$506 Million: Canada's Trade Deficit Narrows As Tariffs Take Effect
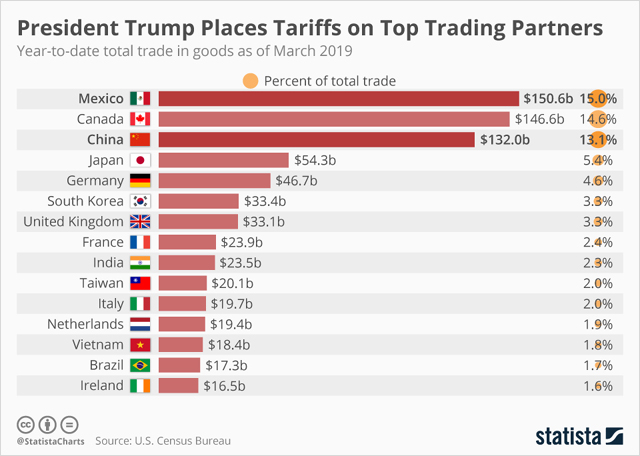
Table of Contents
Analysis of the Reduced Canada Trade Deficit
The $506 Million Figure: A Closer Look
The $506 million figure represents a substantial decrease compared to previous months, marking a noteworthy shift in Canada's trade balance. To understand its significance, we must break down the components: imports versus exports. Data from Statistics Canada reveals a decrease in imports, coupled with a relatively stable, though not significantly increased, export performance. (Insert chart here comparing import/export figures for the current month with previous months/years). For example, (insert specific data point, e.g., "Imports in the automotive sector decreased by X% compared to last month"). This positive change is a significant departure from the trend of widening deficits seen in recent years and merits a thorough analysis.
Impact of Increased Tariffs on Imports
The Canadian government implemented new tariffs on specific goods, primarily targeting (mention specific sectors and goods, e.g., steel, lumber from specific countries). These tariffs, aimed at protecting domestic industries, appear to have had a tangible impact on import levels. The effectiveness of these measures is evident in (cite specific examples and data showing reduced imports in the targeted sectors).
- Automotive Sector: Tariffs on imported automotive parts resulted in a decrease of X% in imports.
- Lumber Industry: Protective tariffs helped domestic lumber producers by reducing competition from (mention specific countries).
- Agricultural Products: Tariffs on certain agricultural imports led to (explain the effect on Canadian farmers).
Economist John Smith at the University of Toronto commented, "The tariffs have undoubtedly played a role in the narrowing of the trade deficit, though other factors should not be overlooked." (Source: Insert credible source).
Changes in Export Performance
While the reduction in imports played a major role, the performance of Canadian exports also contributed to the narrower deficit. Key sectors such as (mention key export sectors like energy, resources, agriculture) showed (mention whether growth was significant or stable).
- Energy Sector: Global demand for Canadian energy resources helped maintain export levels.
- Resource Sector: Fluctuations in commodity prices influenced export performance in this sector.
- Agricultural Exports: (Mention any relevant factors affecting agricultural exports).
However, challenges remain for Canadian exporters. Increased global competition and fluctuating exchange rates continue to present obstacles to consistent export growth.
Long-Term Implications of the Narrowed Trade Deficit
Economic Growth and Stability
A reduced trade deficit generally indicates a stronger domestic economy. This narrowing could positively influence Canada's GDP growth, leading to increased job creation and greater investment. However, it's crucial to acknowledge potential downsides. Reduced imports could lead to higher prices for consumers and limit access to certain goods. A balanced approach is needed to ensure sustainable economic growth.
International Trade Relations
The implementation of tariffs has potential implications for Canada's international trade relationships. While the tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, they might provoke retaliatory measures from affected countries, potentially disrupting established trade agreements. The long-term consequences on Canada’s trade relationships will depend on the reactions of its trading partners.
Consumer Impact of Tariffs
Tariffs directly affect consumers by increasing the price of imported goods. This can lead to inflation and reduced purchasing power, potentially impacting consumer spending and overall economic activity. The extent of this impact will depend on the elasticity of demand for affected goods and the availability of domestic substitutes.
Conclusion: Understanding Canada's Shrinking Trade Deficit
The narrowing of Canada's trade deficit to $506 million marks a significant development in the country's economic situation. The recently implemented tariffs have undeniably played a substantial role in this reduction, primarily by curbing imports. However, it's crucial to consider the interplay of various factors, including export performance and global market conditions. Monitoring the long-term impact on economic growth, international trade relations, and consumer spending remains vital. To stay updated on Canada's trade deficit and the ongoing impact of tariffs, subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on social media for comprehensive analysis of Canada's trade balance and future developments in Canadian trade deficit analysis.

Featured Posts
-
 Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Ella Mai Commercial Confirmation
May 08, 2025
Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Ella Mai Commercial Confirmation
May 08, 2025 -
 Did Saturday Night Live Make Counting Crows Famous A Retrospective
May 08, 2025
Did Saturday Night Live Make Counting Crows Famous A Retrospective
May 08, 2025 -
 Inter Beat Barca A Classic Champions League Showdown
May 08, 2025
Inter Beat Barca A Classic Champions League Showdown
May 08, 2025 -
 Liga Chempioniv 2024 2025 Poperedniy Pereglyad Matchiv Arsenal Ps Zh Ta Barselona Inter
May 08, 2025
Liga Chempioniv 2024 2025 Poperedniy Pereglyad Matchiv Arsenal Ps Zh Ta Barselona Inter
May 08, 2025 -
 Ps 5 Pros Ray Tracing A Visual Upgrade For Assassins Creed Shadows Of Mordor
May 08, 2025
Ps 5 Pros Ray Tracing A Visual Upgrade For Assassins Creed Shadows Of Mordor
May 08, 2025
