Impact Of Tariffs: China's Approach To Stimulate The Economy Through Rate Cuts
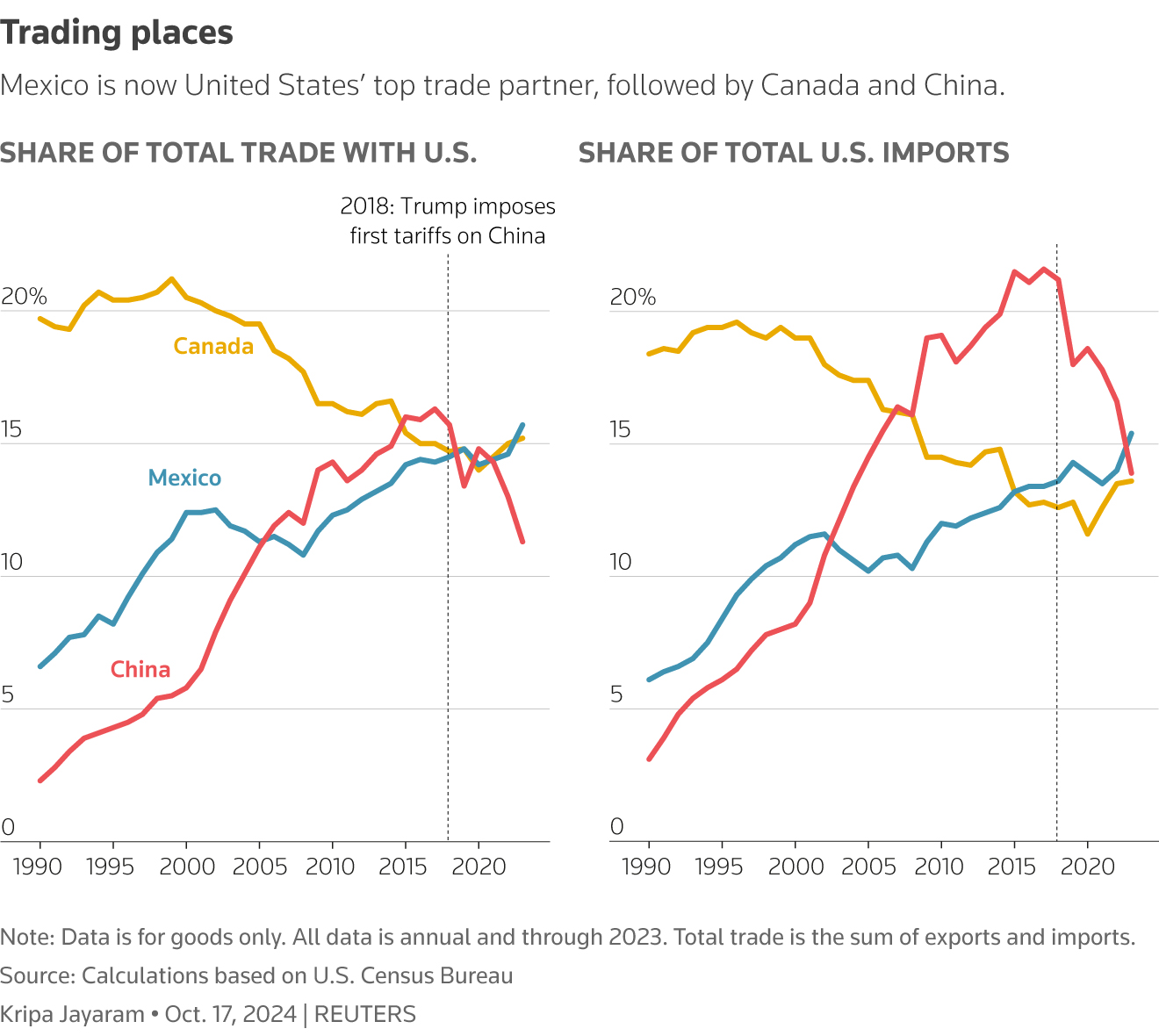
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on the Chinese Economy
The imposition of tariffs, particularly those initiated by the US, has had a demonstrably negative effect on the Chinese economy. These trade barriers have significantly hampered Chinese exports, leading to slower overall economic growth and impacting various sectors.
Disrupted Supply Chains
Tariffs have severely disrupted global supply chains, causing significant problems for Chinese manufacturers and businesses. The increased costs associated with exporting goods have reduced competitiveness in international markets.
- Increased production costs: Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported components and raw materials, making Chinese goods more expensive in global markets.
- Reduced export competitiveness: Higher prices make Chinese products less attractive compared to those from countries not subject to the same tariffs.
- Loss of market share: As a result of reduced competitiveness, Chinese companies have experienced a decline in market share in several key industries.
Reduced Foreign Investment
The uncertainty surrounding tariffs has discouraged foreign direct investment (FDI) in China. Multinational corporations are hesitant to commit significant capital in an environment of unpredictable trade policies.
- Hesitation from multinational corporations: Companies are delaying or reconsidering investment plans due to the risks associated with tariff fluctuations.
- Shifting investment to other countries: To mitigate risks, many businesses are shifting their investment towards countries with more stable trade environments.
- Decreased capital inflow: The reduction in FDI negatively impacts China's economic growth and development.
Domestic Market Slowdown
Tariffs haven't just affected exports; they've also impacted the domestic market. Reduced consumer confidence and decreased business investment have contributed to slower GDP growth.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook has led to decreased consumer spending.
- Decreased business investment: Businesses are less inclined to invest in expansion or new projects due to the uncertainty surrounding future trade policies.
- Slower GDP growth: The combined impact of reduced exports, FDI, and domestic consumption has resulted in slower overall GDP growth.
China's Response: Implementing Rate Cuts
Faced with these economic headwinds, the Chinese government has responded by implementing a series of China's rate cuts. This monetary policy approach aims to stimulate economic activity by making borrowing cheaper and more accessible.
Lowering Interest Rates
Lowering interest rates is a key component of China's stimulus package. Reduced borrowing costs incentivize businesses and consumers to take out loans, boosting investment and spending.
- Cheaper loans for businesses: Lower interest rates make it more affordable for businesses to invest in expansion, equipment upgrades, and hiring.
- Increased investment in infrastructure projects: Government-sponsored infrastructure projects can be funded more easily with cheaper borrowing costs.
- Potential boost to consumer spending: Lower interest rates on mortgages and consumer loans may encourage increased spending.
Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR) Adjustments
Alongside interest rate cuts, the Chinese government has also adjusted the Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR), the proportion of deposits banks must hold in reserve. Lowering the RRR increases the lending capacity of banks.
- Increased lending capacity of banks: By reducing the RRR, banks have more funds available to lend to businesses and consumers.
- More funds available for loans: This increased lending capacity can further stimulate investment and consumption.
- Potential for increased money supply: Lowering the RRR can lead to an increase in the money supply, potentially boosting economic activity.
Other Monetary Policy Tools
China has also employed other monetary policy tools alongside rate cuts, such as quantitative easing (QE) or targeted lending programs focused on specific sectors. These measures aim to supplement the effect of rate cuts.
- Examples of other supportive measures: These may include targeted lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or direct government spending initiatives.
- Their intended effects: These measures aim to address specific bottlenecks in the economy and ensure that the stimulus reaches its intended targets.
- Potential limitations: The effectiveness of these supplementary measures depends on various factors, including the efficiency of implementation and the overall economic climate.
Effectiveness and Challenges of China's Rate Cuts
The effectiveness of China's rate cuts in stimulating economic growth is a complex issue. While lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and investment, several challenges remain.
Debt Levels and Risks
A significant concern is the potential for increased debt levels. China already has a relatively high level of debt, and further borrowing could increase financial instability.
- Increased risk of financial instability: High levels of debt increase the risk of defaults and potential financial crises.
- Potential for asset bubbles: Easy access to credit may inflate asset prices, creating bubbles that can burst, leading to economic instability.
- Challenges in debt management: Managing the increasing debt burden requires careful planning and effective policy implementation.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic conditions significantly influence the effectiveness of China's rate cuts. A global recession or increased trade tensions could offset the positive effects of these measures.
- Impact of global recessionary pressures: Global economic downturns can reduce demand for Chinese exports, mitigating the impact of domestic stimulus measures.
- Influence of currency fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates can impact export competitiveness and the effectiveness of monetary policy.
- Effects of international trade tensions: Ongoing trade disputes can negatively affect investor confidence and hinder economic growth.
Structural Reforms
For long-term sustainable growth, China needs to complement its monetary policy with structural reforms. These reforms aim to improve economic efficiency and promote innovation.
- Examples of necessary structural reforms: These could include reducing state-owned enterprise dominance, improving regulatory efficiency, and fostering innovation in technology sectors.
- Their role in boosting long-term growth: Structural reforms create a more dynamic and competitive economy, fostering long-term sustainable growth.
Conclusion
China's strategic use of China's rate cuts in response to the economic challenges posed by tariffs highlights the complex interplay between international trade and domestic monetary policy. While rate cuts can offer short-term stimulus by encouraging borrowing and investment, their long-term effectiveness depends heavily on managing debt levels and implementing complementary structural reforms. Understanding the impact of China's rate cuts is crucial for navigating the evolving global economic landscape. To stay informed about the latest developments regarding China's economic strategy and the ongoing impact of tariffs, continue researching the effects of China's rate cuts and related monetary policies.

Featured Posts
-
 Jayson Tatum Wrist Injury Boston Celtics Head Coachs Statement
May 08, 2025
Jayson Tatum Wrist Injury Boston Celtics Head Coachs Statement
May 08, 2025 -
 Jayson Tatum Faces Ongoing Criticism From Colin Cowherd
May 08, 2025
Jayson Tatum Faces Ongoing Criticism From Colin Cowherd
May 08, 2025 -
 Road Rage Incident Van Strikes Motorcycle Cnn Coverage
May 08, 2025
Road Rage Incident Van Strikes Motorcycle Cnn Coverage
May 08, 2025 -
 The Importance Of Trustworthy Crypto News Sources In A Volatile Market
May 08, 2025
The Importance Of Trustworthy Crypto News Sources In A Volatile Market
May 08, 2025 -
 Japanese Trading House Stock Prices Climb Following Berkshires Acquisition
May 08, 2025
Japanese Trading House Stock Prices Climb Following Berkshires Acquisition
May 08, 2025
