Understanding The Increased Rainfall In Western Massachusetts: A Climate Change Study
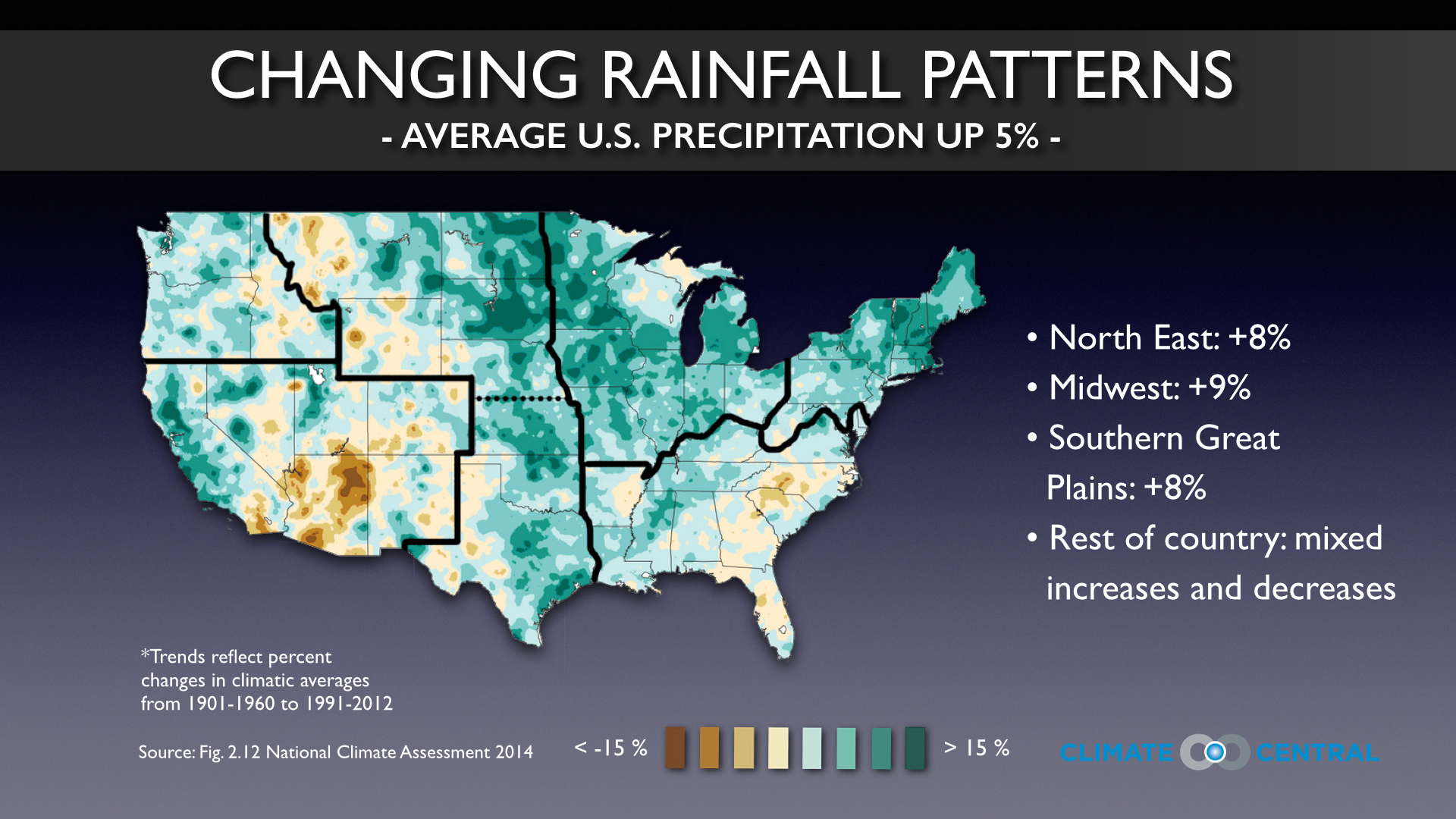
Table of Contents
Evidence of Increased Rainfall in Western Massachusetts
Data Analysis from Meteorological Stations
Long-term rainfall data collected from multiple meteorological stations across Western Massachusetts paints a clear picture: rainfall is increasing significantly. Analysis of this data, spanning several decades, reveals a consistent upward trend in both annual and seasonal rainfall totals. Graphs and charts illustrating this trend clearly demonstrate the escalating precipitation levels.
- Specific years of exceptionally high rainfall: For instance, the year 2023 (and potentially others, depending on the most recent data) exhibited unusually high rainfall totals, exceeding historical averages by a considerable margin. These extreme rainfall events resulted in widespread flooding and significant economic losses.
- Comparison to historical averages: Comparing current rainfall data with historical averages highlights the statistical significance of the increase. This comparison strengthens the argument for a discernible change in rainfall patterns.
- Location-specific variations: Certain areas within Western Massachusetts, such as those located near the Connecticut River and its tributaries, have experienced particularly pronounced increases in rainfall, making them more vulnerable to flooding.
Impact on Local Water Bodies and Rivers
The increased rainfall has had a substantial impact on Western Massachusetts' water bodies and rivers. The most visible consequence is a surge in flooding and river overflow incidents.
- Increased flooding: More frequent and severe flooding events have damaged property, disrupted transportation, and impacted local economies.
- Changes in water levels and aquatic ecosystems: The altered water levels are affecting aquatic ecosystems, impacting fish populations and overall biodiversity.
- Infrastructure damage: Infrastructure near rivers and water bodies, including roads, bridges, and homes, is increasingly vulnerable to damage from flooding and erosion. The Connecticut River, Westfield River, and numerous smaller waterways have all experienced heightened flood risks.
The Link to Climate Change
Scientific Consensus on Climate Change and Precipitation
The scientific consensus strongly supports the link between climate change and increased precipitation. Warmer air holds more moisture, leading to more intense and frequent rainfall events.
- Scientific basis: The fundamental physics of atmospheric moisture content directly explains why a warming climate leads to heavier rainfall.
- Relevant scientific reports: Reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and other reputable scientific bodies provide overwhelming evidence supporting this connection. These reports detail the mechanisms through which climate change alters global precipitation patterns.
- Mechanisms of impact: Climate change affects rainfall patterns through various mechanisms, including changes in atmospheric circulation, increased evaporation rates, and altered storm tracks.
Modeling and Projections for Future Rainfall
Climate models project a continuation of this trend, predicting even more intense rainfall events in Western Massachusetts in the coming decades.
- Climate model projections: Sophisticated climate models forecast a significant increase in both the frequency and intensity of heavy rainfall events.
- Implications for the future: These projections have significant implications for the region's infrastructure, economy, and environment, demanding proactive measures to mitigate potential risks. Increased rainfall means increased pressure on existing drainage systems and increased flooding risk.
Consequences of Increased Rainfall in Western Massachusetts
Impact on Agriculture
The increased rainfall poses significant challenges to agriculture in Western Massachusetts.
- Crop damage: Excessive rainfall and flooding can lead to crop damage, reduced yields, and substantial economic losses for farmers.
- Soil erosion and nutrient loss: Intense rainfall can cause soil erosion, washing away valuable nutrients and reducing soil fertility.
- Challenges to farming practices: Farmers are forced to adapt their practices to cope with the increased rainfall, increasing costs and potentially reducing profitability.
Infrastructure Impacts
The increased rainfall significantly impacts Western Massachusetts' infrastructure.
- Flooding risk: Roads, bridges, and buildings are increasingly vulnerable to damage from flooding.
- Repair and maintenance costs: The increased frequency of repairs and maintenance needed due to flood damage places a significant strain on local and state budgets.
- Transportation disruptions: Flooding can cause significant disruptions to transportation networks, affecting both daily commutes and the movement of goods.
Environmental Impacts
The consequences extend to the region's environment.
- Ecosystem changes: Altered rainfall patterns are changing ecosystems and habitats, potentially impacting biodiversity.
- Landslides and mudslides: Increased rainfall increases the risk of landslides and mudslides, particularly in areas with steep slopes.
- Water quality: Increased runoff can lead to water pollution, impacting the quality of drinking water sources.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Individual Actions
Individuals can play a crucial role in mitigating and adapting to increased rainfall.
- Water conservation: Implementing water conservation measures at home can help reduce the strain on water resources.
- Flood preparation: Preparing for potential flooding by developing emergency plans and securing valuable possessions can minimize losses.
- Sustainable land management: Supporting sustainable land management practices can help reduce soil erosion and improve water absorption.
Community and Governmental Actions
Communities and governments must also take action.
- Infrastructure improvements: Investing in improved drainage systems and flood defenses is crucial for protecting communities.
- Climate change adaptation plans: Developing comprehensive climate change adaptation plans will help guide regional responses to the changing climate.
- Research and support: Supporting research into the impacts of climate change and investing in mitigation strategies is essential.
Understanding the Increased Rainfall in Western Massachusetts: A Call to Action
The evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates a significant increase in rainfall in Western Massachusetts, directly linked to climate change. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting agriculture, infrastructure, and the environment. The potential for future impacts is substantial, emphasizing the urgency of proactive measures. Understanding the increased rainfall in Western Massachusetts is crucial for our future. By learning more about climate change, supporting local initiatives focused on water management and infrastructure improvements, and advocating for sustainable practices, we can work together to build a more resilient community.

Featured Posts
-
 Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Peran Masyarakat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah
May 28, 2025
Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Peran Masyarakat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah
May 28, 2025 -
 Chicago Med Season 10 Underrated Duos Crossover Payoff
May 28, 2025
Chicago Med Season 10 Underrated Duos Crossover Payoff
May 28, 2025 -
 Wawali Susetyo Janji Bangun Taman Di Setiap Kecamatan Balikpapan
May 28, 2025
Wawali Susetyo Janji Bangun Taman Di Setiap Kecamatan Balikpapan
May 28, 2025 -
 Game Winning Grand Slam Kyle Stowers Leads Marlins To Victory
May 28, 2025
Game Winning Grand Slam Kyle Stowers Leads Marlins To Victory
May 28, 2025 -
 Rotterdam Thriller Psv Beat Feyenoord 2 3 Closing In On Ajax
May 28, 2025
Rotterdam Thriller Psv Beat Feyenoord 2 3 Closing In On Ajax
May 28, 2025
