Smaller QE Programs: A More Prudent Approach For The BOE, According To Greene
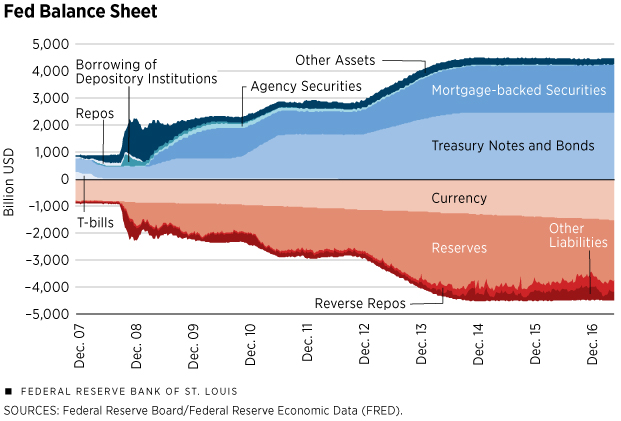
Table of Contents
The Risks of Large-Scale QE Programs
Large-scale QE programs, while potentially effective in stimulating short-term economic activity, carry substantial risks. These risks outweigh the benefits, particularly in the current economic context, according to Greene.
Inflationary Pressures
Injecting vast sums of liquidity into the economy through large QE programs can significantly fuel inflationary pressures. This happens because increased money supply, without a corresponding increase in goods and services, drives up prices.
- The 2008-2009 global financial crisis saw many central banks, including the BOE, implement large-scale QE programs. While these initially helped stabilize markets, they also contributed to subsequent inflationary pressures.
- Quantitative easing inflation is a complex issue, influenced by factors like supply chain disruptions and global commodity prices. However, the direct link between increased money supply and rising prices remains a key concern.
- Maintaining price stability is a primary mandate for central banks. Large QE programs can jeopardize this crucial objective, leading to a vicious cycle of inflation and potentially damaging economic consequences.
Asset Bubbles
Large QE programs can inflate asset bubbles, particularly in the stock market and real estate sectors. This occurs because the newly injected liquidity seeks returns, often pushing up asset prices beyond their fundamental value.
- The rapid increase in property prices following previous QE initiatives serves as a prime example of asset price inflation fueled by readily available capital.
- Such bubbles are inherently unstable. When they burst, the resulting market corrections can have devastating consequences for financial stability and the broader economy.
- The risks associated with quantitative easing risks are amplified when QE is used indiscriminately, leading to systemic issues within the financial markets.
Reduced Effectiveness Over Time
The effectiveness of QE diminishes with repeated use and increased scale. Markets can become less responsive to further QE injections, leading to diminishing returns on this monetary policy tool.
- Central banks may need to inject ever-larger sums to achieve the same effect, exacerbating the inflationary and asset bubble risks discussed above.
- The BOE's experience with past QE programs highlights the potential for diminished effectiveness over time, supporting the need for a more strategic and targeted approach.
- Understanding the limitations of QE effectiveness is crucial for developing a more sustainable and responsible monetary policy.
The Advantages of Smaller, Targeted QE Programs
Smaller, more targeted QE programs offer a compelling alternative, mitigating the risks associated with large-scale interventions while still providing effective economic stimulus.
Improved Control and Precision
Smaller programs allow for more precise targeting of specific sectors or economic issues. This tailored stimulus can address particular economic weaknesses without the widespread inflationary consequences of broader injections.
- For example, targeted QE could focus on supporting specific industries struggling with reduced demand or supply chain bottlenecks.
- This approach offers a higher degree of control and precision, enabling the BOE to fine-tune its response to evolving economic conditions.
- Precision monetary policy, achieved through tailored stimulus, minimizes the risk of unintended side effects.
Reduced Systemic Risk
Smaller interventions significantly reduce the risk of creating systemic imbalances in the financial system. The lower scale minimizes the probability of unintended consequences that could destabilize markets.
- The reduced risk of asset bubbles and inflationary pressures are key benefits of this approach to risk management.
- Smaller, carefully calibrated QE programs enhance financial stability by preventing excessive liquidity from causing broader market distortions.
- Prudent monetary policy emphasizes minimizing systemic risk, and smaller QE aligns perfectly with this objective.
Enhanced Credibility
A more cautious and targeted approach to QE can enhance the central bank's credibility. Maintaining trust and confidence in the BOE's monetary policy decisions is paramount for its effectiveness.
- By demonstrating a commitment to price stability and avoiding excessive risk-taking, smaller QE programs reinforce market confidence in the central bank's judgment.
- Central bank credibility is essential for effective monetary policy implementation.
- Monetary policy credibility, built through responsible interventions like smaller QE programs, promotes long-term economic stability.
Greene's Argument and Supporting Evidence
[Greene's Name] argues that the risks associated with large-scale QE significantly outweigh the potential benefits in the current economic environment. Their research [cite relevant research/publications here], suggests that smaller, targeted interventions are more effective in achieving desired economic outcomes while minimizing the risk of inflation and asset bubbles. [Insert quotes from Greene here, if available, properly cited]. Their analysis emphasizes the importance of a cautious and nuanced approach to monetary policy, prioritizing long-term stability over short-term gains. The supporting evidence often highlights the diminishing returns of large-scale programs and the increased potential for negative unintended consequences.
Conclusion: Smaller QE Programs: A More Prudent Path Forward for the BOE?
In conclusion, the advantages of smaller, targeted QE programs are clear. They offer improved control, reduced systemic risk, and enhanced central bank credibility compared to large-scale interventions. [Greene's Name]'s argument strongly supports this perspective, highlighting the significant risks associated with larger QE programs and advocating for a more cautious and precise approach. Consider the implications of large-scale QE and explore alternative monetary policy approaches. Learn more about smaller QE programs and their potential to contribute to a more stable and sustainable economic environment. Ultimately, adopting a more prudent approach to QE, focusing on smaller, targeted programs, represents a more responsible and effective monetary policy tool for the BOE in navigating the complexities of the current economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Toute L Actualite Economique Du 24 Fevrier Avec Good Morning Business
Apr 23, 2025
Toute L Actualite Economique Du 24 Fevrier Avec Good Morning Business
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Canadas Economic Future Recession Concerns Despite Tariff Cuts
Apr 23, 2025
Canadas Economic Future Recession Concerns Despite Tariff Cuts
Apr 23, 2025 -
 L Integrale De Good Morning Business Lundi 24 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025
L Integrale De Good Morning Business Lundi 24 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025 -
 77 Inch Lg C3 Oled Was It The Right Choice For Me
Apr 23, 2025
77 Inch Lg C3 Oled Was It The Right Choice For Me
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Wildfire Wagers Analyzing The Trend Of Betting On Natural Disasters In Los Angeles
Apr 23, 2025
Wildfire Wagers Analyzing The Trend Of Betting On Natural Disasters In Los Angeles
Apr 23, 2025
