Record-Breaking Forest Loss: Wildfires Drive Global Deforestation
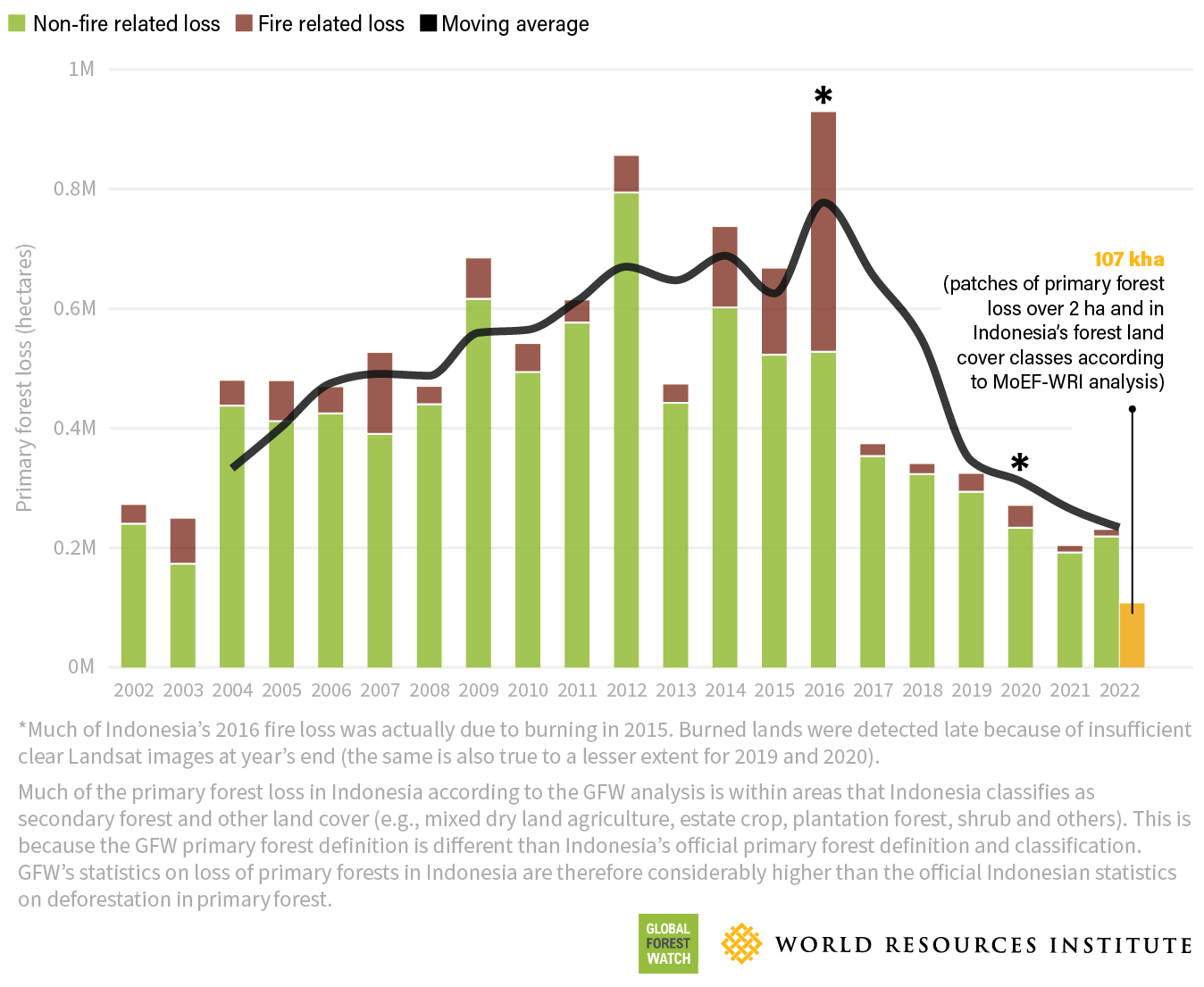
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Global Deforestation
Wildfires are increasingly recognized as a major contributor to global deforestation. Their frequency and intensity are escalating, leading to unprecedented levels of forest loss worldwide.
Increased Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
Climate change is a primary driver of this alarming trend. Rising global temperatures and prolonged periods of drought create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Warmer, drier conditions also increase the flammability of vegetation, leading to more intense and uncontrollable blazes.
- 2023 witnessed record-breaking wildfire seasons across the globe, including devastating events in Canada, Australia, and parts of the Amazon rainforest.
- The Siberian forests have also suffered significant losses due to increasingly frequent and intense wildfires.
- The area of forest lost to wildfires in the past decade represents a significant portion of the overall global deforestation figures. Precise figures vary depending on the source and methodologies used, but the trend is undeniably upward.
The Role of Human Activities in Wildfire Spread
Human activities play a significant role in both the ignition and spread of wildfires, exacerbating the problem of deforestation. Deforestation itself creates drier landscapes, increasing wildfire risk.
- Deforestation for agriculture: Clearing forests for crops like soy and palm oil, and for cattle ranching, leaves behind vast expanses of dry, flammable vegetation.
- Logging activities: Illegal logging and unsustainable forestry practices create fuel loads and access points that facilitate wildfire spread.
- Urban sprawl: Expanding urban areas encroach on forestlands, creating interfaces where wildfires can easily ignite and spread into surrounding forests.
- Accidental and deliberate ignition: Human negligence and arson account for a significant number of wildfire starts each year, contributing substantially to deforestation. Poor forest management practices further increase the likelihood of human-caused wildfires.
Studies consistently show that a high percentage of wildfires are human-caused. While naturally occurring wildfires have always existed, the combination of climate change and human activity has created a perfect storm for devastating forest fires.
Beyond Wildfires: Other Factors Contributing to Global Deforestation
While wildfires are a significant driver of global deforestation, other factors also contribute to this alarming trend.
Illegal Logging and its Devastating Consequences
Illegal logging remains a pervasive problem globally, contributing significantly to deforestation. Weak governance, corruption, and a lack of effective monitoring allow illegal operations to thrive.
- The Amazon rainforest, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa are particularly hard-hit by illegal logging, leading to extensive habitat destruction and biodiversity loss.
- The economic losses associated with illegal logging are substantial, while the environmental damage is incalculable.
- The illegal timber trade fuels further deforestation and undermines efforts to sustainably manage forest resources.
Agricultural Expansion and its Impact on Forest Cover
The expansion of agriculture for crops and livestock remains a major driver of global deforestation. Unsustainable agricultural practices often involve clearing vast tracts of forest for short-term economic gains.
- Palm oil plantations, cattle ranching, and large-scale monoculture farming are particularly damaging to forest ecosystems.
- The conversion of forestland for agriculture leads to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and soil degradation.
- The demand for agricultural products drives deforestation, necessitating a shift toward more sustainable and responsible agricultural practices.
The Consequences of Record-Breaking Forest Loss
The consequences of record-breaking forest loss are far-reaching and devastating, impacting the planet and its inhabitants.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Deforestation significantly contributes to climate change by releasing vast amounts of stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This creates a dangerous feedback loop, where deforestation accelerates climate change, leading to warmer, drier conditions that increase wildfire risk, and further deforestation.
- Deforestation is responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- The loss of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, further exacerbating climate change.
- The resulting climate change impacts increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including droughts and wildfires, further intensifying the cycle.
Biodiversity Loss and its Far-Reaching Effects
The loss of forests leads to catastrophic habitat loss and biodiversity decline. Numerous plant and animal species are threatened with extinction as their habitats are destroyed.
- Many endangered species rely on intact forest ecosystems for survival.
- The loss of biodiversity reduces the resilience of ecosystems and weakens their capacity to provide essential ecosystem services.
- The consequences extend beyond the loss of individual species, impacting the intricate web of life that supports all life on Earth.
Socioeconomic Impacts
Deforestation negatively impacts the livelihoods of millions of people, particularly indigenous communities who depend on forests for their survival. It also has significant economic consequences.
- Indigenous communities often lose their traditional lands and sources of income.
- Deforestation can lead to economic instability in regions heavily reliant on forest resources.
- The loss of ecosystem services associated with forests can have significant economic and social costs.
Conclusion
Record-breaking forest loss, fueled by wildfires and other factors, presents a severe global crisis. The devastating consequences for climate, biodiversity, and human society demand immediate and decisive action. Combating global deforestation requires a multi-pronged approach involving governments, corporations, and individuals. We must support sustainable forestry practices, reduce our carbon footprint, and advocate for stronger environmental protection policies. Addressing global deforestation is not just an environmental imperative; it’s crucial for the future of humanity. Let's work together to protect our forests and safeguard the planet for future generations. The fight against global deforestation starts now.

Featured Posts
-
 Teslas Future How Elon Musks Approach Impacts The Company
May 26, 2025
Teslas Future How Elon Musks Approach Impacts The Company
May 26, 2025 -
 The Art Of The Deal Trump And Republican Negotiations
May 26, 2025
The Art Of The Deal Trump And Republican Negotiations
May 26, 2025 -
 Les Diables Rouges Et La Rtbf Un Partenariat Renouvele
May 26, 2025
Les Diables Rouges Et La Rtbf Un Partenariat Renouvele
May 26, 2025 -
 Andalusian Farmstay Your Perfect Country Escape
May 26, 2025
Andalusian Farmstay Your Perfect Country Escape
May 26, 2025 -
 Solving Supply Chain Issues Sg Wireless Enhanced Manufacturing Partnerships
May 26, 2025
Solving Supply Chain Issues Sg Wireless Enhanced Manufacturing Partnerships
May 26, 2025
