Understanding The Current Measles Outbreak In The United States
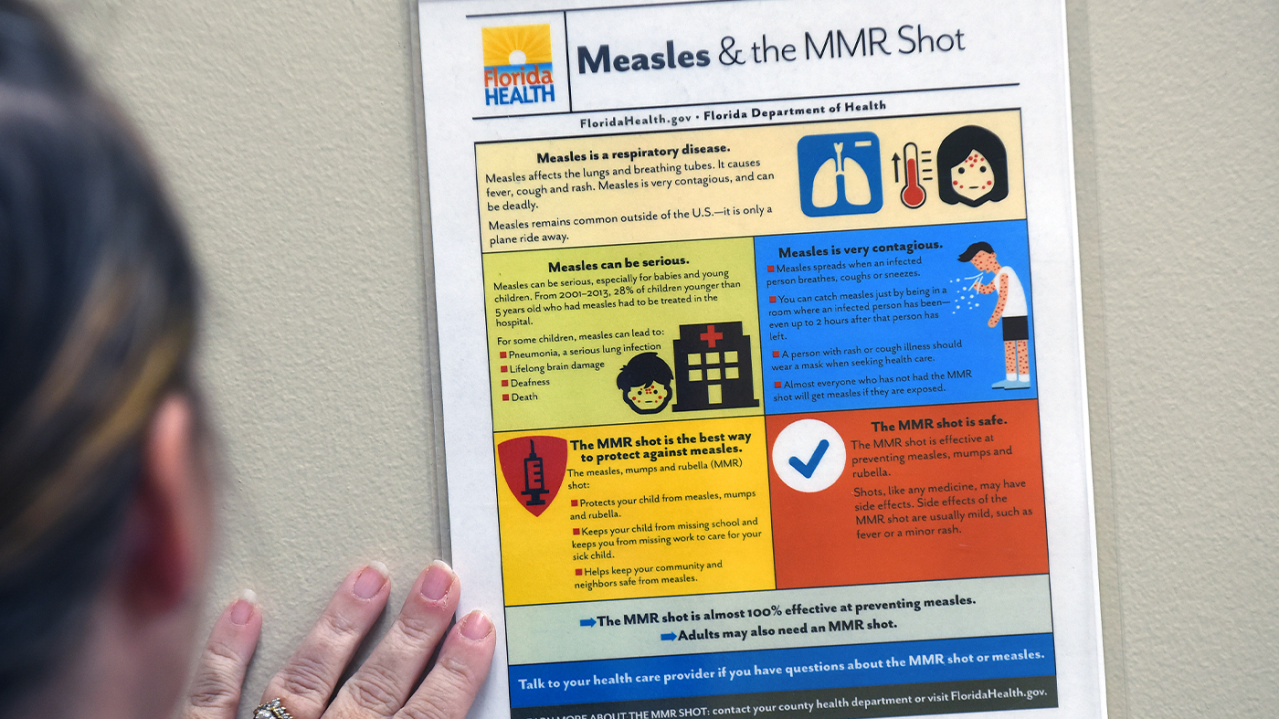
Table of Contents
Causes of the Resurgence in Measles Cases in the USA
The rise in measles cases in the US is a complex issue stemming from multiple factors. A significant contributor is the decline in vaccination rates, coupled with increased international travel and the dynamics of community transmission.
Declining Vaccination Rates
A strong correlation exists between lower vaccination rates and the increase in measles cases. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveals significant variations in MMR (Measles, Mumps, and Rubella) vaccination coverage across different states and demographics.
- Reasons for Vaccine Hesitancy: Misinformation spread through social media and distrust in medical institutions are major contributors to vaccine hesitancy. Concerns about vaccine safety, often unfounded, also play a role.
- MMR Vaccine Effectiveness: The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, with a >97% efficacy rate after two doses. This makes widespread vaccination a crucial tool in controlling outbreaks.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Public health campaigns aiming to address misinformation and build trust in the medical community are essential. Providing accurate information about vaccine safety and efficacy is crucial in combating vaccine hesitancy and improving vaccination rates across the USA.
International Travel and Importation of Measles
Measles cases imported from other countries significantly contribute to outbreaks within the US. Individuals traveling internationally can unknowingly bring the virus back and initiate community transmission.
- Outbreak Examples: Several recent outbreaks in the US have been directly linked to travelers returning from countries with higher measles incidence.
- Airport and Border Control: Improved disease surveillance at airports and border crossings is crucial for early detection and rapid response to potential outbreaks. Strengthening these measures can help prevent the importation of measles.
- Global Measles: The global landscape of measles must be considered; high incidence rates in other parts of the world necessitate vigilant monitoring and preventative measures in the US.
Community Transmission and Outbreak Dynamics
Measles is highly contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets produced during coughing or sneezing. The virus's incubation period (the time between infection and symptom onset) can range from 7 to 21 days, making containment challenging.
- Contagious Nature: The virus can remain infectious in the air for hours, leading to easy transmission in crowded spaces like schools and public transportation.
- Vulnerable Populations: Unvaccinated children and immunocompromised individuals are particularly vulnerable to severe measles complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.
- Community Spread: Understanding the patterns of community spread helps in implementing targeted interventions to control the outbreak.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Measles
Recognizing the symptoms of measles is crucial for early diagnosis and prevention of further spread. Prompt medical attention is vital to manage the illness and limit potential complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Measles typically begins with fever, cough, runny nose, and conjunctivitis (red, watery eyes). A characteristic measles rash develops a few days later, starting on the face and spreading to the rest of the body.
- Measles Rash: The rash appears as flat, red spots that may become slightly raised. Images illustrating the typical measles rash can be found on the CDC website.
- Symptom Progression: Symptoms usually appear in a specific order, making it easier for healthcare providers to make a diagnosis.
- Early Diagnosis: Early recognition is critical for prompt treatment and preventing transmission.
Seeking Medical Attention
If measles is suspected, immediate medical attention is essential. A blood test can confirm the diagnosis.
- Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests detect the presence of measles antibodies, confirming infection.
- Treatment Options: While there is no specific cure for measles, supportive care, such as fluids and fever reducers, is crucial to manage symptoms.
- Healthcare Providers: Consult with your healthcare provider or local health department if you suspect measles.
Prevention and Control Measures for Measles Outbreak USA
Preventing further spread of the Measles Outbreak USA requires a multi-pronged approach combining vaccination, robust public health measures, and personal hygiene practices.
Vaccination as the Primary Prevention
The MMR vaccine is the cornerstone of measles prevention. Getting vaccinated is the most effective way to protect yourself and others.
- MMR Vaccine Schedule: The recommended schedule involves two doses, typically given during childhood.
- Vaccine Safety: Extensive research confirms the safety and efficacy of the MMR vaccine.
- Vaccination Resources: The CDC website provides comprehensive information about the MMR vaccine and where to find vaccination services.
Public Health Measures
Public health agencies play a vital role in controlling outbreaks. Contact tracing, isolation of infected individuals, and quarantine of exposed individuals are crucial interventions.
- Contact Tracing: Identifying and contacting individuals who have been in close contact with infected persons is essential in limiting the spread.
- Public Health Interventions: Rapid and effective public health responses can significantly reduce the duration and severity of outbreaks.
- CDC Resources: The CDC offers guidelines and resources for healthcare providers and public health officials on managing measles outbreaks.
Personal Hygiene and Prevention Tips
Simple hygiene practices can reduce the risk of measles transmission.
- Handwashing: Frequent handwashing with soap and water is crucial.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Infection Control: Practicing good hygiene and infection control measures helps prevent the spread of various contagious diseases, including measles.
Conclusion
The current Measles Outbreak USA underscores the critical importance of vaccination in preventing this highly contagious disease. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies is key to protecting individuals and communities. The resurgence highlights the need for increased vaccination rates, robust public health interventions, and proactive measures to prevent the importation of measles. Get vaccinated, stay informed about updates from public health authorities like the CDC, and advocate for vaccination within your community. Share this article to raise awareness and help prevent the spread of measles. Together, we can combat the Measles Outbreak USA and protect public health.

Featured Posts
-
 French Open 2024 Norries Shock Win Djokovics Smooth Sailing
May 30, 2025
French Open 2024 Norries Shock Win Djokovics Smooth Sailing
May 30, 2025 -
 Addressing Urban Heat Islands The Role Of Advanced Materials In Indian Cities
May 30, 2025
Addressing Urban Heat Islands The Role Of Advanced Materials In Indian Cities
May 30, 2025 -
 Jordans Amman Final Of 24th Chinese Bridge Competition Concludes
May 30, 2025
Jordans Amman Final Of 24th Chinese Bridge Competition Concludes
May 30, 2025 -
 Six Months Jon Joness Request For Aspinall Bout Preparation
May 30, 2025
Six Months Jon Joness Request For Aspinall Bout Preparation
May 30, 2025 -
 Priglashenie Na Otkrytiy Seminar Russkoy Inzhenernoy Shkoly V Tolyatti
May 30, 2025
Priglashenie Na Otkrytiy Seminar Russkoy Inzhenernoy Shkoly V Tolyatti
May 30, 2025
