UK Energy Policy Reform: A Change Of Course? (Guido Fawkes)
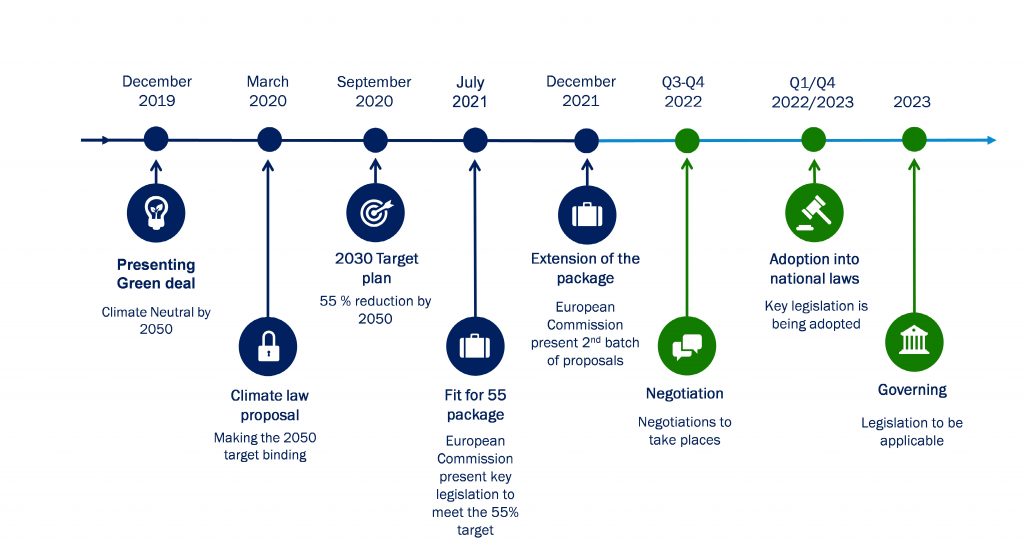
Table of Contents
The Drivers of UK Energy Policy Reform
Several interconnected factors have propelled the UK towards significant energy policy reform. These drivers are pushing the nation towards a more sustainable and secure energy future, albeit with considerable challenges.
Net-Zero Targets and Climate Change
The UK's ambitious net-zero targets by 2050 are a primary catalyst for the current reforms. Achieving this requires a rapid decarbonization of the energy sector, necessitating a fundamental shift away from fossil fuels. This ambitious goal is driving significant changes across the energy landscape:
- Increased investment in renewables: Massive investments are flowing into renewable energy sources, including onshore and offshore wind, solar power, and tidal energy. This involves substantial government subsidies, tax breaks, and streamlined planning processes to accelerate project deployment.
- Phasing out coal power plants: The UK has made significant strides in phasing out coal-fired power plants, a key step in reducing carbon emissions from the electricity sector. This transition necessitates replacing this lost capacity with cleaner alternatives.
- Incentivizing energy efficiency improvements: Government initiatives are promoting energy efficiency improvements in buildings and industries through grants, tax incentives, and stricter building codes. These measures aim to reduce overall energy consumption and lower carbon emissions.
- Development of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies: The government is investing heavily in research and development of CCS technologies, aiming to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities and store them underground, preventing their release into the atmosphere.
Energy Security Concerns
The war in Ukraine starkly highlighted the UK's vulnerability to volatile global gas markets and the risks associated with over-reliance on foreign energy sources. This has intensified the push for greater energy independence and resilience:
- Investment in domestic energy production: There's renewed focus on exploring and developing domestic energy resources, including North Sea oil and gas, albeit within the context of the transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Exploration of alternative energy sources: The search for diverse energy sources is ongoing, including exploring the potential of geothermal energy, hydrogen power, and advanced nuclear technologies.
- Strengthening energy infrastructure resilience: Upgrading and reinforcing the national grid is crucial to accommodate the influx of renewable energy and ensure a reliable and secure energy supply. This involves significant investment in smart grids and energy storage solutions.
- Diversification of energy supply chains: The government is actively working to diversify its energy supply sources, reducing reliance on any single supplier and strengthening its negotiating power in international energy markets.
Rising Energy Prices and Consumer Affordability
Soaring energy bills have placed immense pressure on households and businesses, forcing policymakers to implement measures to alleviate the burden:
- Government schemes to reduce energy bills: The government has introduced various schemes, including subsidies, price caps, and targeted support for vulnerable households, to mitigate the impact of rising energy costs.
- Support for vulnerable households: Specific programs are designed to protect vulnerable households from energy poverty, ensuring access to affordable energy.
- Measures to improve energy affordability long-term: Long-term solutions focus on improving energy efficiency, diversifying energy supplies, and fostering competition in the energy market to curb price volatility.
Key Policy Changes and their Impact
The UK's energy policy reforms are manifested in several key areas, each with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Investment in Renewable Energy
Increased funding and streamlined planning permissions are accelerating the deployment of renewable energy projects across the UK. However, several key considerations remain:
- Effectiveness of renewable energy subsidies: The long-term effectiveness of various subsidies and support mechanisms needs ongoing evaluation to ensure optimal resource allocation.
- Environmental impact of large-scale renewable projects: Balancing the environmental benefits of renewable energy with the potential impacts on biodiversity and landscape needs careful management.
- Challenges in grid infrastructure upgrades: Adapting the national grid to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources requires significant infrastructure investments and technological advancements.
Nuclear Power's Role
Nuclear power is being reconsidered as a low-carbon energy source, alongside renewables, to ensure energy security and meet net-zero targets:
- Cost and safety of nuclear power plants: The high upfront costs and safety concerns associated with nuclear power plants remain major considerations.
- Potential for small modular reactors (SMRs): SMRs are seen as a potentially more cost-effective and flexible alternative to traditional large-scale nuclear reactors.
- Public perception of nuclear power: Addressing public concerns and misconceptions about nuclear safety is vital for securing public support for nuclear power expansion.
Regulation and Market Reforms
Changes to energy market regulations aim to enhance competition, protect consumers, and drive energy efficiency:
- Impact of deregulation on energy prices: The impact of regulatory changes on energy prices needs constant monitoring to ensure a balance between competition and consumer affordability.
- Consumer rights and protections: Strong consumer protections are essential to prevent exploitation and ensure fair energy pricing and service.
- Effectiveness of market mechanisms in driving energy efficiency: The role of market-based mechanisms in incentivizing energy efficiency improvements needs continuous assessment and refinement.
Conclusion
The UK's energy policy reform signifies a significant shift, driven by climate commitments, energy security concerns, and the pressing need to address rising energy costs. While the transition to a cleaner, more secure energy system is underway, significant challenges remain. The long-term effectiveness hinges on continued investment in renewable energy, technological innovation, prudent regulation, and a steadfast commitment to achieving net-zero targets. Further research into the specific impacts of these reforms across various sectors and demographics is crucial. Understanding the complexities of UK energy policy reform is vital for navigating the evolving energy landscape. Stay informed on the latest developments in UK energy policy reform and its implications for your business and household.

Featured Posts
-
 Eneco Innomotics And Johnson Controls Partner On Gigantic Heat Pump Project
May 03, 2025
Eneco Innomotics And Johnson Controls Partner On Gigantic Heat Pump Project
May 03, 2025 -
 La Douleur Des Victimes Israeliennes Emmanuel Macron Temoigne De Son Emotion
May 03, 2025
La Douleur Des Victimes Israeliennes Emmanuel Macron Temoigne De Son Emotion
May 03, 2025 -
 Naujas Hario Poterio Parkas Sanchajuje Datos Atrakcijos Ir Kainos
May 03, 2025
Naujas Hario Poterio Parkas Sanchajuje Datos Atrakcijos Ir Kainos
May 03, 2025 -
 Kocaeli Nde 1 Mayis Kutlamalarinin Goelgesinde Kalan Arbede
May 03, 2025
Kocaeli Nde 1 Mayis Kutlamalarinin Goelgesinde Kalan Arbede
May 03, 2025 -
 Reintroducing Ow Subsidies A Potential Solution For Increased Bidding In The Netherlands
May 03, 2025
Reintroducing Ow Subsidies A Potential Solution For Increased Bidding In The Netherlands
May 03, 2025
