U.S. Measles Outbreak: Tracking The Spread Of Cases
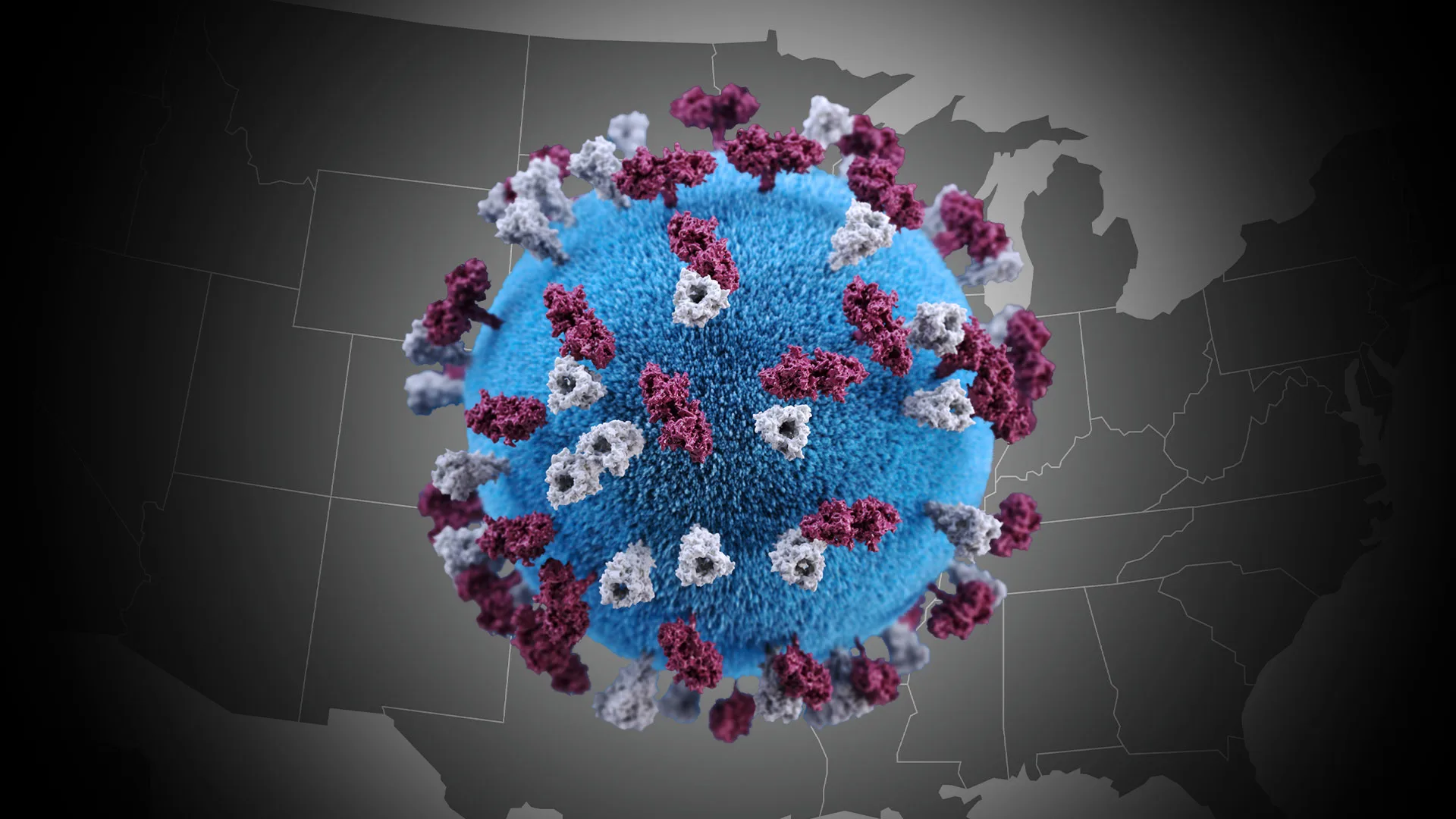
Table of Contents
Understanding the Current U.S. Measles Outbreak
The current U.S. measles outbreak presents a serious public health concern. Tracking the exact number of measles cases requires constant monitoring, as data is updated frequently. To stay abreast of the most current information, refer to the for real-time updates on measles statistics and the geographic distribution of cases. The CDC's measles outbreak map provides a visual representation of affected areas.
- Total number of measles cases reported nationally: (This needs to be updated with the current number from the CDC)
- States with the highest number of cases: (This needs to be updated with the current states from the CDC)
- Age demographics of those affected: Outbreaks often disproportionately affect unvaccinated children, but adults can also contract measles.
- Any identified common sources of infection: Recent outbreaks have been linked to international travel and clusters within unvaccinated communities.
Factors Contributing to the Spread of Measles
Measles is a highly contagious airborne disease. The measles virus spreads through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Even brief contact with an infected individual can lead to transmission. Several factors contribute to the current U.S. measles spread:
- Measles transmission: Airborne transmission makes measles incredibly easy to spread, particularly in crowded settings like schools and public transportation.
- Vaccine hesitancy: A decline in MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccination rates has significantly weakened herd immunity, allowing the virus to thrive. Misinformation and unfounded concerns about vaccine safety contribute to this hesitancy.
- Unvaccinated population: Unvaccinated individuals represent a vulnerable population and serve as reservoirs for the virus, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
- Herd immunity: High vaccination rates are vital for achieving herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated (due to medical reasons). Low vaccination rates break down herd immunity, making entire communities susceptible.
- International travel: International travel plays a significant role in importing measles into the U.S. Individuals who contract measles abroad can unknowingly spread the virus upon their return.
Preventing Further Spread of Measles
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination. The MMR vaccine is safe and highly effective in preventing measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Importance of the MMR vaccine and its effectiveness: The MMR vaccine is over 97% effective in preventing measles after two doses.
- Recommended vaccination schedule for children and adults: The CDC recommends two doses of the MMR vaccine for children, typically administered at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age. Adults who lack documented proof of vaccination should also get vaccinated.
- Public health measures such as quarantine and contact tracing: Public health officials utilize quarantine and contact tracing to contain outbreaks and prevent further spread.
- Encouraging vaccination through public health campaigns and education: Addressing vaccine hesitancy through education and public awareness campaigns is crucial for promoting vaccination rates.
Resources and Further Information
For reliable and up-to-date information on measles, consult these resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
- World Health Organization (WHO):
Conclusion
The U.S. measles outbreak underscores the importance of vaccination in protecting public health. The highly contagious nature of measles, combined with declining vaccination rates, has created a vulnerable population susceptible to widespread outbreaks. Staying informed about the U.S. measles outbreak, understanding the risks, and taking proactive steps to protect yourself and your community through vaccination are crucial. Consult your healthcare provider for vaccination advice and stay updated on the latest information from reliable sources like the CDC. Get vaccinated against measles and protect your family from this preventable disease. Learn more about measles prevention today.

Featured Posts
-
 Enhanced Emergency Response Advanced Care Paramedics In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Enhanced Emergency Response Advanced Care Paramedics In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025 -
 Man United Transfers Real Madrid Eyeing Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025
Man United Transfers Real Madrid Eyeing Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025 -
 Former Opponent Speaks Out Jon Joness Alleged Psychological Warfare Against Tom Aspinall
May 30, 2025
Former Opponent Speaks Out Jon Joness Alleged Psychological Warfare Against Tom Aspinall
May 30, 2025 -
 Carjacking Prevention On Test Drives Dealer And Buyer Responsibilities
May 30, 2025
Carjacking Prevention On Test Drives Dealer And Buyer Responsibilities
May 30, 2025 -
 Prawie 3 Lata Po Katastrofie Odrzanskiej Ryzyko Powtorki
May 30, 2025
Prawie 3 Lata Po Katastrofie Odrzanskiej Ryzyko Powtorki
May 30, 2025
