Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Argument For Investor Calm
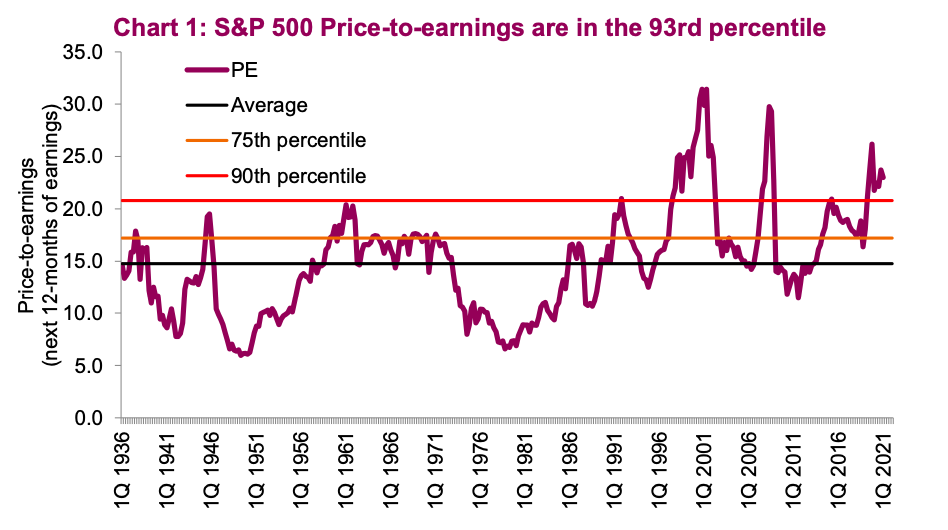
Table of Contents
BofA's Key Arguments for a Less Bearish Outlook
BofA's recent reports advocate for a less bearish outlook on the stock market, primarily focusing on the disconnect between current market prices and underlying company fundamentals. Their analysis suggests that many assets are undervalued, presenting potential opportunities for long-term investors.
-
Emphasis on the disconnect between current market prices and underlying fundamentals: BofA highlights that while market sentiment might be negative, reflecting concerns about inflation and interest rates, the actual earnings growth of many companies remains robust. This suggests that the current market correction may not fully reflect the underlying strength of the economy. Analyzing the relationship between stock prices and earnings per share (EPS) is key to this argument.
-
Highlighting specific sectors or industries undervalued according to BofA's analysis: BofA's research often points to specific sectors, such as certain technology companies or energy producers, as being particularly undervalued based on their future earnings potential. These sectors might be currently experiencing temporary headwinds, but their long-term prospects remain strong according to BofA's assessment.
-
Discussion of BofA's assessment of macroeconomic factors and their impact on valuations: BofA incorporates macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical risks into their valuation models. While acknowledging the impact of these factors, they argue that the current market downturn has over-corrected, leading to undervaluation in certain areas.
-
Mention of specific valuation metrics used by BofA (e.g., P/E ratios, PEG ratios): BofA employs various valuation metrics, including Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios, Price-to-Earnings-Growth (PEG) ratios, and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios. By comparing these ratios to historical averages and those of similar companies, they identify potential discrepancies that suggest undervaluation. (Include a hypothetical chart here showing a comparison of current P/E ratios to historical averages, illustrating BofA's point.)
-
Analyzing discounted cash flow (DCF) models: BofA likely also uses more complex models like DCF analysis to project future cash flows and determine intrinsic value. This provides a longer-term perspective on valuation, less susceptible to short-term market fluctuations.
Understanding Different Valuation Methods
Understanding various valuation methods is essential for interpreting stock market data and forming your own informed opinions. Here are some commonly used methods:
-
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E): This is a crucial metric calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio might indicate that the market expects high future growth, but it can also signal overvaluation. A low P/E ratio may indicate undervaluation or potential risks.
-
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B): This ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). A low P/B ratio might suggest undervaluation, especially for companies with substantial tangible assets.
-
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S): This ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its revenue. It is particularly useful for valuing companies with little or no earnings, such as young, high-growth technology firms.
-
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis: DCF analysis is a more complex method that involves projecting a company's future cash flows and discounting them back to their present value. This provides a measure of intrinsic value, independent of market sentiment.
Addressing Investor Concerns: Common Market Fears and BofA's Response
Investors often have several concerns influencing their decisions regarding stock market valuations. Let's examine some common fears and how BofA's analysis addresses them:
-
Inflation: BofA acknowledges inflation's impact on valuations but might argue that the market has already priced in a significant portion of expected inflation, leading to a more attractive entry point for long-term investors.
-
Interest Rate Hikes: While interest rate hikes increase borrowing costs for companies, BofA's analysis might show that the current rate increases are already factored into market prices and that long-term growth prospects remain strong.
-
Geopolitical Risks: Geopolitical events undoubtedly introduce uncertainty, but BofA's perspective might be that the market often overreacts to such events, creating buying opportunities for those with a longer-term view.
-
Recessions: BofA's research would likely address recessionary concerns by analyzing the strength of underlying company fundamentals. Strong balance sheets and consistent earnings growth can help companies weather economic downturns.
(Include a table summarizing BofA's responses to these concerns, citing specific data points from their reports, if possible.) It's crucial to remember that relying solely on one source, even a reputable one like BofA, is risky. Always conduct your own thorough independent research.
The Importance of Long-Term Investment Strategies
Navigating market volatility requires a long-term perspective. Short-term fluctuations don't necessarily reflect long-term value.
-
Long-term value vs. short-term fluctuations: Focusing on the long-term fundamentals of a company, rather than daily price movements, is key.
-
Diversification: A diversified portfolio across different asset classes and sectors can mitigate risk significantly.
-
Well-defined investment plan: Having a clear investment plan, tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals, is essential. Regularly review and adjust your plan based on market conditions and your evolving needs.
Conclusion:
Understanding stock market valuations is crucial for making informed investment decisions. While market volatility can be unsettling, BofA's analysis provides a reasoned perspective, suggesting that current valuations might present opportunities for long-term investors. By carefully considering BofA's arguments and employing diverse valuation methods, you can navigate the market with greater confidence. Remember to conduct your own thorough research and develop a robust investment strategy to effectively manage your portfolio. Don't let short-term market fluctuations overshadow the potential for long-term growth in understanding stock market valuations. Begin your research today and learn more about effective stock market valuation techniques.

Featured Posts
-
 Fin Del Camino Para Paolini Y Pegula En El Wta 1000 De Dubai
Apr 27, 2025
Fin Del Camino Para Paolini Y Pegula En El Wta 1000 De Dubai
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Svitolinas Convincing First Round Victory At The Us Open
Apr 27, 2025
Svitolinas Convincing First Round Victory At The Us Open
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Anti Trump Sentiment In Canada Albertas Unique Position
Apr 27, 2025
Anti Trump Sentiment In Canada Albertas Unique Position
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Tennis Star Sinner Resolves Doping Case
Apr 27, 2025
Tennis Star Sinner Resolves Doping Case
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Rybakina Wins Three Set Battle Against Jabeur In Abu Dhabi
Apr 27, 2025
Rybakina Wins Three Set Battle Against Jabeur In Abu Dhabi
Apr 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Posthaste Measuring The Us Economic Fallout From The Canadian Travel Boycott
Apr 28, 2025
Posthaste Measuring The Us Economic Fallout From The Canadian Travel Boycott
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Ev Mandate Opposition Intensifies Car Dealers Push Back
Apr 28, 2025
Ev Mandate Opposition Intensifies Car Dealers Push Back
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Court Rules On E Bays Liability For Banned Chemicals Under Section 230
Apr 28, 2025
Court Rules On E Bays Liability For Banned Chemicals Under Section 230
Apr 28, 2025 -
 E Bay Faces Legal Action Section 230 And The Sale Of Banned Chemicals
Apr 28, 2025
E Bay Faces Legal Action Section 230 And The Sale Of Banned Chemicals
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Individual Charged With Millions In Losses From Office365 Executive Account Hacks
Apr 28, 2025
Individual Charged With Millions In Losses From Office365 Executive Account Hacks
Apr 28, 2025
