WTO Accession Accelerated: Navigating The Privilege Dilemma

Table of Contents
The Allure of Accelerated WTO Accession
The appeal of accelerated WTO accession is powerful, offering numerous economic and political advantages.
Economic Benefits
Joining the WTO unlocks significant economic opportunities:
-
Increased market access for exports: WTO membership eliminates or reduces tariffs and other trade barriers, providing access to vast new markets for exporting nations. This is particularly crucial for developing countries seeking to diversify their economies and increase their export revenues. For example, Vietnam's accession to the WTO in 2007 led to a significant surge in its exports.
-
Attracting foreign direct investment (FDI): WTO membership signals a commitment to open markets and predictable trade policies, making countries more attractive to foreign investors. FDI inflows can boost economic growth, create jobs, and transfer technology and know-how.
-
Improved trade relations and diversification: Membership fosters stronger trade relationships with WTO members, leading to greater trade diversification and reduced reliance on a few key trading partners. This can enhance resilience to external shocks.
-
Access to WTO dispute settlement mechanisms: The WTO’s dispute settlement system provides a robust mechanism for resolving trade disputes, protecting member countries' interests and ensuring a fair and predictable trading environment.
Political Advantages
Beyond economic benefits, accelerated WTO accession also offers considerable political advantages:
-
Enhanced international standing and diplomatic influence: WTO membership grants a country a seat at the table in global trade governance, enhancing its voice and influence in international affairs.
-
Alignment with international trade rules and norms: Accession requires aligning domestic regulations with international trade rules, promoting transparency and predictability in the trading system.
-
Potential for greater political stability through economic integration: Increased trade and economic interdependence fostered by WTO membership can contribute to greater regional and global stability.
The Challenges of Rapid WTO Integration
While the benefits are substantial, rapid WTO integration presents considerable challenges:
Domestic Economic Adjustments
Accelerated accession requires swift and substantial domestic economic adjustments:
-
Need for rapid structural reforms: Meeting WTO commitments often necessitates rapid structural reforms, potentially impacting various sectors of the economy.
-
Potential for increased competition and job displacement: Increased competition from foreign imports can lead to job losses in certain sectors, requiring proactive measures to mitigate the negative impacts, like retraining programs and social safety nets.
-
Requirement for substantial investment in infrastructure and capacity building: Meeting WTO obligations may require significant investments in infrastructure, such as customs modernization and improved transportation networks.
Regulatory Hurdles and Implementation Gaps
Implementing WTO rules and regulations quickly poses significant challenges:
-
Difficulties in implementing complex WTO rules and regulations quickly: The WTO’s rules are complex and require significant technical expertise to implement effectively.
-
Potential for regulatory inconsistencies and enforcement challenges: Rapid implementation can lead to inconsistencies in the application of regulations and difficulties in effective enforcement.
-
Risk of undermining domestic policy objectives: The pressure to comply with WTO rules might necessitate compromises on domestic policy objectives, particularly in areas such as public health, environmental protection, or labor standards.
Vulnerability to External Shocks
Rapid integration increases vulnerability to external economic shocks:
-
Increased exposure to global economic fluctuations and trade wars: Accelerated accession exposes economies to greater volatility in global markets and increased vulnerability to trade wars or other protectionist measures.
-
Potential for exploitation by larger, more established trading partners: Newly acceded members may find themselves at a disadvantage in negotiations with larger, more established trading partners.
-
Need for effective safeguards and contingency planning: Effective safeguards and contingency plans are crucial to mitigate the risks associated with increased exposure to external shocks.
Strategies for Navigating the Privilege Dilemma
Careful planning and strategic implementation are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks of accelerated WTO accession:
Phased Approach to Implementation
A gradual approach can mitigate risks:
-
Advantages of a gradual integration strategy to mitigate risks: A phased approach allows countries to gradually adapt to the demands of WTO membership, reducing the potential for disruptive economic and social consequences.
-
Prioritizing specific sectors for early integration: Focusing on sectors with strong export potential or high capacity for rapid adaptation can generate early wins and build momentum.
-
Building domestic capacity to effectively manage WTO commitments: Investing in capacity building ensures the country has the necessary expertise and institutional framework to manage its WTO obligations effectively.
Capacity Building and Technical Assistance
Seeking external support is essential:
-
Importance of seeking technical assistance from international organizations: Organizations like the WTO, the World Bank, and the IMF offer valuable technical assistance to help countries prepare for and implement WTO commitments.
-
Investing in training programs for government officials and businesses: Training programs can enhance the expertise of government officials and private sector actors in navigating the complexities of WTO rules and procedures.
-
Strengthening domestic institutions responsible for trade policy and regulation: Strengthening institutions ensures effective implementation and enforcement of WTO rules and regulations.
Strategic Partnerships and Regional Cooperation
Collaboration is key:
-
Leveraging regional trade agreements to ease the transition to WTO membership: Regional trade agreements can provide a stepping stone towards WTO membership, allowing countries to gradually adapt to international trade rules.
-
Collaborating with other developing countries to share experiences and best practices: Sharing experiences and best practices can help countries learn from each other and avoid common pitfalls.
-
Seeking support from developed countries to address capacity gaps: Developed countries can provide valuable financial and technical assistance to help developing countries overcome capacity gaps.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices in Accelerated WTO Accession
Accelerated WTO accession presents a "privilege dilemma," offering substantial economic and political benefits but also posing significant challenges. Careful planning, a phased approach to implementation, robust capacity building initiatives, and strategic partnerships are crucial for successful navigation. Thorough research, informed policy discussions, and a strategic approach are essential. Understanding the complexities of WTO Accession Accelerated and its associated privilege dilemma is crucial for making informed choices that maximize the benefits and minimize the risks. Further research into specific aspects of WTO accession, particularly those relating to accelerated timelines, is highly recommended.

Featured Posts
-
 Simone Biles Bahamas Getaway Bikini Photos And Girls Trip Details
May 07, 2025
Simone Biles Bahamas Getaway Bikini Photos And Girls Trip Details
May 07, 2025 -
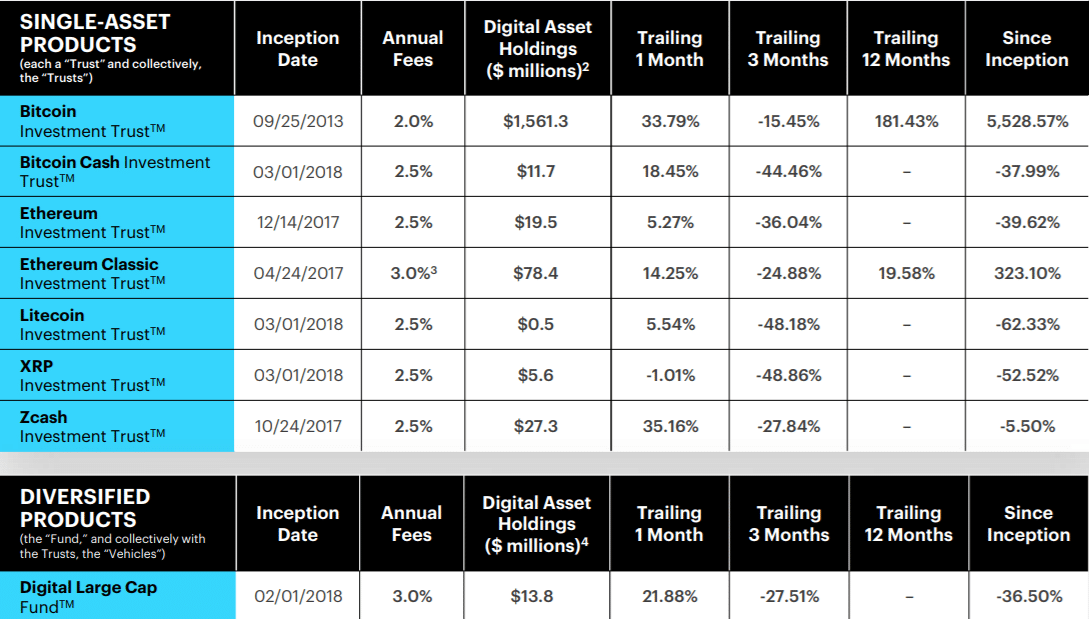 Xrp On The Verge Of A Record High Grayscale Etf Application And Market Analysis
May 07, 2025
Xrp On The Verge Of A Record High Grayscale Etf Application And Market Analysis
May 07, 2025 -
 Ep Why Dont You
May 07, 2025
Ep Why Dont You
May 07, 2025 -
 Improving Air Traffic Control Overcoming The I Dont Know Where You Are Challenge
May 07, 2025
Improving Air Traffic Control Overcoming The I Dont Know Where You Are Challenge
May 07, 2025 -
 Mkhtt Alkhtwt Almlkyt Almghrbyt Lzyadt Edd Alrhlat Aljwyt Byn Saw Bawlw Waldar Albydae
May 07, 2025
Mkhtt Alkhtwt Almlkyt Almghrbyt Lzyadt Edd Alrhlat Aljwyt Byn Saw Bawlw Waldar Albydae
May 07, 2025
