Office365 Security Flaw Exploited: Millions In Losses Reported

Table of Contents
Understanding the Office365 Security Flaw
This recent Office365 security breach leveraged vulnerabilities in the platform's authentication process. Attackers exploited a zero-day exploit, meaning Microsoft was unaware of the vulnerability before the attack. This specific flaw allowed attackers to bypass standard security measures and gain unauthorized access to user accounts.
-
How the Attackers Operated: The primary attack vector involved sophisticated phishing campaigns. These emails appeared legitimate, often mimicking internal communications or invoices, tricking employees into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments. This resulted in malware installation, providing attackers with persistent access to the compromised accounts.
-
Technical Details (Simplified): The vulnerability resided within the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework, specifically in how it handled delegated permissions. Attackers manipulated the process to obtain elevated privileges, allowing access beyond what should have been granted. While specific technical details are often withheld to prevent further exploitation, understanding the general mechanism helps organizations focus preventative measures.
-
Examples of Specific Vulnerabilities:
- Compromised API Access: Attackers gained unauthorized access to sensitive data through compromised Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
- Insufficient MFA: A lack of robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) allowed attackers to easily take over accounts once credentials were compromised.
- Outdated Software: Many affected organizations were running outdated versions of Office365 applications and services, leaving them susceptible to known vulnerabilities.
Impact of the Office365 Security Breach
The financial repercussions of this Office365 security breach are staggering. Early reports indicate losses exceeding $50 million across multiple businesses, a figure that is expected to rise as more organizations assess the full extent of the damage. This represents not only direct financial loss but also significant indirect costs.
-
Financial Losses: The millions lost encompass direct theft of funds, costs associated with data recovery, incident response, and legal fees.
-
Reputational Damage: The breach severely damaged the reputation of affected companies, eroding customer trust and potentially impacting future business prospects. Public disclosure of a data breach can have devastating long-term consequences.
-
Legal Ramifications: Companies face hefty fines under regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) due to the unauthorized access and potential loss of sensitive customer data.
-
Business Disruption: The attack caused significant business disruption due to system downtime, compromised operations, and the time-consuming process of data recovery and remediation.
-
Loss of Sensitive Data: The breach resulted in the exposure of confidential customer information, intellectual property, and other sensitive business data, leading to potential further exploitation and long-term risks.
Preventing Future Office365 Security Breaches
Proactive measures are crucial to prevent similar Office365 security breaches. Organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to bolster their defenses.
-
Robust Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA is paramount. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if they obtain passwords.
-
Regular Software Updates: Keeping all Office365 applications, services, and operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches is essential to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
-
Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies, including length requirements, complexity rules, and regular password changes. Encourage the use of password managers.
-
Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
-
Advanced Threat Detection: Invest in advanced threat detection and response systems to proactively identify and neutralize malicious activities.
-
Security Awareness Training: Provide comprehensive security awareness training to employees to educate them about phishing scams, malware, and other social engineering tactics.
-
Email Filtering and Anti-Malware: Utilize robust email filtering and anti-malware software to prevent malicious emails and attachments from reaching users' inboxes.
-
Regular Permission Reviews: Regularly review user permissions and access controls to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
Conclusion
The recent Office365 security flaw exploited highlights the ever-present threat of cyberattacks, even on seemingly secure platforms. The millions of dollars in losses underscore the urgent need for robust security measures. Don't become another victim. Protect your business from Office365 security breaches by implementing the preventative measures discussed above. Take control of your Office365 security today and safeguard your valuable data and reputation. Learn more about securing your Office365 environment and prevent costly Office365 security flaws.

 Uber Stock Recession Proof Analyst Insights
Uber Stock Recession Proof Analyst Insights
 Whos Playing Spring Breakout 2025 Roster Preview
Whos Playing Spring Breakout 2025 Roster Preview
 Fortune Coins Achieve Your Financial Fortune
Fortune Coins Achieve Your Financial Fortune
 Spring Breakout 2025 Roster Composition And Team Strategies
Spring Breakout 2025 Roster Composition And Team Strategies
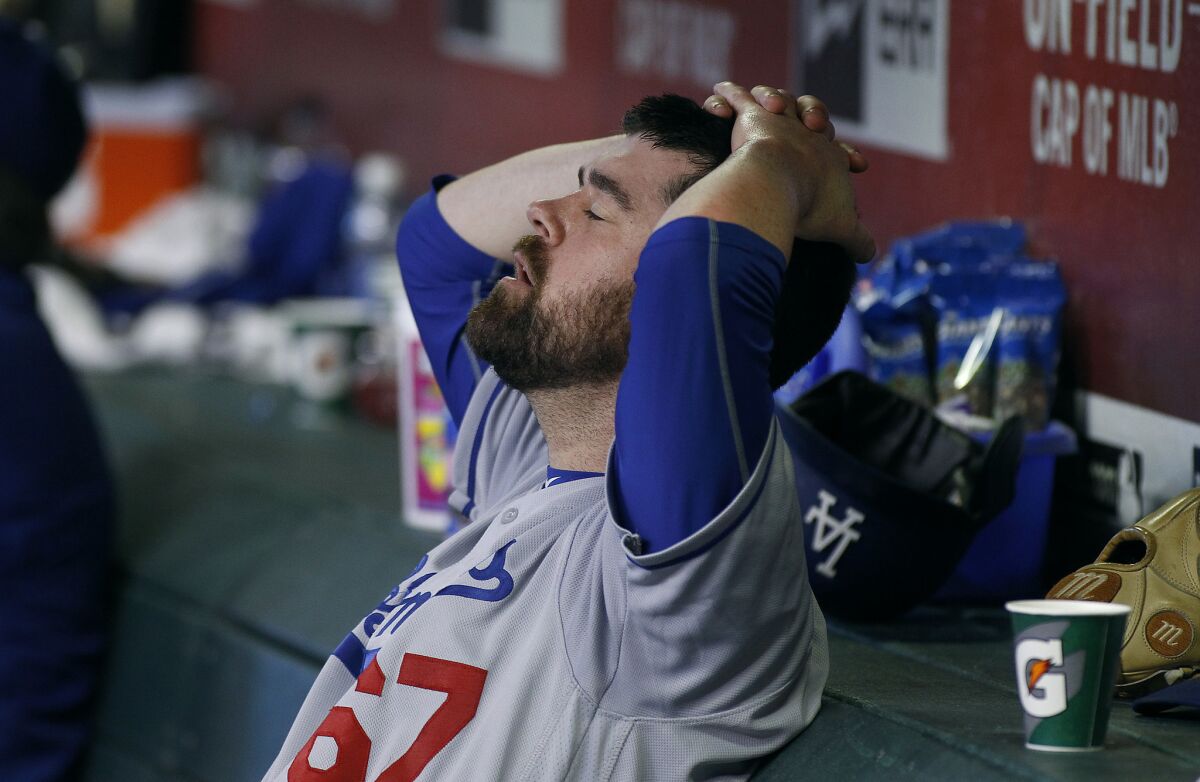 Are The Dodgers Left Handed Batters In A Slump A Performance Review
Are The Dodgers Left Handed Batters In A Slump A Performance Review
