The Impact Of Wildfires: Driving Record Global Forest Loss
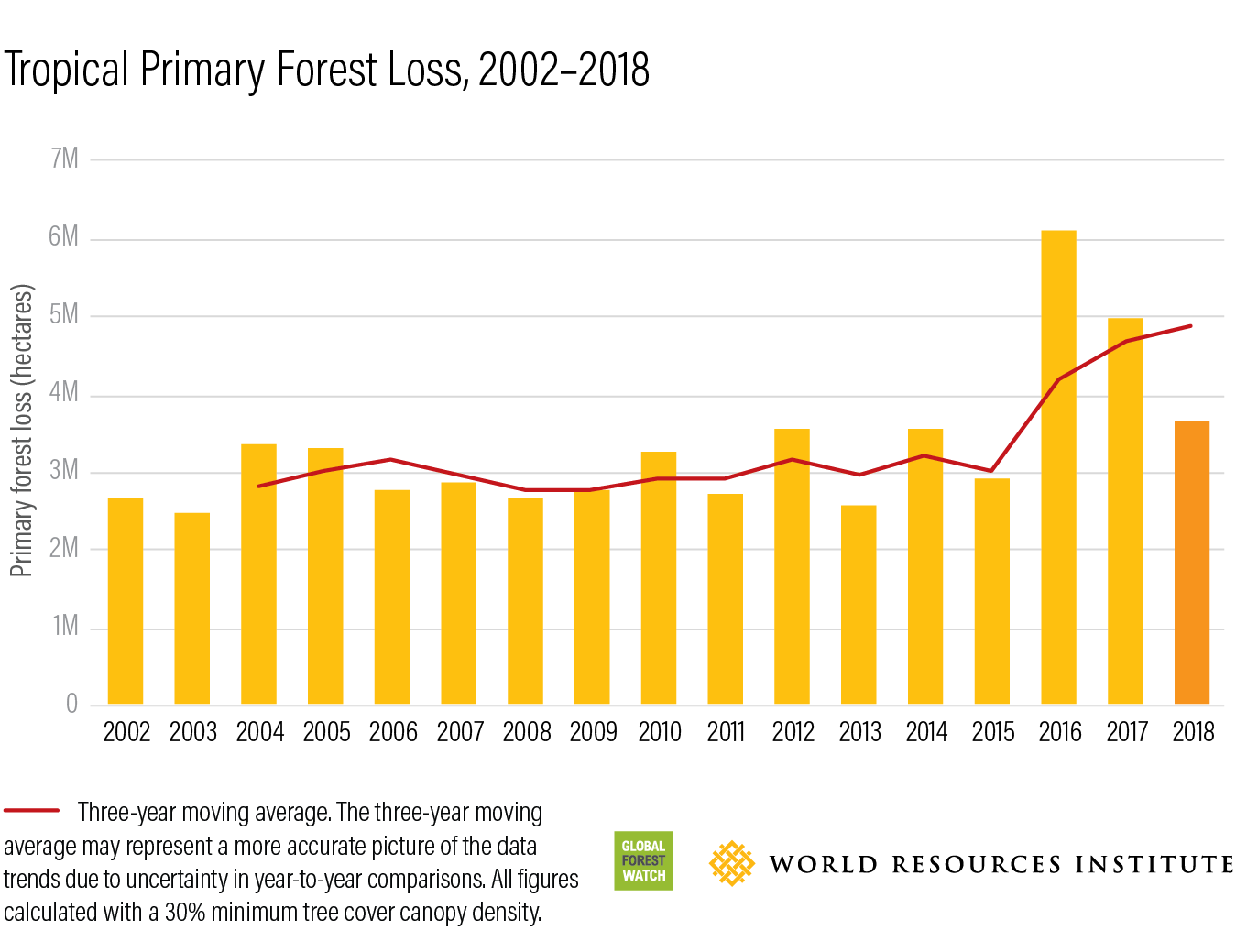
Table of Contents
H2: The Increasing Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
The dramatic increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires is a global concern, significantly contributing to the alarming rates of wildfires and global forest loss. This escalating trend is driven by a complex interplay of factors, primarily climate change and human activities.
H3: Climate Change as a Key Driver:
Rising global temperatures, fueled by greenhouse gas emissions, are creating conditions ripe for wildfires. Prolonged droughts, intensified heatwaves, and altered wind patterns exacerbate the problem, leading to:
- Increased ignition frequency: Dry vegetation and high temperatures increase the likelihood of accidental and naturally occurring ignitions.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer temperatures extend the period when wildfires can ignite and spread, increasing the overall risk.
- Faster fire spread: Stronger winds and drier fuels allow fires to spread rapidly and uncontrollably over vast areas.
- Larger burn areas: The increased intensity and duration of fires result in larger areas of forest being destroyed.
Data from NASA and the IPCC consistently show a strong correlation between rising global temperatures and an increase in both the number and severity of wildfires worldwide. For example, the average global temperature has risen by approximately 1°C since the pre-industrial era, significantly impacting wildfire activity.
H3: Human Activities and Wildfire Risk:
Human activities play a significant role in exacerbating the wildfire problem. Poor land management practices, deforestation for agriculture and urbanization, and accidental ignitions from power lines, discarded cigarettes, and campfires all contribute to the risk.
- Examples of human-caused wildfires: Many large and devastating wildfires are started by human negligence or deliberate acts of arson.
- Impact of poor forest management: Insufficient forest thinning and clearing of underbrush can create a buildup of flammable material, increasing the intensity and spread of fires.
- Role of infrastructure development near forests: Expanding infrastructure in proximity to forested areas increases the risk of ignition and makes firefighting more challenging.
Numerous reports highlight the significant contribution of human activities to wildfire incidents. For instance, a study published in Science showed that human-induced climate change significantly increased the risk of severe wildfires in California.
H2: Environmental Consequences of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The environmental consequences of wildfires and global forest loss are far-reaching and devastating, impacting biodiversity, carbon cycles, and vital ecosystems.
H3: Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction:
Wildfires cause widespread habitat destruction, leading to the loss of countless plant and animal species. Many endangered species are particularly vulnerable, facing increased extinction risks due to the loss of their habitat and disruption of their food sources.
- Loss of habitat: Wildfires can completely destroy the habitats essential for the survival of numerous plant and animal species.
- Disruption of food chains: The destruction of vegetation and prey animals disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems.
- Extinction risks: Many species are unable to adapt or relocate quickly enough to survive the devastation caused by wildfires.
- Impact on migratory patterns: Wildfires can disrupt the migration routes and breeding grounds of many species, further threatening their survival.
The impact on keystone species, such as the koala in Australia, is particularly concerning, highlighting the widespread implications of wildfires on biodiversity.
H3: Carbon Emissions and Climate Change Feedback Loop:
Wildfires release enormous quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to climate change. This creates a dangerous feedback loop: climate change increases the frequency and intensity of wildfires, which in turn release more greenhouse gases, further accelerating climate change.
- Carbon sequestration lost: Burning forests eliminate the capacity of trees to absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: Wildfires are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating global warming.
- The positive feedback loop between wildfires and climate change: This cyclical relationship intensifies the climate crisis.
Studies indicate that wildfires contribute substantially to global CO2 emissions, creating a devastating and self-perpetuating cycle.
H3: Soil Degradation and Water Cycle Disruption:
Wildfires severely damage the soil, leading to erosion, nutrient depletion, and disruption of the water cycle.
- Loss of topsoil: The intense heat of wildfires destroys the organic matter in the soil, leading to topsoil loss and reduced fertility.
- Increased soil erosion: The loss of vegetation cover exposes the soil to erosion by wind and water.
- Changes in water runoff: Burned areas experience altered water runoff patterns, leading to increased flooding and reduced water infiltration.
- Impact on water quality: Wildfires can contaminate water sources with ash, sediment, and chemicals.
The long-term effects on soil health and water resources can have severe consequences for agriculture and human populations.
H2: Economic and Social Impacts of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The economic and social costs associated with wildfires and global forest loss are substantial, impacting communities, economies, and public health.
H3: Economic Losses from Damage and Suppression:
Fighting wildfires is incredibly expensive, requiring significant resources and personnel. Beyond the costs of firefighting, property damage, loss of timber resources, and disruption to tourism severely impact local and national economies.
- Costs of firefighting efforts: The expense of deploying firefighters, equipment, and air support is immense.
- Insurance claims: Wildfires generate massive insurance claims, straining insurance companies and impacting premiums.
- Damage to infrastructure: Wildfires can destroy homes, businesses, roads, and other vital infrastructure.
- Loss of tourism revenue: Damage to forests and recreational areas can significantly impact tourism revenues.
The economic impact of major wildfires is often measured in billions of dollars, causing long-term financial strain on affected regions.
H3: Public Health Impacts of Wildfire Smoke:
Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that significantly impact public health, causing respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Air quality degradation: Wildfire smoke drastically reduces air quality, leading to hazardous levels of pollutants.
- Respiratory problems: Exposure to wildfire smoke can exacerbate asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Studies have linked wildfire smoke exposure to increased risks of heart attacks and strokes.
- Mental health impacts: The stress, displacement, and trauma associated with wildfires can have significant mental health consequences.
The health impacts of wildfire smoke extend far beyond the immediate vicinity of the fire, affecting large populations downwind.
H3: Displacement of Communities and Loss of Livelihoods:
Wildfires often force communities to evacuate their homes, leading to displacement, loss of livelihoods, and social disruption.
- Evacuations: Wildfires necessitate large-scale evacuations, disrupting lives and creating significant hardship.
- Loss of housing: Many homes and properties are destroyed by wildfires, leaving residents homeless.
- Impact on employment: Wildfires can cause significant job losses in affected industries, such as forestry and tourism.
- Social disruption: The trauma and displacement caused by wildfires have lasting social and psychological impacts on communities.
The social costs of wildfires are profound and often overlooked, impacting the well-being and resilience of affected communities.
3. Conclusion:
The devastating impacts of wildfires and global forest loss are multifaceted, encompassing severe environmental damage, substantial economic losses, and significant social consequences. The increasing frequency and intensity of these events demand urgent attention and collaborative action. Understanding the devastating impact of wildfires and global forest loss is crucial. Take action today by supporting organizations dedicated to forest conservation and wildfire prevention. Let's work together to mitigate the effects of wildfires and protect our planet's precious forests. Investing in preventative measures, improving forest management practices, and addressing climate change are vital steps toward reducing the risk and minimizing the catastrophic consequences of future wildfires and the resulting global forest loss.

Featured Posts
-
 The Blake Lively Taylor Swift And Gigi Hadid Drama A Familys Response
May 22, 2025
The Blake Lively Taylor Swift And Gigi Hadid Drama A Familys Response
May 22, 2025 -
 Trans Australia Run A Record In Jeopardy
May 22, 2025
Trans Australia Run A Record In Jeopardy
May 22, 2025 -
 Will Internal Gop Divisions Sink Trumps Tax Plan
May 22, 2025
Will Internal Gop Divisions Sink Trumps Tax Plan
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Positieve Kwartaalcijfers Leiden Tot Koersstijging
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Positieve Kwartaalcijfers Leiden Tot Koersstijging
May 22, 2025 -
 Yevrokomisar Pro Riziki Vstupu Ukrayini Do Nato Golovna Zagroza
May 22, 2025
Yevrokomisar Pro Riziki Vstupu Ukrayini Do Nato Golovna Zagroza
May 22, 2025
