Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Derailment: Months-Long Impact On Buildings
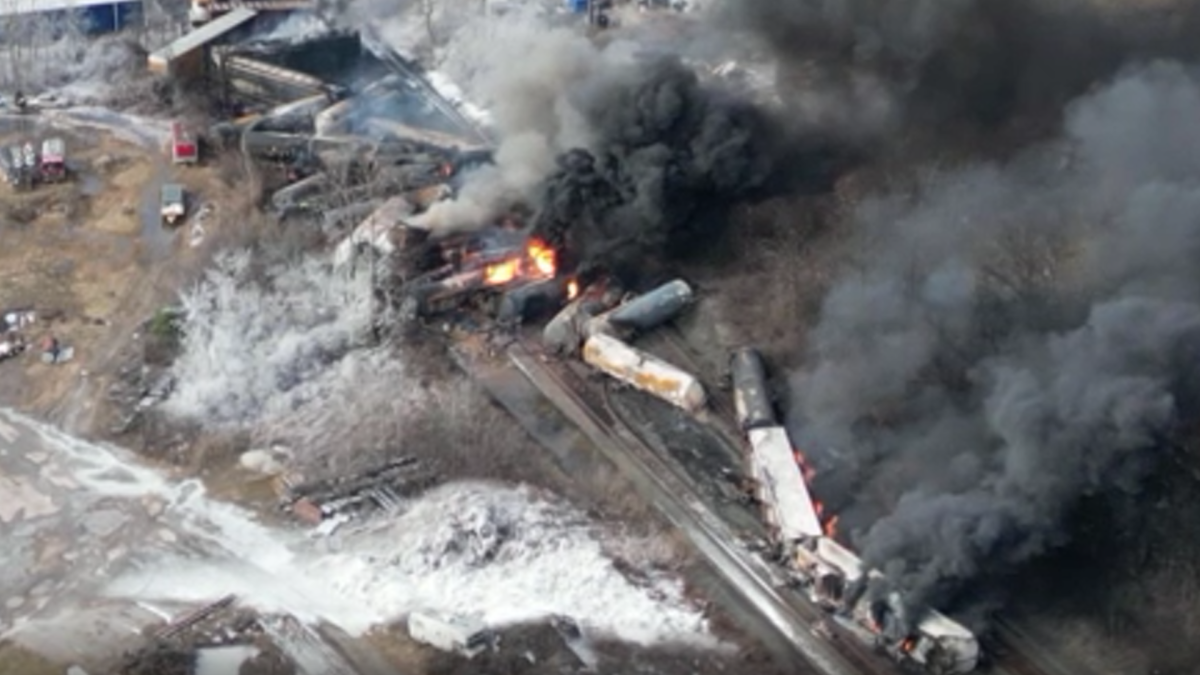

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Impact on Building Materials
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, including vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. These chemicals, known for their reactivity, pose a significant threat to various building materials.
-
Vinyl chloride: A colorless gas used in PVC production, vinyl chloride is a known carcinogen. Its interaction with building materials can lead to long-term degradation and potential structural weakening, particularly in older structures with less robust construction methods. It can also leach into the air within a building causing respiratory problems and other health issues.
-
Butyl acrylate: A colorless liquid used in paints, adhesives, and plastics, butyl acrylate can react with certain building materials causing discoloration, degradation, and potentially weakening structural elements over time. Long-term exposure to butyl acrylate vapors can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system.
-
Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether: Used as a solvent, this chemical can degrade various materials, including wood and some types of paint and coatings. Its impact on building materials might not be immediately apparent, but prolonged exposure can cause significant weakening over time, contributing to structural instability.
The potential for corrosion of metal components, like pipes and support beams, is also a major concern. The chemical reactions can lead to accelerated rusting and weakening, increasing the risk of structural failure. Similarly, wood structures are vulnerable to degradation, becoming brittle and less resistant to stress. Even concrete, though durable, can be affected by chemical reactions leading to cracking and a reduction in its load-bearing capacity. Materials like porous bricks and plaster are particularly susceptible to absorbing these chemicals, presenting ongoing risks.
Assessing and Mitigating Contamination in Buildings
Thorough assessment of building contamination is crucial to ensure the safety and habitability of structures in the affected area. This process involves a multi-faceted approach:
-
Building inspection: A detailed visual inspection of the building's structure, identifying areas with potential chemical residue, damage, or discoloration. Particular attention needs to be paid to areas with potential for chemical accumulation, such as basements and lower floors.
-
Environmental testing: Comprehensive testing of air, water, and soil samples to determine the extent and type of chemical contamination present. This data is essential for determining the appropriate remediation strategies. Sampling should be conducted by experienced environmental professionals to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
-
Remediation techniques: Depending on the level of contamination, remediation techniques may range from simple cleaning and ventilation to more extensive procedures like material removal and replacement. Decontamination protocols must be rigorously followed to protect workers and prevent further spread of contaminants.
-
Professional assistance: Engaging experienced environmental remediation specialists is essential for a safe and effective cleanup. Their expertise is vital in developing a tailored remediation plan and ensuring compliance with all safety regulations.
Long-Term Health Risks Associated with Building Contamination
Prolonged exposure to the toxic chemicals released during the derailment poses significant long-term health risks to residents and building occupants:
-
Respiratory problems: Inhalation of these chemicals can lead to various respiratory issues, ranging from irritation and coughing to more serious conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
-
Cancer risk: Several of the released chemicals are known or suspected carcinogens, increasing the risk of various cancers over time. The longer the exposure, the higher the risk.
-
Neurological effects: Some of these chemicals can affect the nervous system, leading to neurological problems ranging from headaches and dizziness to more severe cognitive impairments.
-
Other health effects: Exposure can also lead to skin irritation, eye irritation, and other health problems depending on the specific chemical and level of exposure. The insidious nature of these chemicals, capable of lingering in building materials for extended periods, poses a sustained threat to health. Ongoing monitoring and health assessments are vital for those living in affected areas.
The Psychological Impact on Building Inhabitants
The Ohio derailment's impact extends beyond physical health and structural damage. The event has created substantial psychological distress among residents:
-
Stress and anxiety: The fear of long-term health consequences, combined with property damage and uncertainty about the future, generates significant stress and anxiety.
-
Displacement and disruption: Evacuations and disruptions to daily life add further psychological strain, impacting mental well-being and exacerbating pre-existing conditions.
-
Community impact: The collective trauma experienced by the community necessitates the provision of adequate mental health support and resources. Access to counseling and community support networks is essential for facilitating healing and recovery.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's impact extends far beyond the immediate aftermath. The persistent presence of toxic chemical residue in buildings poses significant long-term health and structural risks. Thorough building inspections, effective remediation strategies, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for mitigating these threats. Understanding the potential dangers of long-term exposure to these chemicals is vital for protecting the health and well-being of the community. The psychological impact further underscores the need for comprehensive support and long-term monitoring.
Call to Action: Learn more about the ongoing impact of toxic chemical residue from the Ohio derailment and find resources for building inspections and remediation. Don't let the threat of toxic chemical residue in your building go unaddressed. Take action today to ensure the safety and well-being of your community. Contact your local authorities or environmental agencies to access resources and support related to building contamination from the Ohio derailment.

Featured Posts
-
 Palantir Technologies Stock Buy Sell Or Hold
May 10, 2025
Palantir Technologies Stock Buy Sell Or Hold
May 10, 2025 -
 The Billionaire Without Berkshire Shares Canadas Potential For Leadership In Investing
May 10, 2025
The Billionaire Without Berkshire Shares Canadas Potential For Leadership In Investing
May 10, 2025 -
 Live Stock Market Updates Trumps China Tariffs And Uk Trade Deal
May 10, 2025
Live Stock Market Updates Trumps China Tariffs And Uk Trade Deal
May 10, 2025 -
 Aoc Delivers Brutal Fact Check To Foxs Jeanine Pirro
May 10, 2025
Aoc Delivers Brutal Fact Check To Foxs Jeanine Pirro
May 10, 2025 -
 Gods Mercy Reaching All Faiths In 1889
May 10, 2025
Gods Mercy Reaching All Faiths In 1889
May 10, 2025
