The Ultimate Guide To Creatine: Benefits, Dosage, And Safety

Table of Contents
Understanding Creatine: What it is and How it Works
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring nitrogenous organic acid that plays a crucial role in energy production within muscle cells. Your body naturally produces creatine, and it's also found in small amounts in certain foods, primarily red meat and fish. Creatine's primary function is to help your muscles produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for muscle contractions. Different forms of creatine exist, with creatine monohydrate being the most studied and widely used.
- Key Facts about Creatine:
- It's a naturally occurring compound.
- It's primarily stored in skeletal muscle.
- It aids in ATP resynthesis, crucial for muscle energy.
- Creatine monohydrate is the most researched and effective form.
How Creatine Works in the Body
Creatine works by increasing the levels of phosphocreatine (PCr) in your muscles. PCr acts as a reservoir of high-energy phosphates, readily donating a phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to regenerate ATP. This rapid ATP regeneration allows for increased power output during short bursts of intense activity and reduces muscle fatigue.
- Creatine's Mechanism of Action:
- Creatine is transported into muscle cells.
- It's phosphorylated to form phosphocreatine (PCr).
- During intense exercise, PCr donates a phosphate to ADP, reforming ATP.
- This process provides quick energy for muscle contractions.
- Increased ATP availability leads to improved strength, power, and endurance.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Numerous studies show that creatine supplementation significantly enhances athletic performance, particularly in high-intensity activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and other anaerobic exercises. The increased ATP availability translates to improved strength, power, and increased work capacity.
- Athletic Activities Improved by Creatine:
- Weightlifting
- Sprinting
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
- Jumping and plyometrics
- Powerlifting
Muscle Growth and Hypertrophy
Creatine's impact extends beyond immediate performance gains. It plays a role in muscle protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass and hypertrophy (muscle growth). By promoting cell hydration and nutrient uptake, creatine creates a more favorable environment for muscle growth.
- Studies Showing Creatine's Positive Effect on Muscle Growth: Numerous peer-reviewed studies demonstrate significant increases in muscle mass and strength with creatine supplementation.
Cognitive Benefits
While primarily known for its effects on muscle performance, some research suggests potential cognitive benefits of creatine supplementation, particularly in improving memory and cognitive function in certain populations, although more research is needed in this area.
Creatine Dosage and Supplementation
Recommended Creatine Dosage
The typical creatine loading phase involves consuming 20 grams per day, divided into four 5-gram doses, for 5-7 days. This rapidly saturates your muscles with creatine. Following the loading phase, a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day is usually sufficient to maintain muscle creatine stores. Dosage may vary based on individual factors and training goals; always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- Daily Creatine Intake Guidelines:
- Loading Phase: 20 grams daily for 5-7 days.
- Maintenance Phase: 3-5 grams daily.
Best Ways to Take Creatine
Creatine can be consumed at any time of day, with or without food. Many athletes prefer to take it post-workout, but there's no definitive evidence that this timing significantly impacts effectiveness. Consistency is key – taking your creatine daily is crucial for maintaining elevated muscle creatine levels.
- Methods of Creatine Supplementation:
- Powder (easily mixed with water or juice)
- Capsules
Cycling Creatine
Creatine cycling (periods of supplementation followed by periods of no supplementation) is a commonly discussed strategy. While some believe it prevents potential side effects and maintains effectiveness, there's limited scientific evidence supporting its superiority over continuous supplementation. The decision to cycle creatine should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering individual circumstances.
Safety and Side Effects of Creatine
Potential Side Effects
The most common side effects of creatine supplementation are mild and include water retention (leading to weight gain) and occasional gastrointestinal discomfort. Serious side effects are rare when creatine is used appropriately.
- Potential Side Effects and Their Likelihood:
- Water retention (common)
- Weight gain (common)
- Gastrointestinal upset (less common)
Who Should Avoid Creatine?
Individuals with certain pre-existing medical conditions, such as kidney disease, should avoid creatine supplementation. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor before using creatine.
- Groups Who Should Avoid Creatine Supplementation:
- Individuals with kidney disease
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with pre-existing health conditions (consult your doctor)
Creatine and Kidney Function
Concerns about creatine causing kidney damage are largely unfounded. Numerous studies have shown that creatine supplementation does not negatively impact kidney function in healthy individuals. However, individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should avoid creatine supplementation.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate is a safe and effective supplement that can significantly enhance athletic performance, promote muscle growth, and potentially offer cognitive benefits. By following the recommended dosage guidelines, understanding potential side effects, and consulting a healthcare professional, you can safely maximize your fitness potential with creatine. Start your creatine journey safely and responsibly, ensuring you tailor your approach to your individual needs and goals. Learn more about optimizing your creatine intake for optimal results.

Featured Posts
-
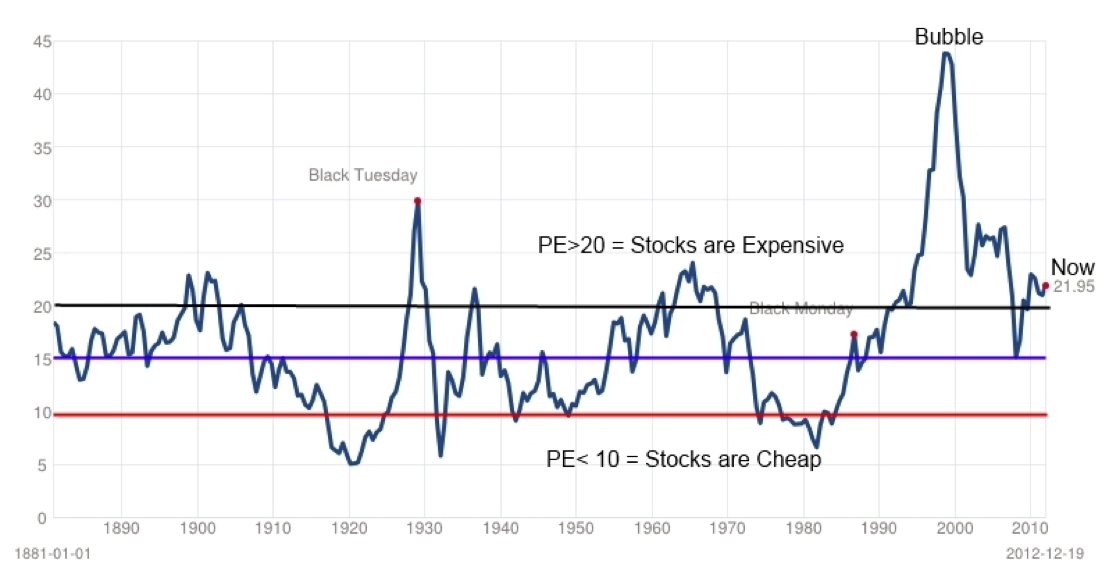 Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Red Flag A Bof A Analysis
May 16, 2025
Why Current Stock Market Valuations Are Not A Red Flag A Bof A Analysis
May 16, 2025 -
 Heat Butler Rift Jersey Numbers Highlight Deep Seated Tension Ho Fers Involvement
May 16, 2025
Heat Butler Rift Jersey Numbers Highlight Deep Seated Tension Ho Fers Involvement
May 16, 2025 -
 Dodgers Comeback Win Freeman And Kims Home Runs Fuel Rally Past Giants
May 16, 2025
Dodgers Comeback Win Freeman And Kims Home Runs Fuel Rally Past Giants
May 16, 2025 -
 Ankle Injury Update Jalen Brunsons Return Set For Sunday
May 16, 2025
Ankle Injury Update Jalen Brunsons Return Set For Sunday
May 16, 2025 -
 Victoria De Portugal Ante Belgica 0 1 Repaso Al Partido
May 16, 2025
Victoria De Portugal Ante Belgica 0 1 Repaso Al Partido
May 16, 2025
