Wildfires And Deforestation: A Record Year Of Global Forest Loss
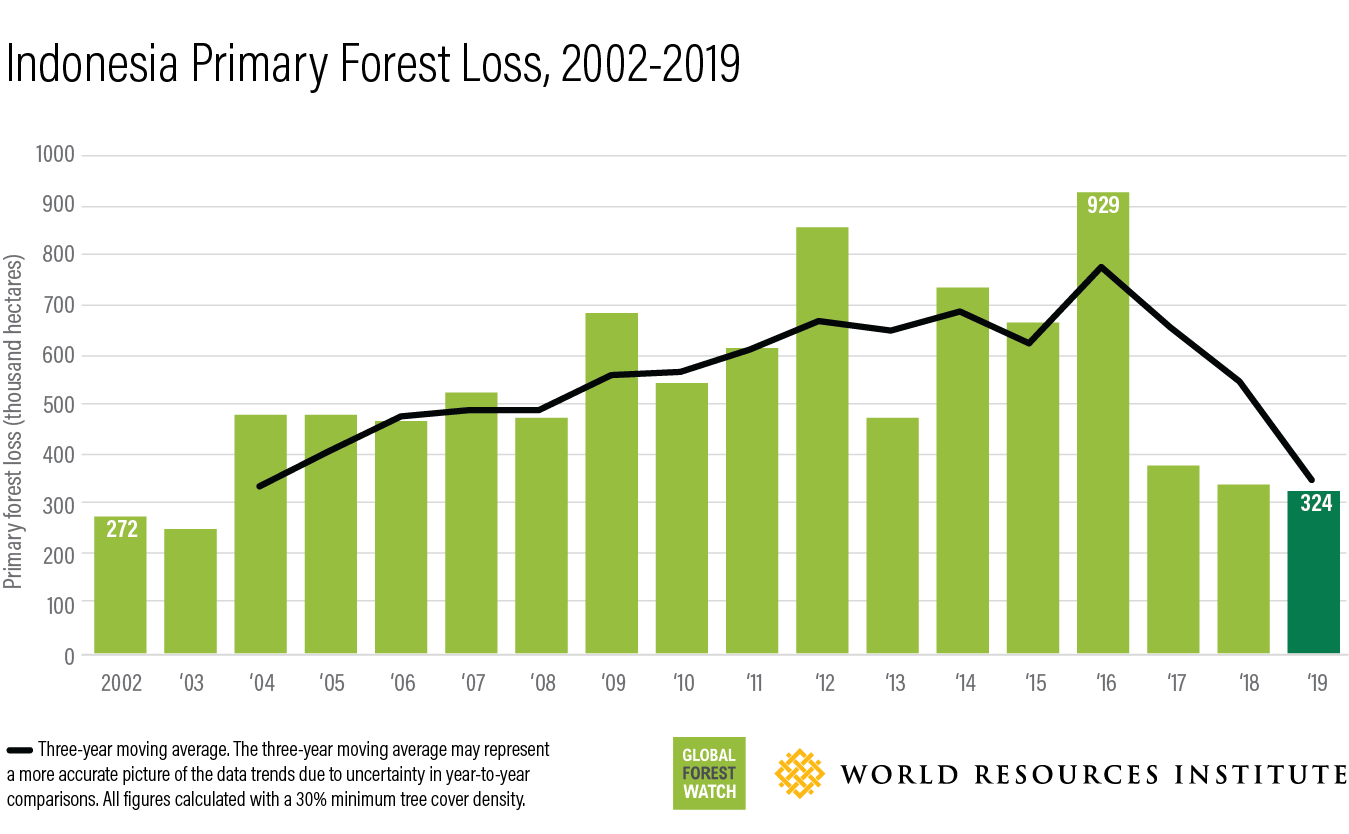
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires
Wildfire impacts are escalating globally, largely due to climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and more frequent heatwaves create ideal conditions for the ignition and rapid spread of forest fires. The consequences are catastrophic, both immediately and in the long term.
-
Immediate and Long-Term Environmental Consequences: Wildfires cause immediate habitat destruction, displacing and killing countless species. The intense heat scorches the earth, leading to severe soil erosion, which further degrades the land’s capacity to support life. The resulting air pollution, particularly from smoke inhalation, poses significant risks to human health, causing respiratory illnesses and other health problems. Finally, wildfires release massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
-
Specific Examples and Statistics: The 2023 wildfire season witnessed devastating blazes across the globe. Australia experienced record-breaking temperatures and extensive bushfires, while parts of Canada and the western United States suffered similarly. The Amazon rainforest, a crucial carbon sink, also experienced significant fire damage. The total area burned globally in 2023 resulted in an estimated X tons of CO2 emissions (insert actual statistic if available).
-
Key Regions Affected:
- Australia: Numerous regions experienced severe bushfires.
- Canada: British Columbia, Alberta, and Ontario were severely impacted.
- United States: California, Oregon, and Washington saw extensive wildfires.
- Amazon Rainforest: Significant areas experienced fires, contributing to deforestation.
The Role of Deforestation in Global Forest Loss
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, is another major driver of global forest loss. This alarming practice contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity loss.
-
Drivers of Deforestation: Several factors fuel deforestation:
- Illegal Logging: Unsustainable and illegal logging practices deplete forest resources at an alarming rate.
- Agricultural Expansion: The demand for agricultural products like palm oil, soy, and beef drives the conversion of vast forest areas into farmland and pastureland.
- Mining: Mining operations clear forests to access mineral resources, leaving behind degraded landscapes.
- Infrastructure Development: Construction of roads, dams, and other infrastructure projects often leads to forest clearing.
-
Geographical Hotspots: The Amazon rainforest, Indonesian rainforests, and the Congo Basin are particularly vulnerable to deforestation, experiencing significant forest loss annually.
-
Long-Term Effects: Deforestation has severe consequences:
- Biodiversity Loss: The destruction of habitats leads to species extinction and a decline in biodiversity.
- Reduced Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a crucial role in absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Deforestation reduces this capacity, exacerbating climate change.
- Disrupted Water Cycles: Forests regulate water cycles; their removal leads to changes in rainfall patterns and increased risk of droughts and floods.
-
Deforestation-Related Issues:
- Amazon: Increased cattle ranching and soy production are major drivers.
- Indonesia: Palm oil plantations are a leading cause of deforestation.
- Congo Basin: Logging and agricultural expansion threaten this vital rainforest.
The Interconnectedness of Wildfires and Deforestation
Wildfires and deforestation are not isolated events but are deeply interconnected, creating a dangerous cycle that accelerates environmental degradation and climate change.
-
Synergistic Effects: Deforestation contributes to wildfire risk by creating drier landscapes with increased fuel loads (dead wood and underbrush). This makes forests more susceptible to ignition and more prone to rapid fire spread.
-
Positive Feedback Loops: Wildfires destroy vast tracts of forest, further contributing to deforestation and releasing substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This, in turn, accelerates climate change, leading to more frequent and intense wildfires, creating a vicious cycle.
-
Examples of Interconnectedness: Deforestation in the Amazon reduces the forest's moisture levels, increasing the risk of wildfires. Subsequent wildfires further degrade the already weakened ecosystem, hindering its ability to regenerate.
-
Land Management Practices: Sustainable forest management practices, including controlled burns and careful planning of land use, are crucial in mitigating the interconnected risks of wildfires and deforestation.
Combating Wildfires and Deforestation: Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the intertwined problems of wildfires and deforestation requires a multi-pronged approach involving prevention, mitigation, and restoration.
-
Wildfire Prevention and Suppression:
- Controlled Burns: Implementing carefully planned and controlled burns can reduce fuel loads and prevent larger, more devastating wildfires.
- Improved Fire Management Techniques: Investing in advanced technologies and training for firefighting personnel is crucial for effective wildfire suppression.
-
Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas (reforestation) and establishing new forests (afforestation) are essential for restoring forest cover and enhancing carbon sequestration.
-
Sustainable Land Management: Promoting responsible forestry practices, supporting alternative livelihoods for communities dependent on forest resources, and implementing sustainable agricultural techniques are critical.
-
International Cooperation and Policy Changes: Strengthening international agreements, enacting stricter regulations on deforestation and illegal logging, and promoting sustainable development initiatives are crucial for global action.
-
Successful Initiatives and Agreements:
- REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation): A UN program supporting developing countries in reducing deforestation.
- Paris Agreement: Includes commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which are linked to both deforestation and wildfires.
Conclusion
The record-breaking levels of global forest loss in the past year, a direct result of the combined forces of wildfires and deforestation, represent a profound environmental crisis. The consequences—loss of biodiversity, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and exacerbated climate change—demand urgent action. We must act now to prevent further global forest loss and mitigate the devastating impact of wildfires. This requires a concerted global effort involving sustainable forestry practices, strengthened environmental policies, international collaboration, and individual responsibility. Learn more about the issue, support conservation organizations, and advocate for change – let’s work together to protect our planet’s precious forests.

Featured Posts
-
 Peppa Pigs Family Celebrates A Gender Reveal Party For Their New Arrival
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pigs Family Celebrates A Gender Reveal Party For Their New Arrival
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The 20 Cent Increase In Gas Prices
May 22, 2025
Understanding The 20 Cent Increase In Gas Prices
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Nato Planindaki Birlikteligi
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Nato Planindaki Birlikteligi
May 22, 2025 -
 From Doubt To Glory Juergen Klopps Impact On Liverpool Fc
May 22, 2025
From Doubt To Glory Juergen Klopps Impact On Liverpool Fc
May 22, 2025 -
 Rio Tinto And The Pilbara A Dispute Over Environmental Sustainability
May 22, 2025
Rio Tinto And The Pilbara A Dispute Over Environmental Sustainability
May 22, 2025
