Wildfires Torch UK's Rarest Animals, Driving Them Towards Extinction
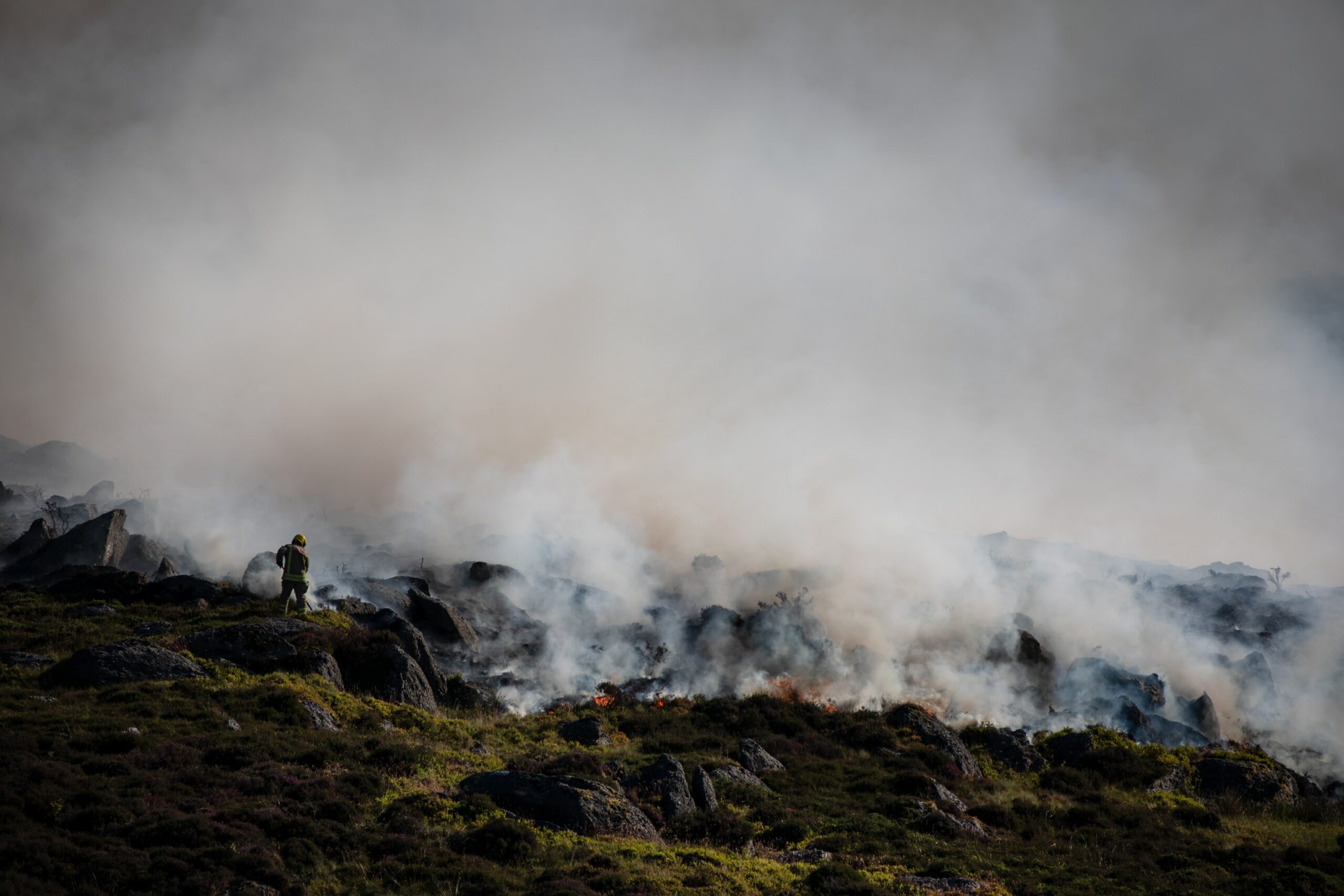

Table of Contents
Devastating Impact of Wildfires on UK Habitats
Wildfires in the UK are not only destroying vast swathes of land but also decimating the intricate ecosystems that support a rich array of species. The consequences are far-reaching and devastating, threatening the very survival of some of our most cherished animals.
Loss of Critical Habitats
Many of the UK's rarest animals rely on specific habitats for survival, habitats that are particularly vulnerable to wildfires. Peat bogs, heathlands, and ancient woodlands, all rich in biodiversity, are particularly susceptible to fire damage. These fires don't just burn vegetation; they destroy the complex soil structures, leaving behind barren landscapes unsuitable for many species for decades.
- Examples of affected habitats: Vast areas of peatland, vital carbon sinks, are highly flammable and slow to recover after a wildfire, impacting species such as the rare bog rosemary and the elusive black grouse. Heathlands, home to the Dartford warbler, are easily ignited and can be lost in a single blaze. Ancient woodlands, rich in biodiversity, are susceptible to devastating crown fires that kill mature trees and destroy ground cover habitats.
- Examples of recent wildfire damage: The devastating wildfires of [Insert recent examples with locations and species affected] dramatically illustrate the scale of the problem, causing significant population declines in various vulnerable species.
- Long-term consequences: The long-term effects of habitat destruction are profound. Even after the flames are extinguished, the loss of shelter, food sources, and breeding grounds can lead to population crashes and, ultimately, local extinctions. Recovering these ecosystems takes decades, if not centuries.
Direct Mortality of Animals
Wildfires don't just destroy habitats; they directly kill animals. The intense heat, smoke inhalation, and the frantic escape from burning areas result in significant animal mortality. Many species are simply unable to flee fast enough or find refuge in time.
- Species particularly vulnerable: Slow-moving reptiles like the smooth snake and the adder, as well as burrowing animals like the natterjack toad, are especially susceptible to direct fire mortality. Young animals and those already weakened by disease or lack of resources are particularly vulnerable.
- Impact on population demographics: The loss of breeding adults through direct mortality has a disproportionately large effect on population recovery. Eliminating key breeding individuals can severely hinder a species' ability to rebound, pushing it closer to the brink of extinction.
- Statistics on animal deaths: [Insert any available statistics on animal deaths from UK wildfires, citing sources].
Endangered Species Facing Extinction
Several UK animals are now critically endangered due to the increasing frequency and severity of wildfires. The loss of these species would have a significant impact on the overall health of the British ecosystem.
Profiling Vulnerable Species
- The Dartford Warbler: This small, colourful bird relies on heathland for breeding and feeding. Wildfires destroy its habitat, leading to population declines. [Include high-quality image].
- The Smooth Snake: This non-venomous snake is highly vulnerable to direct fire mortality. Its slow movement and reliance on specific microhabitats make it particularly susceptible to wildfire impacts. [Include high-quality image].
- The Natterjack Toad: This amphibian relies on specific wetland habitats for breeding. Wildfires can destroy these breeding grounds and directly kill toads and their tadpoles. [Include high-quality image].
- The Adder: Britain's only venomous snake, the Adder, is vulnerable to wildfires, with habitat loss and direct mortality impacting populations. [Include high-quality image]
The Ripple Effect on the Ecosystem
The loss of even a single species due to wildfire can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. These animals play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of nature.
- Impact on the food web: Predators and prey relationships are disrupted, potentially leading to population imbalances and further extinctions.
- Biodiversity loss: The destruction of habitats and the loss of species contribute to a decline in overall biodiversity, making the ecosystem more vulnerable to future disturbances.
- Long-term consequences: The loss of biodiversity can have far-reaching consequences, impacting ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
Combating the Crisis: Conservation and Prevention Strategies
Addressing the threat of wildfires to UK wildlife requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on both prevention and conservation.
Improved Fire Prevention Measures
Effective wildfire prevention is crucial in mitigating the risk to wildlife. This involves a combination of proactive measures and responsible behaviour.
- Improved land management practices: Controlled burns, under expert supervision, can reduce fuel loads and prevent larger, more destructive wildfires. Careful vegetation management around vulnerable habitats can also minimize fire risks.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about fire safety, responsible behaviour in the countryside (e.g., discarding cigarettes properly), and the importance of wildfire prevention is essential.
- Investment in early warning systems and firefighting resources: Investing in advanced technology for early detection and rapid response is crucial for containing wildfires before they spread.
Habitat Restoration and Species Recovery Programs
Conservation efforts are crucial for protecting existing populations and restoring damaged habitats.
- Rewilding projects: Rewilding initiatives can help restore degraded habitats and provide crucial refuges for threatened species.
- Captive breeding programs: Captive breeding programs can help boost populations of critically endangered species before releasing them back into the wild.
- Funding opportunities and organizations involved in conservation: Supporting organizations such as [List relevant organizations] is crucial in funding these vital conservation efforts.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is exacerbating the wildfire threat in the UK. Hotter, drier summers increase the risk of ignition and the intensity of fires.
Increased Frequency and Severity of Wildfires
The link between climate change and more frequent and severe wildfires is undeniable. Warmer temperatures dry out vegetation, creating ideal conditions for fires to start and spread rapidly. Climate models predict an increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in the future.
Long-term Climate Change Adaptation Strategies
Addressing the long-term challenges requires proactive adaptation strategies. This includes investing in climate-resilient land management practices, improving water resource management, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
The devastating impact of wildfires on UK's rarest animals cannot be overstated. The loss of habitat, direct mortality, and the cascading effects on the ecosystem pose an existential threat to many species. The urgency to act is paramount. We must implement comprehensive strategies encompassing improved fire prevention, habitat restoration, and dedicated species recovery programs. Supporting organizations dedicated to wildlife conservation and advocating for policies that promote fire prevention and climate action are crucial steps towards protecting our nation's unique biodiversity. We must act now to prevent the complete extinction of these precious animals due to devastating UK wildfires and safeguard the future of our wildlife. Support conservation efforts and help protect our nation's precious biodiversity.

Featured Posts
-
 Scarlett Johansson A Marvel Univerzum Es A Kult Filmjei
May 13, 2025
Scarlett Johansson A Marvel Univerzum Es A Kult Filmjei
May 13, 2025 -
 Southern California Heatwave Record Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025
Southern California Heatwave Record Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025 -
 No 10 Oregons Overtime Triumph Ncaa Tournament Upset Over No 7 Vanderbilt
May 13, 2025
No 10 Oregons Overtime Triumph Ncaa Tournament Upset Over No 7 Vanderbilt
May 13, 2025 -
 Navi Mumbai Municipalitys Heatwave Prevention Campaign Aala Unhala Niyam Pala
May 13, 2025
Navi Mumbai Municipalitys Heatwave Prevention Campaign Aala Unhala Niyam Pala
May 13, 2025 -
 Zgodovina Romske Glasbe V Prekmurju Poznavanje Muzikantov
May 13, 2025
Zgodovina Romske Glasbe V Prekmurju Poznavanje Muzikantov
May 13, 2025
