What Is Creatine And How Does It Work For Muscle Growth?
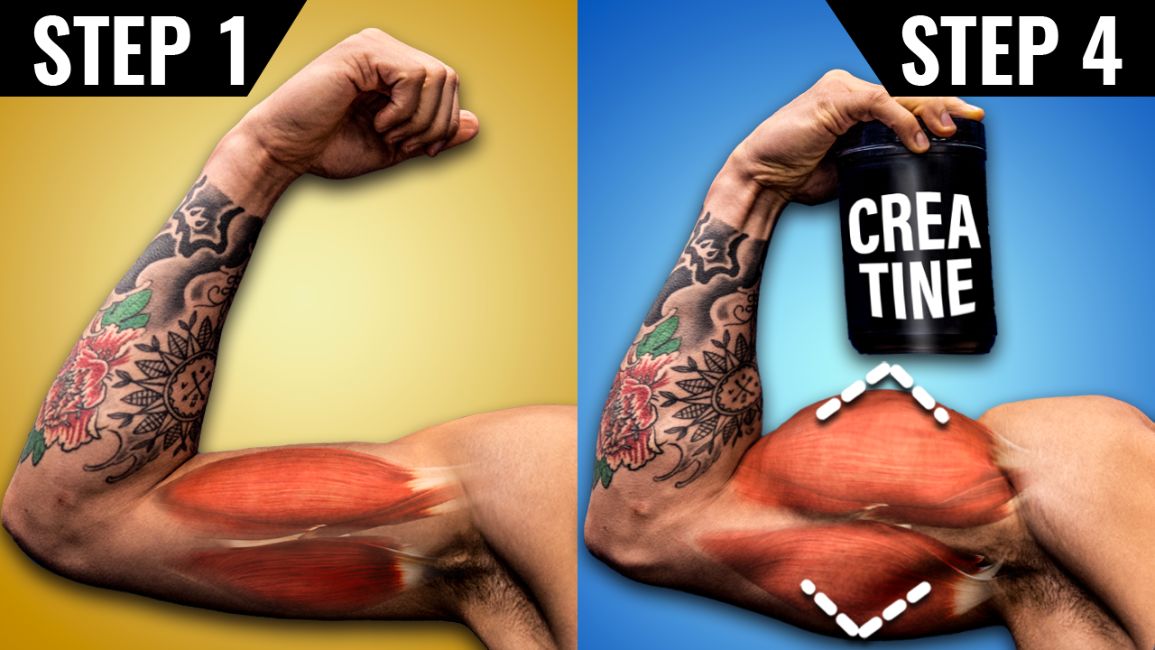

Table of Contents
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic compound synthesized primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It's not just a lab-created substance; your body produces it! Understanding its role in the body is key to understanding its benefits.
Creatine's Role in the Body:
- Energy Production: Creatine's primary function is to replenish adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body's primary energy currency, during high-intensity activities. This rapid energy replenishment is vital for maximal muscle contractions.
- Phosphocreatine (PCr) Storage: In skeletal muscle, creatine is stored as phosphocreatine (PCr). PCr acts as a high-energy phosphate reservoir, readily donating its phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to reform ATP. This process is crucial for short bursts of intense exercise.
- Muscle Contraction Fuel: When you perform intense exercise, like weightlifting or sprinting, your muscles rapidly deplete ATP. PCr acts as a buffer, quickly replenishing ATP levels, allowing you to maintain power and strength.
Types of Creatine Supplements:
While various forms exist, creatine monohydrate reigns supreme in research and effectiveness.
- Creatine Monohydrate: This is the most researched and widely available form of creatine. Decades of studies confirm its safety and efficacy for boosting muscle growth and strength.
- Creatine Hydrochloride (HCl): Marketed for improved absorption, the evidence supporting this claim remains inconclusive. More research is needed to confirm its superiority over monohydrate.
- Creatine Ethyl Ester: Another form with purported enhanced absorption, but the scientific evidence lacks the robustness of creatine monohydrate studies. It's generally less popular and less researched.
Creatine Sources:
While you can obtain creatine naturally, supplementation provides a more controlled and concentrated dose.
- Dietary Sources: Creatine is found naturally in red meat and fish, but the amounts are relatively small.
- Supplementation: Creatine supplements, primarily creatine monohydrate, offer a convenient and effective way to significantly increase your creatine intake and reap its benefits.
How Creatine Works for Muscle Growth:
Creatine's impact on muscle growth is multifaceted, stemming from its influence on several key physiological processes.
Increased Muscle Cell Volume (Cell Volumization):
- Water Retention: Creatine supplementation leads to increased water retention within muscle cells. This isn't just water weight; it's a crucial element in muscle cell growth and function.
- Stimulated Protein Synthesis: The increased cell size (cell volumization) triggered by water retention acts as a signal, stimulating muscle protein synthesis—the process of building new muscle protein.
- Enhanced Protein Synthesis Pathways: Creatine also indirectly enhances the pathways responsible for muscle protein synthesis, further promoting muscle growth.
Enhanced Strength and Power:
- Increased ATP Availability: The replenishment of ATP by creatine leads to more intense and longer workouts. You simply have more energy for more reps and sets.
- Greater Strength Gains: This increased energy availability translates to significant gains in strength and power output, especially during high-intensity training.
- Improved Power Output: This is evident in various exercises, from weightlifting to sprinting, where increased power output is crucial for performance.
Improved Muscle Recovery:
- Reduced Muscle Damage: Creatine may help reduce muscle damage and inflammation following intense exercise, contributing to faster recovery.
- Faster Recovery Times: This means you can train more frequently and intensely without overtraining.
- Positive Muscle Protein Balance: By facilitating faster recovery, creatine helps maintain a positive muscle protein balance, essential for continuous muscle growth.
Benefits of Creatine for Athletes and Bodybuilders:
The benefits of creatine extend across various aspects of athletic performance and physique development.
Strength and Power Gains:
Creatine supplementation is highly effective in increasing maximal strength and power, leading to significant improvements in various strength training exercises.
Muscle Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth):
Creatine contributes significantly to increases in lean muscle mass, making it a valuable tool for those aiming to build muscle size and definition.
Improved Athletic Performance:
The benefits of creatine are widely observed across a range of sports, including weightlifting, sprinting, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and many others. It enhances performance in activities requiring short bursts of intense effort.
Cognitive Function:
Some studies suggest potential benefits for cognitive function, such as improved memory and reasoning. However, further research is needed to fully understand these effects.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions:
While generally safe, creatine can have some side effects, though they are usually mild and temporary.
- Weight Gain: Water retention can lead to a temporary increase in body weight.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as diarrhea or nausea, particularly when starting supplementation.
- Muscle Cramps: Muscle cramps are a rare side effect.
- Medical Consultation: Consult your doctor before using creatine, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions, such as kidney problems.
Conclusion:
Creatine is a safe and effective supplement for boosting muscle growth, strength, and athletic performance when used responsibly. By enhancing ATP availability and promoting muscle cell volumization, creatine helps athletes and bodybuilders achieve significant gains. While some mild side effects are possible, they are generally infrequent and easily managed. If you're aiming to improve your workout performance and maximize muscle growth, consider incorporating creatine into your routine. Remember to always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen. Learn more about the science behind creatine supplementation and unlock your fitness potential!

Featured Posts
-
 Eau Du Robinet Polluee Comment Choisir Le Bon Filtre Pour Une Eau Saine
May 16, 2025
Eau Du Robinet Polluee Comment Choisir Le Bon Filtre Pour Une Eau Saine
May 16, 2025 -
 Dwyane Wade On Jimmy Butlers Decision To Leave The Miami Heat
May 16, 2025
Dwyane Wade On Jimmy Butlers Decision To Leave The Miami Heat
May 16, 2025 -
 Analysis Paddy Pimbletts Path To Victory At Ufc 314
May 16, 2025
Analysis Paddy Pimbletts Path To Victory At Ufc 314
May 16, 2025 -
 Almeria Eldense Resumen Estadisticas Y Goles De La Liga Hyper Motion
May 16, 2025
Almeria Eldense Resumen Estadisticas Y Goles De La Liga Hyper Motion
May 16, 2025 -
 Tarifkonflikt Bvg Schlichtung Streik Und Moegliche Entlassungen
May 16, 2025
Tarifkonflikt Bvg Schlichtung Streik Und Moegliche Entlassungen
May 16, 2025
