Will The Fed Hold Rates? Analyzing Current Economic Pressures
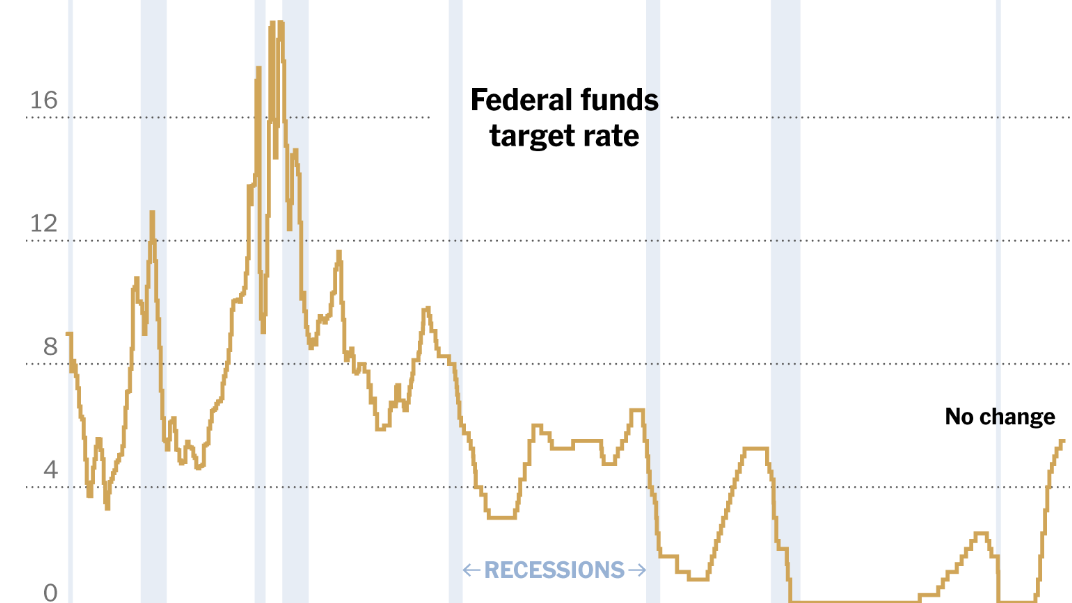
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Mandate
The Federal Reserve's dual mandate is to promote maximum employment and price stability. This means striving for low and stable inflation while maintaining a healthy employment level. Current inflation rates, however, are deviating significantly from the Fed's target of 2%. We've seen inflation significantly above this target for an extended period, fueled by several factors:
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability of goods, driving up prices.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in oil and gas prices have significantly contributed to inflationary pressures, impacting transportation costs and consumer spending.
- Wage growth: While wage increases are generally positive, rapid wage growth can contribute to inflationary pressures if it outpaces productivity gains.
- Consumer demand: Strong consumer demand, particularly post-pandemic, has put upward pressure on prices in various sectors.
Persistent inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to higher inflation expectations, creating a self-perpetuating cycle. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) are key indicators the Fed closely monitors to gauge inflationary pressures. The Fed's decision-making on interest rate hikes is heavily influenced by the trajectory of these key inflation metrics.
Unemployment Rates and Labor Market Dynamics
Analyzing current unemployment figures is crucial for understanding the Fed's approach to interest rates. While a low unemployment rate is generally positive, it can also contribute to inflationary pressures if it leads to increased wage demands. The Fed faces a classic economic trade-off – the Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. Lowering unemployment might lead to higher inflation, and vice versa. Current labor market dynamics present complexities:
- Job growth numbers: While job growth has been relatively strong, the pace is slowing in some sectors.
- Wage stagnation vs. wage increases: Wage growth varies significantly across sectors, with some experiencing stagnation while others see rapid increases.
- Labor force participation rate: The labor force participation rate remains below pre-pandemic levels, indicating potential untapped labor supply.
The Fed must carefully consider these complexities when deciding on interest rate adjustments. Raising interest rates too aggressively could stifle job growth and lead to a recession, while failing to act decisively enough could allow inflation to spiral out of control.
Global Economic Uncertainty and its Influence
The US economy is deeply interconnected with the global economy. Geopolitical instability, global recessionary fears, and international interest rate movements significantly influence the Fed's strategy. Several key global economic factors are at play:
- Geopolitical risks: Conflicts and geopolitical tensions can disrupt global supply chains and increase uncertainty, impacting US markets and the Fed's outlook.
- Global supply chains: Disruptions to global supply chains continue to impact inflation and economic growth worldwide, creating ripple effects in the US.
- International interest rate movements: Interest rate changes in other major economies can affect capital flows and exchange rates, influencing the Fed's decisions.
The Fed acknowledges the interconnectedness of global markets and considers global factors when setting its monetary policy. The potential for spillover effects from international economic events requires a nuanced approach to interest rate decisions.
Analyzing Recent Fed Statements and Market Reactions
Recent statements from Fed officials provide insight into their current thinking regarding interest rates. These statements often hint at future rate hikes or pauses, depending on the economic data. Financial markets react swiftly to these pronouncements, with bond yields and stock prices often moving in response to Fed expectations. A hawkish stance (suggesting further rate increases) typically leads to higher bond yields, reflecting anticipation of tighter monetary policy. Conversely, a dovish stance (suggesting a more cautious approach) may lead to lower yields.
Conclusion
The decision of whether the Fed will hold rates or continue increasing them is a complex one, hinging on a delicate balancing act between combating inflation and preserving economic growth and employment. Analyzing inflation data, unemployment figures, and global economic factors is crucial to understanding the potential scenarios. The Fed's approach will likely involve a careful assessment of incoming data and a gradual adjustment of monetary policy.
Call to Action: Staying informed about the Fed's decisions on Fed interest rates is vital for both businesses and individuals. Continue monitoring economic indicators like CPI, PPI, and unemployment rates and follow expert analysis to better understand the implications of future changes in Fed interest rates. Regularly reviewing economic news and Fed statements will help you stay ahead of potential shifts in the financial landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Microsoft And Asus Xbox Handheld Leaked Images Surface Online
May 10, 2025
Microsoft And Asus Xbox Handheld Leaked Images Surface Online
May 10, 2025 -
 Activist Suggests Womb Transplants To Enable Transgender Women To Give Birth
May 10, 2025
Activist Suggests Womb Transplants To Enable Transgender Women To Give Birth
May 10, 2025 -
 Vozmozhniy Noviy Potok Ukrainskikh Bezhentsev V Germaniyu Vliyanie Politiki S Sh A
May 10, 2025
Vozmozhniy Noviy Potok Ukrainskikh Bezhentsev V Germaniyu Vliyanie Politiki S Sh A
May 10, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnson Apuesta Por Hereu La Marca Catalana Que Conquista A Las Celebrities
May 10, 2025
Dakota Johnson Apuesta Por Hereu La Marca Catalana Que Conquista A Las Celebrities
May 10, 2025 -
 Madhyamik 2025 Results Official Merit List Release Date
May 10, 2025
Madhyamik 2025 Results Official Merit List Release Date
May 10, 2025
