Weak Retail Sales: Precursor To Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Cuts?
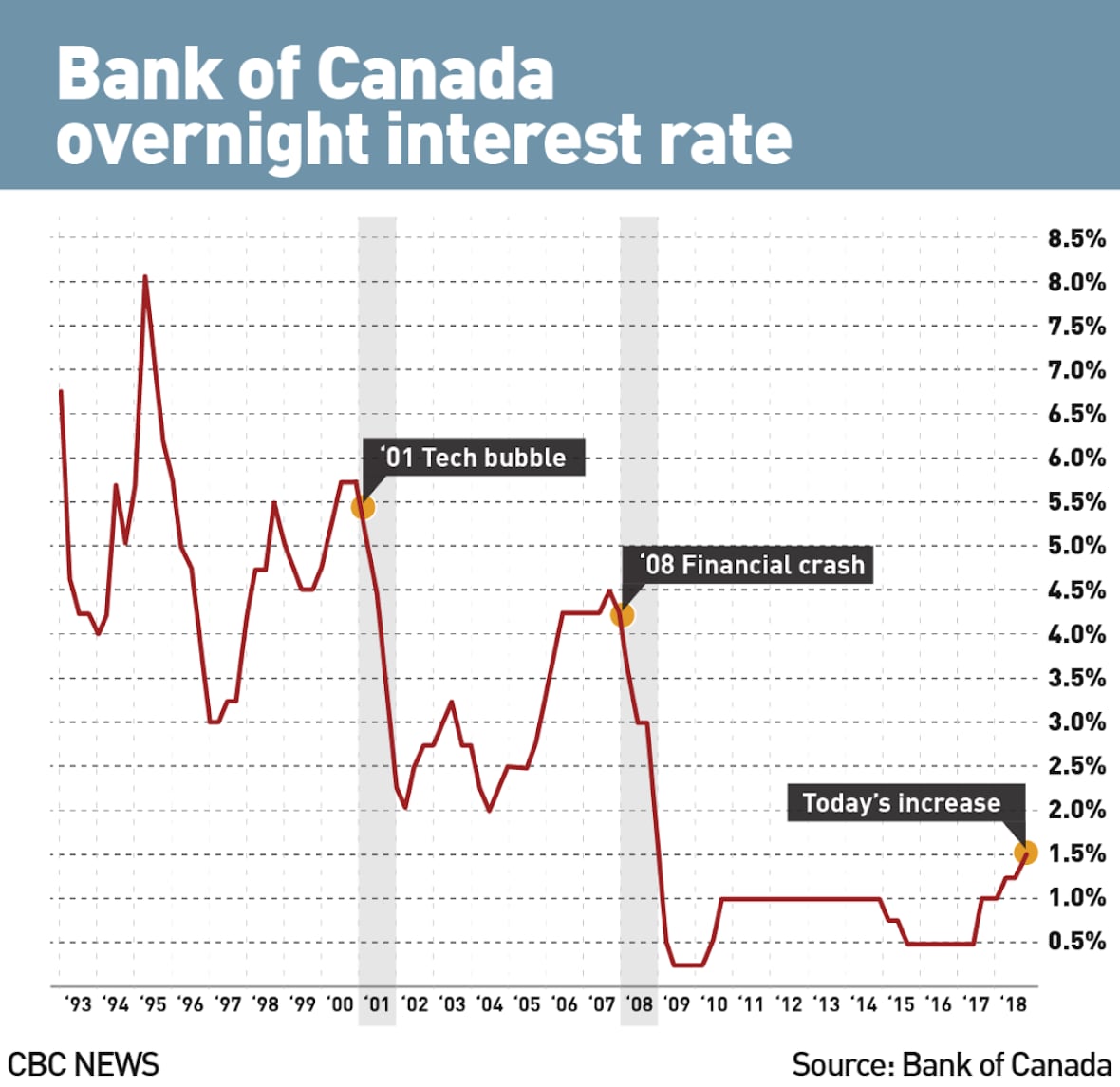
Table of Contents
The Current State of Retail Sales in Canada
Declining Consumer Spending
Recent data from Statistics Canada reveals a concerning drop in retail sales figures. This decline indicates weakening consumer spending, a crucial driver of Canada's economic growth. The impact is widespread, affecting various sectors.
-
Examples of declining sales:
- Clothing sales have fallen by X% in the last quarter (Source: Statistics Canada).
- Furniture and home furnishings sales have experienced a Y% decrease (Source: Statistics Canada).
- Automobile sales have shown a Z% reduction (Source: Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers' Association).
-
Factors contributing to the decline:
- High inflation: Soaring prices for essential goods and services are eroding consumer purchasing power.
- Increased interest rates: Higher borrowing costs are making it more expensive for Canadians to finance purchases, impacting both big-ticket items and everyday spending.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Uncertainty about the economic outlook is leading consumers to become more cautious with their spending.
Impact on Economic Growth
Weakening retail sales have significant implications for Canada's overall economic growth and GDP. Consumer spending constitutes a substantial portion of the Canadian economy. A sustained decline in retail sales can trigger a ripple effect across various industries, potentially leading to job losses and reduced business investment.
- Relationship between consumer spending and economic health: Consumer spending is a major indicator of economic health; a decline signifies reduced economic activity.
- Potential for a recessionary environment: If the trend of weak retail sales continues, it could increase the risk of a recessionary environment in Canada. This necessitates close monitoring of economic indicators and potential government interventions.
The Bank of Canada's Current Monetary Policy
Interest Rate Hikes and Their Impact
The Bank of Canada has implemented a series of interest rate hikes over the past year in an attempt to combat inflation. These increases have directly impacted borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
- Timeline of interest rate increases: (Insert a concise timeline of rate hikes with dates and percentage changes).
- Rationale behind the Bank of Canada's previous decisions: The Bank of Canada aimed to curb inflation by slowing down economic activity through higher interest rates. This approach, however, has inadvertently impacted consumer spending.
Signs of an Economic Slowdown
Beyond weak retail sales, other indicators suggest a potential economic slowdown in Canada. These factors further support the argument for potential interest rate adjustments.
- Correlation between these indicators and the probability of rate cuts: The convergence of these indicators increases the likelihood of the Bank of Canada altering its monetary policy.
- Mention any dissenting opinions or alternative viewpoints: Some economists argue that the current slowdown is temporary and that the Bank of Canada should maintain its hawkish stance to control inflation effectively. However, others advocate for easing monetary policy to prevent a deeper economic contraction. These differing perspectives highlight the complexity of the situation. (Cite reputable sources for these viewpoints).
The Likelihood of Interest Rate Cuts
Analyzing the Bank of Canada's Response
Given the weak retail sales and other concerning economic indicators, the Bank of Canada may respond by cutting interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
- Historical precedents for similar situations and the Bank of Canada's past actions: (Cite historical examples of the Bank of Canada's response to similar economic situations).
- Statements made by Bank of Canada officials regarding future monetary policy: (Summarize any recent public statements from Bank of Canada officials regarding future policy decisions).
Potential Timing and Magnitude of Cuts
Predicting the exact timing and magnitude of potential interest rate cuts is challenging, depending on several factors.
- Factors influencing the timing and magnitude:
- Inflation rate: The persistence of high inflation could delay interest rate cuts.
- Unemployment rate: A significant rise in unemployment might accelerate the need for rate cuts.
- Expert opinions and market predictions: (Include forecasts from reputable economic analysts and financial institutions).
Conclusion
Weak retail sales in Canada are signaling a concerning economic slowdown. This trend, coupled with other indicators such as rising unemployment and softening housing markets, suggests a potential shift in the Bank of Canada's monetary policy. While the Bank of Canada's previous interest rate hikes aimed to combat inflation, the resulting impact on consumer spending raises the possibility of upcoming interest rate cuts to stimulate economic activity. The timing and magnitude of any such cuts will depend on various economic factors, including inflation and unemployment rates. However, the current data strongly suggests that a change in monetary policy is increasingly likely.
Call to Action: Stay informed on the evolving situation and continue to monitor the Bank of Canada's announcements and economic indicators for further insight into the potential for future interest rate cuts. Understanding the relationship between weak retail sales and Bank of Canada policy is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Regularly check for updates on weak retail sales and their implications for interest rates in Canada.

Featured Posts
-
 Market Downturn Did Retail Investors Capitalize On Professional Selling
Apr 28, 2025
Market Downturn Did Retail Investors Capitalize On Professional Selling
Apr 28, 2025 -
 2000 Yankees Diary Joe Torres Meetings And Andy Pettittes Shutout Of The Twins
Apr 28, 2025
2000 Yankees Diary Joe Torres Meetings And Andy Pettittes Shutout Of The Twins
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Warna Baru Jetour Dashing Kejutan Di Iims 2025
Apr 28, 2025
Warna Baru Jetour Dashing Kejutan Di Iims 2025
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Blue Jays Vs Yankees Spring Training Live Stream Time And Channel Info
Apr 28, 2025
Blue Jays Vs Yankees Spring Training Live Stream Time And Channel Info
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Has Mets Pitcher Shown Enough For A Rotation Spot
Apr 28, 2025
Has Mets Pitcher Shown Enough For A Rotation Spot
Apr 28, 2025
