Strengthening Bilateral Security: China-Indonesia Partnership

Table of Contents
H2: Economic Cooperation as a Foundation for Security
Economic interdependence is a cornerstone of strong bilateral relations, and the China-Indonesia partnership is no exception. Investing in shared economic growth reduces the likelihood of conflict and fosters mutual reliance. This is achieved through several key initiatives:
H3: Joint Infrastructure Projects:
Investing in shared infrastructure is a powerful tool for strengthening economic ties and reducing security risks. By building interconnected infrastructure, both countries benefit from increased trade, improved connectivity, and enhanced regional integration. Specific examples include:
- High-speed rail projects: Improved transportation links facilitate trade and people-to-people exchanges, bolstering economic integration.
- Port development: Modernizing ports enhances trade efficiency and regional connectivity, creating jobs and economic opportunities.
- Digital infrastructure collaboration: Investing in digital connectivity improves communication, facilitates e-commerce, and supports the growth of the digital economy, further reducing the potential for conflict stemming from unequal access to resources.
These projects not only boost economic growth but also directly contribute to security by improving regional connectivity and reducing economic disparities that can fuel instability. For example, the improved transportation networks resulting from these projects enhance the ability of both countries to respond effectively to crises and emergencies.
H3: Trade and Investment:
Increased bilateral trade and investment create a web of interconnected interests that incentivize peaceful cooperation. The expansion of trade agreements, attraction of foreign direct investment (FDI), and promotion of technological exchange are all crucial aspects of this strategy.
- Expanding trade agreements: Agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) significantly boost trade volumes and create a mutually beneficial economic ecosystem.
- Attracting foreign direct investment: FDI from both countries fuels economic growth, creates jobs, and promotes technological advancement, strengthening mutual reliance.
- Promoting technological exchange: Sharing technological advancements fosters innovation, economic competitiveness, and mutual dependence, reducing incentives for conflict.
Analyzing the growth trajectory of bilateral trade reveals a significant upward trend across various sectors, including energy, manufacturing, and agriculture. This economic interconnectedness forms a strong basis for maintaining peaceful relations.
H2: Maritime Security Collaboration: Addressing Shared Challenges
The South China Sea is a crucial maritime region for both China and Indonesia. Cooperation on maritime security is therefore paramount to addressing shared challenges and maintaining regional stability.
H3: Combating Transnational Crime:
Joint efforts are crucial for combating piracy, smuggling, and terrorism, which threaten maritime security and regional stability. These collaborative efforts include:
- Joint naval exercises: Regular exercises improve interoperability, enhance coordination, and build trust between the naval forces.
- Intelligence sharing: The exchange of sensitive information is essential for effectively identifying and neutralizing threats.
- Coordinated patrols: Joint patrols help deter criminal activity, enhance situational awareness, and maintain order in shared maritime spaces.
The successful interception of smuggling vessels and the disruption of terrorist networks through joint operations demonstrate the tangible benefits of collaboration in combating transnational crime.
H3: Managing Maritime Disputes:
Establishing clear communication channels and mechanisms for resolving disputes peacefully is crucial for preventing escalation. This requires:
- Confidence-building measures: Initiatives that build trust and transparency between the navies, such as port visits and exchange programs, are essential for conflict prevention.
- Adherence to international law: Respecting and upholding the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is fundamental for resolving disputes peacefully.
- Diplomatic dialogue: Maintaining open communication channels and utilizing diplomatic mechanisms for resolving disputes peacefully is paramount.
By adhering to international law and engaging in diplomatic dialogue, both nations can effectively manage maritime disputes and prevent them from escalating into conflict.
H2: Defense Cooperation and Military Exchanges
Strengthening defense cooperation and fostering military-to-military exchanges enhance trust and understanding, reducing the risk of miscalculation and promoting stability.
H3: Joint Military Exercises:
Regular joint military exercises build interoperability, trust, and understanding between the armed forces. These exercises cover a range of scenarios, including:
- Types of joint exercises: Exercises can range from small-scale training to large-scale joint operations, focusing on disaster relief, counter-terrorism, and maritime security.
- Frequency of collaboration: Regular and frequent exercises solidify the partnership and demonstrate commitment to mutual security.
- Areas of focus: Exercises often concentrate on specific areas of concern, such as enhancing maritime domain awareness and coordinating responses to regional threats.
These joint exercises contribute significantly to building defense capabilities and mitigating the risk of miscalculation or unintended escalation.
H3: Arms Sales and Technology Transfer:
Controlled and transparent arms transfers can contribute to stability while mitigating the risk of an arms race. Transparency and safeguards are crucial to ensure responsible arms trade practices.
- Types of defense technology exchanged: The exchange should focus on technologies that enhance shared security goals, while avoiding transfers that could destabilize the region.
- Transparency measures: Open communication about arms transfers is crucial for building trust and preventing misunderstandings.
- Safeguards against misuse: Strict measures must be in place to ensure that transferred technologies are not misused and do not contribute to regional instability.
3. Conclusion:
Strengthening bilateral security between China and Indonesia requires a comprehensive approach encompassing economic cooperation, maritime security collaboration, and defense cooperation. By fostering deeper economic interdependence, addressing shared maritime challenges constructively, and enhancing military-to-military exchanges, both nations can build a stronger, more secure, and prosperous partnership. Continued investment in strengthening bilateral security: the China-Indonesia partnership will be crucial for maintaining regional stability and promoting shared prosperity in the Asia-Pacific region. Investing in and further developing this crucial partnership will be vital for long-term regional security and prosperity.

Featured Posts
-
 Pope Francis Death A Global Loss
Apr 22, 2025
Pope Francis Death A Global Loss
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Analyzing Chinas Economic Exposure To Increased Tariffs
Apr 22, 2025
Analyzing Chinas Economic Exposure To Increased Tariffs
Apr 22, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1 050 Price Increase From Broadcom
Apr 22, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1 050 Price Increase From Broadcom
Apr 22, 2025 -
 5 Essential Dos And Don Ts Succeeding In The Private Credit Market
Apr 22, 2025
5 Essential Dos And Don Ts Succeeding In The Private Credit Market
Apr 22, 2025 -
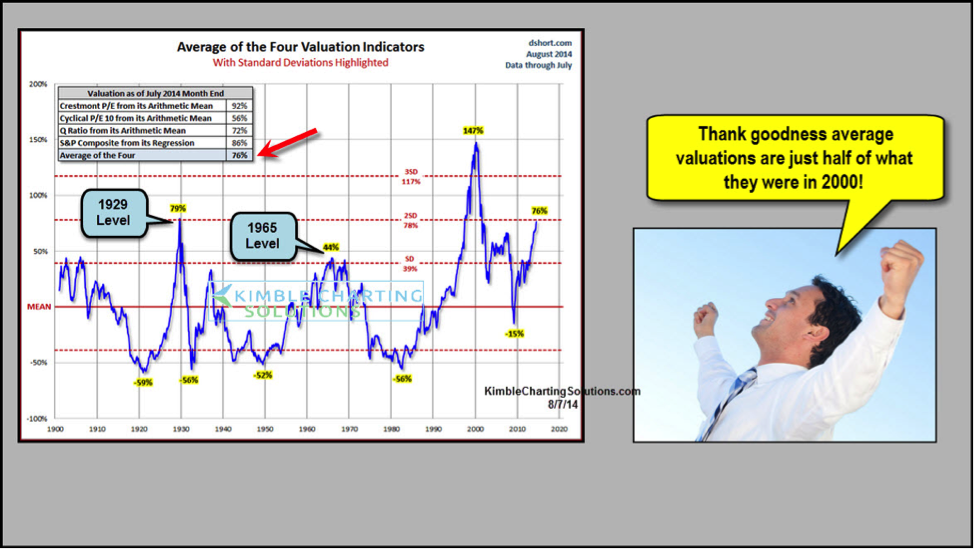 The Bof A View Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Cause For Alarm
Apr 22, 2025
The Bof A View Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Cause For Alarm
Apr 22, 2025
