentives for renewable energy adoption: Stronger incentives for renewable energy adoption in Southeast Asia create greater demand for solar panels.
- Investment policies: Attractive investment policies in India can enhance the country's solar manufacturing capacity and competitiveness.
Conclusion
The Trump-era tariffs significantly impacted the global solar industry, creating a complex trade environment. While initially challenging, these tariffs inadvertently opened doors for Indian solar exporters to expand their presence in the rapidly growing Southeast Asian market. However, success hinges on addressing non-tariff barriers, enhancing cost competitiveness, and fostering strong partnerships. Understanding the interplay between Trump Tariffs, India solar exports, and the Southeast Asia solar market is critical for shaping future energy strategies and trade policies. We encourage further research into specific case studies of successful Indian solar companies operating in Southeast Asia and a deeper dive into relevant policy documents to gain a more comprehensive understanding of this dynamic sector.

Featured Posts
-
 Se Cae Ticketmaster Noticias De Grupo Milenio Del 8 De Abril
May 30, 2025
Se Cae Ticketmaster Noticias De Grupo Milenio Del 8 De Abril
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillaz London Shows To Feature First Three Albums In Full
May 30, 2025
Gorillaz London Shows To Feature First Three Albums In Full
May 30, 2025 -
 The Serial Killers Death Bath A Detailed Examination Of The Six Dismembered Bodies
May 30, 2025
The Serial Killers Death Bath A Detailed Examination Of The Six Dismembered Bodies
May 30, 2025 -
 Silniy Shtorm Posle Anomalnoy Zhary Preduprezhdenie Mada Dlya Izrailya
May 30, 2025
Silniy Shtorm Posle Anomalnoy Zhary Preduprezhdenie Mada Dlya Izrailya
May 30, 2025 -
 Guillermo Del Toros Cryptic Frankenstein Teaser Sparks Fan Debate
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toros Cryptic Frankenstein Teaser Sparks Fan Debate
May 30, 2025
