Understanding The Wonder Of Animals: Their Importance In Our Ecosystem
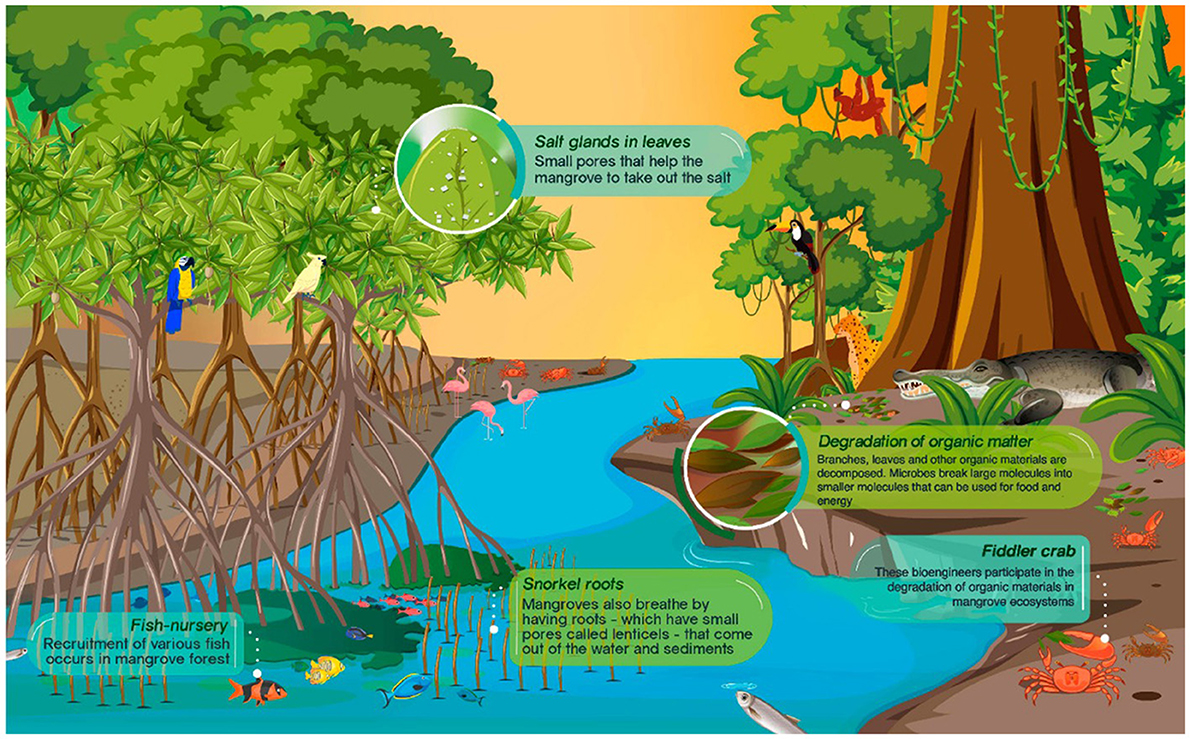
Table of Contents
Animals as Pollinators: Essential for Plant Reproduction
Animals play a crucial role in plant reproduction, acting as vital pollinators. Without them, many plant species, and consequently, the ecosystems they support, would struggle to survive.
The Crucial Role of Bees and Other Insects
Bees are arguably the most well-known pollinators, but countless other insects, like butterflies, moths, flies, and beetles, also contribute significantly to this essential process. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred from the anther (male part) of a flower to the stigma (female part), enabling fertilization and seed production.
- Examples of plants relying on animal pollination: Almonds, apples, blueberries, cranberries, and sunflowers all heavily depend on animal pollination for successful fruit and seed production. The economic impact of this pollination is staggering, with billions of dollars in agricultural output reliant on these crucial services.
- Threats to pollinators: Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture, along with the widespread use of pesticides, are major threats to pollinator populations. Climate change also poses a significant risk, altering flowering times and disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Beyond Insects: Birds, Bats, and Other Vertebrate Pollinators
While insects are the primary pollinators, birds and bats also play a critical role, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. These vertebrate pollinators often pollinate plants with specific adaptations, such as large, brightly colored flowers for birds or night-blooming, fragrant flowers for bats.
- Examples of bird and bat-pollinated plants: Hummingbirds pollinate many plants in the Americas, while bats are important pollinators of cacti and agave plants. The unique adaptations of these animals, like long beaks in hummingbirds or echolocation in bats, are perfectly suited to their respective floral partners.
Animals as Seed Dispersers: Facilitating Plant Growth and Distribution
Seed dispersal is another crucial ecological function performed by animals. By carrying seeds away from the parent plant, animals ensure the survival and genetic diversity of plant populations.
The Role of Animals in Seed Germination
Animals disperse seeds through various mechanisms, promoting plant growth and distribution across wider areas. This process is vital for forest regeneration and overall ecosystem health.
- Examples of animals dispersing seeds: Birds, mammals (like squirrels and monkeys), and even ants play crucial roles in seed dispersal. Some seeds are ingested and later deposited in droppings, while others are attached to fur or feathers and carried to new locations.
- Different dispersal mechanisms: Ingestion and subsequent defecation, external attachment (epizoochory), and caching (storing seeds for later consumption) are all common dispersal mechanisms employed by animals.
The Importance of Seed Dispersal for Forest Regeneration
In forest ecosystems, animal seed dispersal is particularly crucial for regeneration and maintaining biodiversity. Animals ensure that seeds are dispersed far enough from the parent tree to avoid competition for resources, promoting forest expansion and creating a more diverse forest structure.
- The impact of seed dispersal on forest structure: Without animal-mediated seed dispersal, forests would be less diverse, with fewer species and a less complex structure. Seed dispersal contributes to forest resilience and helps in post-disturbance recovery.
- The consequences of disrupting seed dispersal patterns: Deforestation and habitat fragmentation disrupt natural seed dispersal patterns, hindering forest regeneration and reducing biodiversity.
Animals in the Food Web: Maintaining Ecological Balance
Animals are integral components of food webs, influencing population dynamics and nutrient cycling, thereby maintaining the ecological balance.
Predators and Prey: The Dynamic of Population Control
Predators regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining biodiversity. This dynamic interaction is crucial for ecosystem stability.
- Examples of predator-prey relationships: Wolves and deer, lions and zebras, and owls and mice are classic examples of predator-prey relationships. The balance between predator and prey populations is a constant dynamic influenced by factors like prey availability and environmental conditions.
- The consequences of imbalances in the food web: The loss of a key predator or prey species can have cascading effects throughout the food web, leading to population booms or busts and ecosystem instability.
Decomposers and Scavengers: Essential for Nutrient Cycling
Decomposers and scavengers play a critical role in breaking down organic matter, recycling nutrients, and maintaining soil health.
- Examples of decomposers and scavengers: Fungi and bacteria are essential decomposers, while vultures, beetles, and other scavengers help break down carcasses. Their work is crucial for nutrient cycling and maintaining the fertility of the soil.
- Their contribution to soil health and nutrient availability: Decomposers and scavengers release nutrients back into the environment, making them available for plants and other organisms. Healthy soil is essential for supporting plant growth and overall ecosystem productivity.
The Economic Importance of Animals: Beyond Ecosystem Services
The importance of animals extends beyond their ecological roles to encompass significant economic contributions.
Animals as a Source of Food and Income
Animals provide essential sources of food and income for billions of people worldwide, supporting livelihoods through livestock farming and fishing.
- The economic value of animal products: Meat, dairy, eggs, wool, and other animal products represent a substantial portion of global agricultural output and trade. Sustainable animal husbandry practices are crucial for long-term economic viability.
- The importance of sustainable practices: Overfishing, unsustainable farming practices, and habitat destruction threaten the long-term sustainability of animal-based industries.
Ecotourism and Conservation Efforts
Wildlife tourism and conservation initiatives generate significant economic benefits for local communities and support conservation efforts.
- Examples of ecotourism destinations: National parks, wildlife reserves, and other protected areas attract millions of tourists annually, generating revenue for local economies and creating incentives for conservation.
- The financial incentives for conservation: Ecotourism provides financial incentives for protecting biodiversity and maintaining natural habitats, demonstrating the economic value of preserving wildlife and their habitats.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of animals in our ecosystem is crucial for their conservation. From pollination and seed dispersal to regulating populations and nutrient cycling, animals play multifaceted roles that are essential for a healthy planet. Their economic contributions, through food production and ecotourism, further highlight their value. Let's work together to protect the wonder of animals and ensure the health of our planet. Learn more about how you can contribute to animal conservation efforts and understand the vital importance of animals in our shared ecosystem.

Featured Posts
-
 Controversy Erupts Tory Lanez And 50 Cent Confront Reporter Over A Ap Rocky Wager
May 13, 2025
Controversy Erupts Tory Lanez And 50 Cent Confront Reporter Over A Ap Rocky Wager
May 13, 2025 -
 Gromkiy Skandal Muzh Kadyshevoy Vstal Na Zaschitu Syna Zaputavshegosya V Dolgakh
May 13, 2025
Gromkiy Skandal Muzh Kadyshevoy Vstal Na Zaschitu Syna Zaputavshegosya V Dolgakh
May 13, 2025 -
 Luxury Presence Expands With Dedicated Off Market Property Hub
May 13, 2025
Luxury Presence Expands With Dedicated Off Market Property Hub
May 13, 2025 -
 Efl Highlights Key Matches And Memorable Goals
May 13, 2025
Efl Highlights Key Matches And Memorable Goals
May 13, 2025 -
 Menangani Konflik Myanmar Hikmah Dari Pendekatan Sby
May 13, 2025
Menangani Konflik Myanmar Hikmah Dari Pendekatan Sby
May 13, 2025
