What Is Creatine And Should You Take It? A Complete Guide
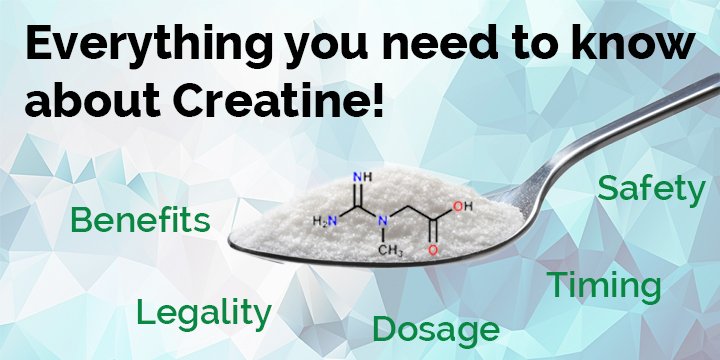
Table of Contents
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic compound primarily found in skeletal muscle. Its chemical structure is relatively simple, and the body produces a small amount naturally, primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. However, supplementing with creatine significantly boosts its levels in the muscles. Creatine plays a crucial role in energy production within muscle cells. Specifically, it helps in the regeneration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the body. Higher ATP levels translate to increased power output and enhanced performance during high-intensity activities.
Different types of creatine supplements are available, each with slight variations in absorption and effectiveness:
- Creatine Monohydrate: This is the most researched and widely available form of creatine, considered the gold standard due to its proven efficacy and safety.
- Creatine Hydrochloride (HCL): Claimed to have better solubility and absorption than creatine monohydrate, though more research is needed to definitively confirm this.
- Creatine Ethyl Ester: Another form with purported enhanced absorption, but its effectiveness compared to creatine monohydrate remains a topic of ongoing research.
Regardless of the type, creatine supplementation is primarily aimed at improving overall athletic performance by increasing the availability of energy for muscle contractions.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation offers a range of benefits, impacting muscle growth, athletic performance, and even cognitive function.
Enhanced Muscle Growth and Strength
Creatine enhances muscle growth and strength primarily through two mechanisms: increased muscle cell hydration (cell volumization) and boosted protein synthesis. By increasing water retention within muscle cells, creatine creates a more anabolic environment, promoting muscle growth. Additionally, it facilitates protein synthesis, the process by which the body builds new muscle proteins. This leads to significant increases in both lean muscle mass and overall strength.
Scientific studies extensively support creatine's muscle-building effects:
- A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition showed that creatine supplementation significantly increases muscle mass and strength gains compared to placebo.
- Several other studies have demonstrated improvements in various strength metrics, such as:
- Increased repetitions performed during resistance training exercises.
- Ability to lift heavier weights.
- Faster recovery times between sets and workouts.
Improved Athletic Performance
Creatine's impact extends beyond muscle growth, significantly improving athletic performance, especially in high-intensity activities:
- Weightlifting: Creatine enhances power output, allowing for more explosive movements and heavier lifts.
- Sprinting: It boosts speed and reduces fatigue during short bursts of intense activity.
- Interval Training: Creatine improves performance during high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions by increasing the capacity for repeated high-power output.
- Other Sports: Many athletes in sports like basketball, soccer, and hockey also benefit from creatine supplementation.
Creatine's effectiveness in these activities stems from its ability to replenish ATP rapidly, reducing muscle fatigue and enhancing power output.
Cognitive Benefits
While primarily known for its impact on physical performance, emerging research suggests that creatine may also offer cognitive benefits:
- Some studies indicate potential improvements in memory and cognitive function in both healthy individuals and those with certain cognitive impairments, such as traumatic brain injury.
- Improved learning and reasoning abilities have been observed in some studies.
However, it's crucial to note that research in this area is still ongoing, and more studies are needed to establish definitive conclusions about creatine's cognitive effects.
Potential Side Effects of Creatine
While generally considered safe, creatine supplementation can cause some side effects, although they are usually mild and temporary:
- Weight Gain: The most commonly reported side effect is weight gain, primarily due to water retention in muscles. This is not actual fat gain but rather an increase in muscle mass and water weight.
- Stomach Cramps: Some individuals experience mild stomach cramps, particularly when starting creatine supplementation.
- Muscle Aches: Mild muscle aches are possible, especially during the initial loading phase.
These side effects are usually manageable and often resolve within a few days to weeks. Proper hydration is essential to mitigate some of these side effects, particularly water retention. Serious side effects associated with creatine are rare when used as directed.
Creatine Dosage and Usage
The standard recommended daily dosage for creatine monohydrate is 3-5 grams. Many individuals find that a loading phase, where they consume higher doses (20 grams per day) for the first week, followed by a maintenance phase (3-5 grams per day) is effective. However, a loading phase isn't strictly necessary. Consistency is key; taking your daily dose consistently will result in better, sustained results.
Optimal creatine absorption is influenced by diet and hydration. Consuming creatine with carbohydrates and sufficient water can enhance its absorption and reduce potential side effects.
Conclusion
Creatine supplementation offers a range of potential benefits, including enhanced muscle growth, improved athletic performance, and possible cognitive enhancements. While some mild side effects are possible, they are usually temporary and manageable. When used appropriately, creatine is generally safe and effective. If you're looking to enhance your athletic performance, build muscle, or explore its potential cognitive benefits, creatine supplementation may be a valuable addition to your routine. However, always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen, including creatine. Learn more about the different types of creatine supplements available and find the best option for you. Make an informed decision about incorporating creatine into your fitness plan today!

Featured Posts
-
 Hamer Bruins Leeflang Noodzaak Tot Overleg Met Npo Toezichthouder
May 15, 2025
Hamer Bruins Leeflang Noodzaak Tot Overleg Met Npo Toezichthouder
May 15, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimblett Choked Unconscious 35 Second Loss To Ex Soldier
May 15, 2025
Paddy Pimblett Choked Unconscious 35 Second Loss To Ex Soldier
May 15, 2025 -
 A Look At Elizabeth Warrens Defense Of Joe Bidens Cognitive Abilities
May 15, 2025
A Look At Elizabeth Warrens Defense Of Joe Bidens Cognitive Abilities
May 15, 2025 -
 Novi Napadi Na Mediumite Od Tramp I Na Avi Za Chistka Vo Sudstvoto
May 15, 2025
Novi Napadi Na Mediumite Od Tramp I Na Avi Za Chistka Vo Sudstvoto
May 15, 2025 -
 From The Shadows To The Spotlight A Forgotten Dodgers Rise
May 15, 2025
From The Shadows To The Spotlight A Forgotten Dodgers Rise
May 15, 2025
