Understanding High Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Perspective For Investors
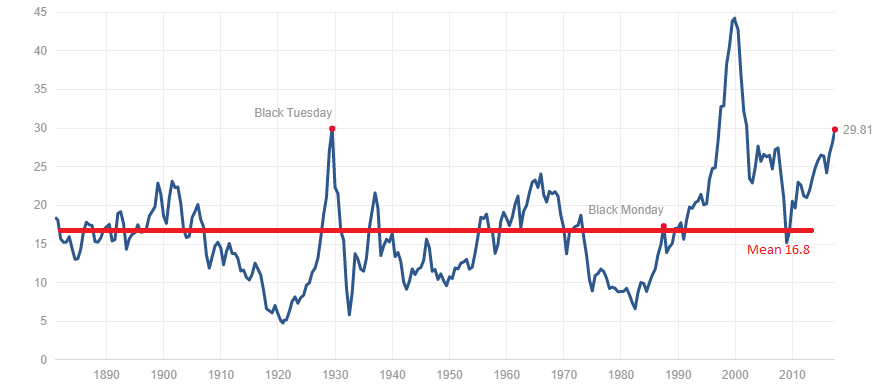
Table of Contents
BofA's Current Market Assessment and Valuation Metrics
BofA's current stance on market valuations often reflects a nuanced view, acknowledging both positive and negative factors. While specific data points change frequently, BofA typically employs a range of valuation metrics to assess the market's overall health. Their analysis considers whether current prices accurately reflect underlying company performance and future growth potential.
-
Key valuation metrics BofA uses: BofA's analysts utilize a variety of metrics including the Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E ratio), the cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings ratio (Shiller P/E), and the Price-to-Sales ratio. They also consider market capitalization and other fundamental data.
-
Comparison of current valuations to historical averages: BofA frequently compares current valuation metrics to historical averages to determine if the market is trading at a premium or discount. This historical context helps provide perspective on whether current valuations are unusually high or within a normal range. Deviations from historical norms are carefully scrutinized for potential risks and opportunities.
-
BofA's assessment of specific sectors or market segments: BofA's analysis isn't solely focused on broad market indices. Their experts dive into specific sectors, identifying those that appear overvalued or undervalued relative to their growth prospects and risk profiles. This granular approach helps investors make sector-specific decisions within their portfolios. For example, they may highlight technology stocks as potentially overvalued in a period of high interest rates, while favoring more defensive sectors.
Identifying Potential Risks Associated with High Valuations
High stock market valuations inevitably bring forth a range of potential risks, and BofA consistently highlights these concerns for investors. Understanding these risks is vital for mitigating potential losses.
-
Risk of a market correction or crash: When valuations are high, the potential for a sharp market correction is increased. A correction could be triggered by a variety of factors, including rising interest rates, unexpected economic news, or geopolitical instability. BofA's analyses frequently model potential downside scenarios to gauge the market's resilience.
-
Impact of rising interest rates on stock valuations: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for companies, impacting profitability and reducing the present value of future earnings. This often leads to lower stock valuations, particularly for growth stocks that rely heavily on future earnings projections. BofA's analysis incorporates interest rate forecasts and their potential effect on various market segments.
-
Geopolitical uncertainties and their influence on market performance: Global events, such as political instability or international conflicts, can significantly impact investor sentiment and market performance. These uncertainties can lead to increased volatility and market corrections, regardless of underlying valuations. BofA's analyses consider these geopolitical factors and assess their potential consequences.
-
Inflation's effect on valuations and earnings: High inflation erodes purchasing power and increases input costs for businesses. This can squeeze profit margins and lead to lower earnings, potentially justifying lower stock valuations. BofA carefully monitors inflation data and its impact on corporate profitability and market sentiment.
BofA's Recommendations and Investment Strategies for Investors
BofA generally advises a cautious but not overly pessimistic approach to investing during periods of high stock market valuations. Their recommendations emphasize strategic risk management and diversification.
-
BofA's suggested portfolio diversification strategies: Diversification across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) and sectors is key to mitigating risk. This reduces the impact of underperformance in any single segment.
-
Recommended sectors or asset classes for current market conditions: BofA's recommendations on specific sectors and asset classes vary depending on the prevailing market conditions and outlook. They may favor defensive sectors (utilities, consumer staples) during periods of uncertainty or rotate towards growth sectors (technology, healthcare) when the outlook improves.
-
Strategies for mitigating risk in a high-valuation market: Risk mitigation strategies include employing stop-loss orders, hedging positions, and diversifying across geographies. BofA emphasizes the importance of a well-defined risk tolerance and investment plan.
-
Importance of long-term investing: BofA consistently underscores the importance of maintaining a long-term investment horizon. Short-term market fluctuations should not dictate long-term investment strategies.
The Role of Quantitative and Qualitative Factors in BofA's Analysis
BofA's analysis of high stock market valuations is not solely reliant on quantitative data; it incorporates qualitative factors for a more comprehensive perspective.
-
Examples of quantitative factors used: These include economic data (GDP growth, inflation rates, unemployment), financial ratios (P/E ratio, debt-to-equity ratio), and market indicators (volatility indices).
-
Examples of qualitative factors considered: Qualitative factors include investor sentiment, geopolitical events, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions. These influence market psychology and can impact valuations regardless of quantitative data.
-
How BofA integrates these factors for a comprehensive assessment: BofA combines quantitative and qualitative analysis to arrive at a holistic view of the market. They understand that purely data-driven analysis can be incomplete without considering the context provided by qualitative factors.
Conclusion
This article reviewed BofA's insights on high stock market valuations, highlighting current market assessments, potential risks, and suggested investment strategies. Understanding these factors is crucial for informed decision-making. BofA's approach, balancing quantitative and qualitative analysis, provides investors with a comprehensive framework for navigating this complex environment.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving landscape of high stock market valuations. Continue to research BofA's analyses and other reputable sources to refine your investment strategy and navigate the market effectively. Learn more about managing risk in periods of high stock market valuations and build a robust, diversified portfolio that aligns with your risk tolerance and long-term financial goals.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding The Surge In The Venture Capital Secondary Market
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding The Surge In The Venture Capital Secondary Market
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Schumer Rejects Leadership Challenges I M Staying Put Cnn Politics
Apr 29, 2025
Schumer Rejects Leadership Challenges I M Staying Put Cnn Politics
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Post Trump Funding Cuts A Global Competition For American Scientific Talent
Apr 29, 2025
Post Trump Funding Cuts A Global Competition For American Scientific Talent
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Solve Nyt Strands Hints And Answers For The March 3 2025 Puzzle
Apr 29, 2025
Solve Nyt Strands Hints And Answers For The March 3 2025 Puzzle
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Finding Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets Strategies And Resources
Apr 29, 2025
Finding Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets Strategies And Resources
Apr 29, 2025
