Understanding And Interpreting The NAV Of The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF
Table of Contents
- What is NAV and how is it calculated for the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF?
- The Relationship Between NAV and Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF Share Price.
- Interpreting NAV Changes and their Significance for Investors.
- Accessing the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV.
- Conclusion:
What is NAV and how is it calculated for the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF?
Net Asset Value (NAV) represents the net value of an ETF's assets minus its liabilities, divided by the number of outstanding shares. For the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF, this means the total value of its holdings in the 30 companies that make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average, less any expenses or liabilities, divided by the total number of ETF shares in circulation.
The calculation process is managed by Amundi, the fund manager. They meticulously track the daily market value of each holding within the ETF portfolio. This involves monitoring price fluctuations of each Dow Jones component stock. The NAV is then calculated at the end of each trading day.
-
Illustrative Example: Imagine the ETF holds shares worth $100 million in Dow Jones companies and has liabilities of $1 million. If there are 1 million shares outstanding, the NAV would be ($100 million - $1 million) / 1 million shares = $99 per share. This is a simplified example; real-world calculations are far more complex.
-
Factors Influencing Daily NAV Fluctuations: The primary driver of daily NAV changes is the movement of the Dow Jones Industrial Average itself. If the index rises, the NAV generally rises, and vice-versa. Other factors include dividend payments from the underlying stocks and any fund management fees.
-
Frequency of NAV Updates: The NAV of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF is typically updated daily, reflecting the closing prices of the constituent stocks.
The Relationship Between NAV and Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF Share Price.
While closely related, the NAV and the market price of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF shares aren't always identical. The market price is determined by supply and demand in the secondary market where the ETF shares are traded.
-
Discrepancies Between NAV and Market Price: Differences arise due to trading costs (brokerage fees, bid-ask spreads), and the overall market sentiment towards the ETF. High demand can push the market price above the NAV (a premium), while low demand may result in a discount.
-
Premium and Discount to NAV: A premium occurs when the market price exceeds the NAV, indicating strong investor demand. A discount means the market price is lower than the NAV, possibly reflecting decreased investor interest.
-
Why the Share Price Might Trade at a Premium or Discount: Market sentiment, investor expectations regarding future performance, and overall market conditions can all affect the ETF's market price relative to its NAV. For example, during periods of market uncertainty, investors might sell, creating a temporary discount.
-
Importance of Monitoring the Difference: Monitoring the difference between NAV and market price can reveal potential arbitrage opportunities (buying low and selling high). However, this requires careful analysis and understanding of market dynamics.
-
Strategies for Leveraging the Price Difference: Sophisticated investors might use the price difference to execute arbitrage strategies. However, this requires advanced trading skills and understanding of market mechanics.
Interpreting NAV Changes and their Significance for Investors.
Analyzing NAV changes over time provides insights into the performance of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF and the underlying Dow Jones Industrial Average.
-
Analyzing Long-Term NAV Trends: Tracking the NAV over extended periods helps to assess the long-term growth or decline of the investment. This provides a clearer picture than short-term fluctuations.
-
Identifying Potential Investment Opportunities: Significant changes in the NAV, especially in relation to market benchmarks, can signal potential investment opportunities. For instance, a sustained period of NAV underperformance might be an indication to reassess the investment.
-
Considering NAV Alongside Other Investment Metrics: While NAV is crucial, investors should consider it alongside other metrics such as expense ratios, historical performance, and risk tolerance when making investment decisions.
-
How NAV Informs Investment Decisions (Buy, Hold, or Sell): A rising NAV suggests positive performance, potentially supporting a hold or buy decision. Conversely, a consistently falling NAV might signal a need to reassess or even sell the investment.
Accessing the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV.
Investors can typically find the daily NAV on Amundi's official website, reputable financial news sources, and through most brokerage platforms that offer the ETF. Always ensure you're consulting reliable sources to avoid misinformation. Regularly checking the NAV is crucial for effective investment management.
Conclusion:
Understanding the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF is crucial for any investor. We've explored its calculation, the relationship between NAV and share price, and how to interpret NAV changes to inform investment decisions. Regular monitoring of the NAV, alongside other market indicators, is paramount for maximizing your investment potential. Master the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV today! Start tracking the NAV of your Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF investment now! For further resources on ETFs and investment strategies, consult your financial advisor or explore reputable online investment resources.
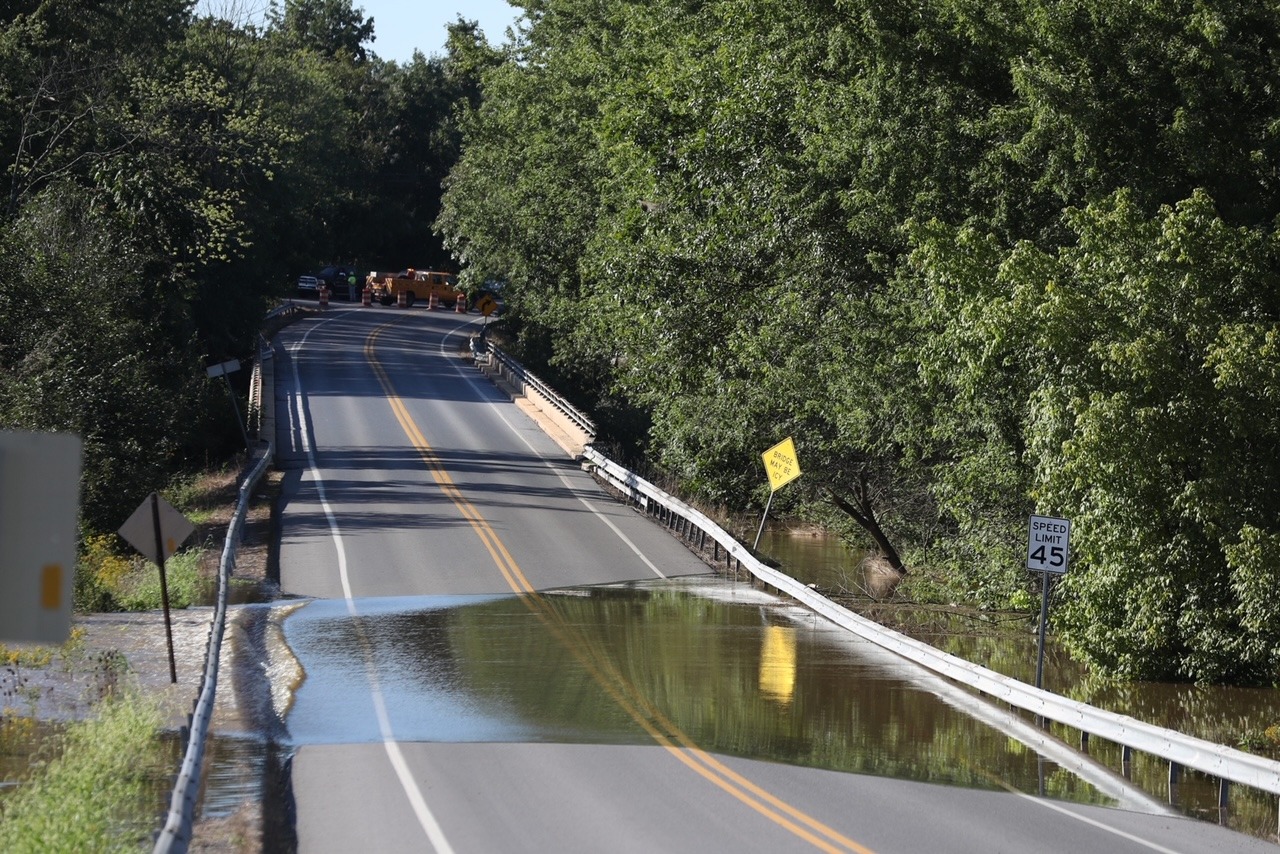
 Significant Downpours Prompt Flash Flood Warning In Pennsylvania
Significant Downpours Prompt Flash Flood Warning In Pennsylvania
 Analisi Dei Prezzi Moda Negli Usa L Influenza Dei Dazi
Analisi Dei Prezzi Moda Negli Usa L Influenza Dei Dazi
 Rsmya Mwnakw Ymdd Eqd Mynamynw Lmwsm 2024
Rsmya Mwnakw Ymdd Eqd Mynamynw Lmwsm 2024
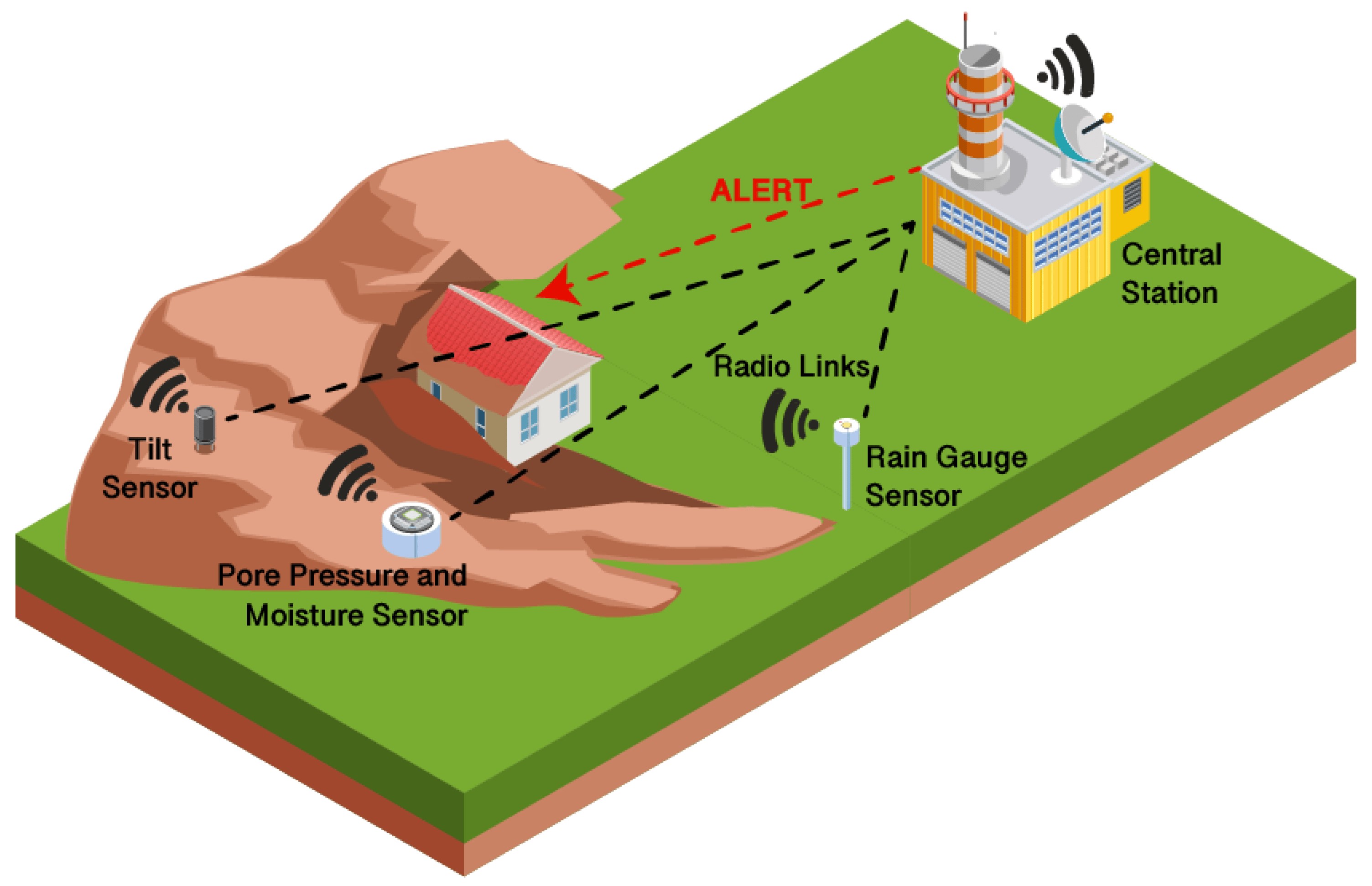 How Flood Alerts Work Early Warning Systems And Response Strategies
How Flood Alerts Work Early Warning Systems And Response Strategies
 Actress Mia Farrow Seeks Legal Action Against Trump Regarding Venezuelan Deportations
Actress Mia Farrow Seeks Legal Action Against Trump Regarding Venezuelan Deportations
