Understanding The New COVID-19 Variant And Its Impact On Case Numbers
Table of Contents
Identifying the New COVID-19 Variant (Variant X)
Variant X, a new lineage of SARS-CoV-2, was first identified in [Insert Location and Date if available]. Its emergence has raised concerns due to several key genetic mutations. These mutations, located in [specify locations in the viral genome e.g., spike protein], may affect its behavior in several ways:
-
Key Mutations and Locations: [List specific mutations and their locations e.g., Spike protein mutation at position 484 (E484K), etc.]. Further research is needed to fully understand the functional implications of each mutation.
-
Increased Transmissibility: Early evidence suggests [state evidence for or against increased transmissibility, e.g., a higher R0 value compared to previous variants or anecdotal evidence from epidemiological studies]. This needs further investigation.
-
Increased Severity: Data on the severity of illness caused by Variant X is still being collected. Initial reports suggest [mention current findings regarding hospitalization and mortality rates, citing sources like the WHO or CDC].
-
Impact on Vaccine Efficacy: The effectiveness of existing vaccines against Variant X is currently under evaluation. Studies are underway to determine whether current vaccines provide sufficient protection, and if booster shots are necessary to enhance immunity. [Cite any available studies on vaccine effectiveness against this variant].
-
Comparison with Previous Variants: Preliminary data suggests that Variant X shares some similarities with [mention similar variants e.g., Omicron subvariants], but also exhibits distinct characteristics that warrant close monitoring.
Analyzing the Impact on Case Numbers
Since the emergence of Variant X, we have observed [describe the trend in case numbers – increase, decrease, plateau, etc.]. [Insert relevant data and statistics here, clearly referencing your sources (e.g., WHO, CDC, national public health agencies)].
-
Case Number Trends: [Provide specific data points – e.g., "Case numbers increased by X% in the first two weeks following the identification of Variant X."]
-
Geographic Distribution: The variant appears to be [Describe the geographic spread of the variant – localized, widespread, etc.]. Regions with [mention factors correlating with higher case numbers e.g., lower vaccination rates] have seen a more pronounced increase in cases.
-
Age Groups Most Affected: Currently available data shows that [mention age demographics most affected, citing your source].
-
Hospitalization and Death Rates: [Present data on hospitalization and death rates associated with the variant, referencing reliable sources].
Understanding the Spread and Transmission of the New Variant
The rapid spread of Variant X may be attributed to several factors, including:
-
Increased Transmissibility: As mentioned earlier, [reiterate information about transmissibility, potentially including the R0 value if available].
-
Waning Immunity: Decreased immunity from previous infection or vaccination might contribute to increased susceptibility.
-
Behavior Changes: Relaxation of public health measures could have facilitated the spread.
-
Preventative Measures: The effectiveness of existing preventative measures, such as vaccination, masking, and social distancing, in controlling the spread of Variant X is crucial. [Discuss findings on the effectiveness of each measure].
-
R0 Value: [If available, include the R0 value and explain its significance].
-
Vaccine and Treatment Effectiveness: The effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments against Variant X requires ongoing evaluation. [Summarize the current understanding].
-
Potential for Future Mutations: The ongoing evolution of the virus underscores the importance of continued surveillance and preparedness for future variants.
The Role of Vaccination and Public Health Measures
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of our defense against COVID-19, even with the emergence of new variants.
-
Vaccination Rates: High vaccination rates are crucial in minimizing severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
-
Effectiveness of Booster Shots: Booster shots can significantly enhance protection against new variants, including Variant X. [Discuss current recommendations for booster shots].
-
Public Health Measures: Even with vaccination, public health measures, including mask-wearing in high-risk settings, social distancing, and good hygiene, remain vital tools in limiting transmission.
-
Recommendations from Public Health Organizations: Following the guidance of reputable organizations such as the WHO and CDC is paramount.
Conclusion: Staying Informed About the New COVID-19 Variant and its Impact on Case Numbers
Variant X, like previous variants, highlights the dynamic nature of the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding its characteristics and impact on case numbers is crucial for effective public health strategies. While vaccines remain effective, ongoing surveillance, vaccination, and public health measures are vital to manage the virus. Staying informed about the latest developments is key. Consult reliable sources such as the World Health Organization (WHO) [link to WHO website] and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) [link to CDC website] for up-to-date information on the new COVID-19 variant and its impact on case numbers. Your vigilance and informed actions are crucial in mitigating the spread and impact of this evolving virus.

Featured Posts
-
 The Good Life Practical Steps For A More Fulfilling Life
May 31, 2025
The Good Life Practical Steps For A More Fulfilling Life
May 31, 2025 -
 How To Achieve The Good Life A Step By Step Plan
May 31, 2025
How To Achieve The Good Life A Step By Step Plan
May 31, 2025 -
 Navigate Office Lunch With Confidence 6 Etiquette Rules
May 31, 2025
Navigate Office Lunch With Confidence 6 Etiquette Rules
May 31, 2025 -
 Experienced Glastonbury Goers The One Item That Saves You Cash
May 31, 2025
Experienced Glastonbury Goers The One Item That Saves You Cash
May 31, 2025 -
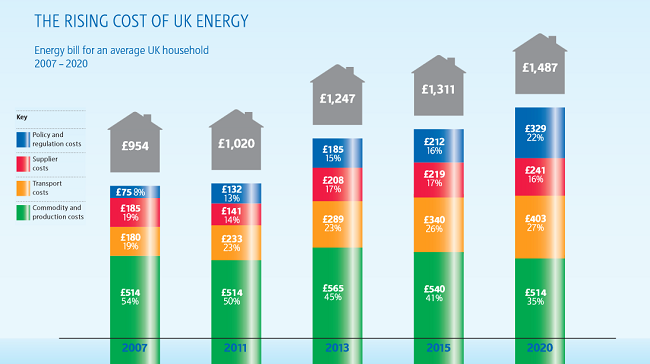 Are Corporate Targets To Blame For Rising Uk Pet Healthcare Costs
May 31, 2025
Are Corporate Targets To Blame For Rising Uk Pet Healthcare Costs
May 31, 2025
