Global Forest Destruction: Wildfires Exacerbate Record Losses
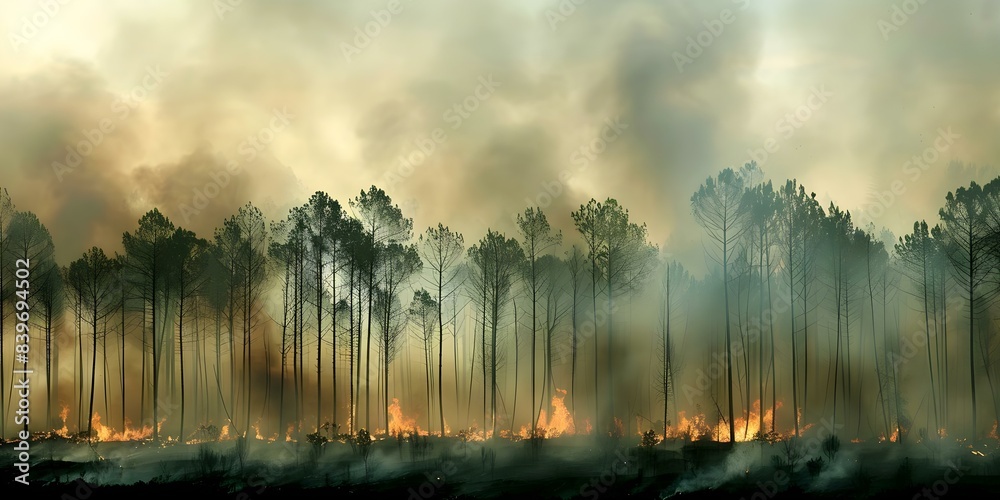

Table of Contents
H2: The Scale of Global Forest Destruction
The scale of global forest destruction is staggering. Record deforestation rates are pushing numerous ecosystems to the brink of collapse. Reliable sources like the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) and Global Forest Watch consistently report alarming trends in forest loss statistics and tree cover loss.
H3: Record Deforestation Rates
- Data indicates that millions of hectares of forest are lost annually, a figure that has been steadily increasing over the past decades. The rate of deforestation varies significantly across regions, with some areas experiencing drastically higher losses than others.
- The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the "lungs of the planet," is a key area experiencing severe deforestation rates, along with vast boreal forests in the northern latitudes.
- The consequences of this extensive deforestation are far-reaching, impacting biodiversity loss, accelerating climate change through reduced carbon sequestration, and disrupting crucial ecosystem services like water regulation and soil stabilization.
H2: The Role of Wildfires in Forest Destruction
Wildfires are playing an increasingly significant role in global forest destruction. The link between climate change, wildfire intensity, and extreme weather events is undeniable.
H3: Increased Frequency and Intensity
- Hotter and drier conditions, exacerbated by climate change, create ideal environments for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Longer and more intense fire seasons are now commonplace in many parts of the world.
- Devastating wildfires in recent years, such as those in Australia, California, and Siberia, have consumed vast tracts of forest, releasing massive amounts of greenhouse gases and causing irreparable damage to ecosystems.
- Preventing and suppressing these increasingly ferocious wildfires presents enormous challenges, requiring significant resources and international cooperation.
H2: Environmental Consequences of Forest Loss
The environmental consequences of global forest destruction are profound and far-reaching. Biodiversity loss is one of the most devastating impacts.
H3: Biodiversity Loss
- Deforestation leads to widespread habitat destruction and fragmentation, isolating populations of plants and animals and making them more vulnerable to extinction.
- Many plant and animal species face an increased extinction risk due to habitat loss, directly related to deforestation and exacerbated by wildfires.
- The loss of forests disrupts critical ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration – crucial in mitigating climate change – and water regulation, affecting regional water cycles and increasing the risk of droughts and floods.
H2: Socioeconomic Impacts of Forest Destruction
The socioeconomic impacts of global forest destruction are severe, particularly for indigenous communities. These communities often depend on forests for their livelihoods and cultural survival.
H3: Indigenous Communities
- Deforestation threatens the access of indigenous communities to essential resources such as food, medicine, and building materials, disrupting their traditional ways of life.
- Displacement from their ancestral lands due to deforestation and wildfire damage results in social and economic hardship, impacting their health, education, and overall well-being.
- Protecting indigenous land rights is crucial for ensuring the long-term health of forests and the rights and livelihoods of these communities. Sustainable forestry practices are essential in this regard.
3. Conclusion:
Global forest destruction is a crisis of immense proportions, with wildfires significantly accelerating the rate of loss. The consequences are devastating, impacting biodiversity, climate change, and the livelihoods of countless people, particularly indigenous communities. The scale of deforestation rates and the increasing intensity of wildfires necessitate urgent action.
To combat global forest destruction and prevent further devastating losses, we must take immediate action. We need to support conservation organizations working to protect forests, advocate for policies that promote sustainable forest management and combat wildfires, and actively reduce our carbon footprint to mitigate climate change. Each of us has a role to play in preventing deforestation. Let’s protect our forests—our planet's future depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Liverpool Awaits Klopps Return Ahead Of Final Match
May 22, 2025
Liverpool Awaits Klopps Return Ahead Of Final Match
May 22, 2025 -
 The Goldbergs Characters Relationships And Lasting Legacy
May 22, 2025
The Goldbergs Characters Relationships And Lasting Legacy
May 22, 2025 -
 The Goldbergs Why The Show Resonates With Audiences
May 22, 2025
The Goldbergs Why The Show Resonates With Audiences
May 22, 2025 -
 How Google Is Making Virtual Meetings Better
May 22, 2025
How Google Is Making Virtual Meetings Better
May 22, 2025 -
 G 7 Finance Ministers Navigating Trade Disputes With The Us
May 22, 2025
G 7 Finance Ministers Navigating Trade Disputes With The Us
May 22, 2025
