Sharp Decline In Indonesia's Reserves: Impact Of Rupiah Depreciation
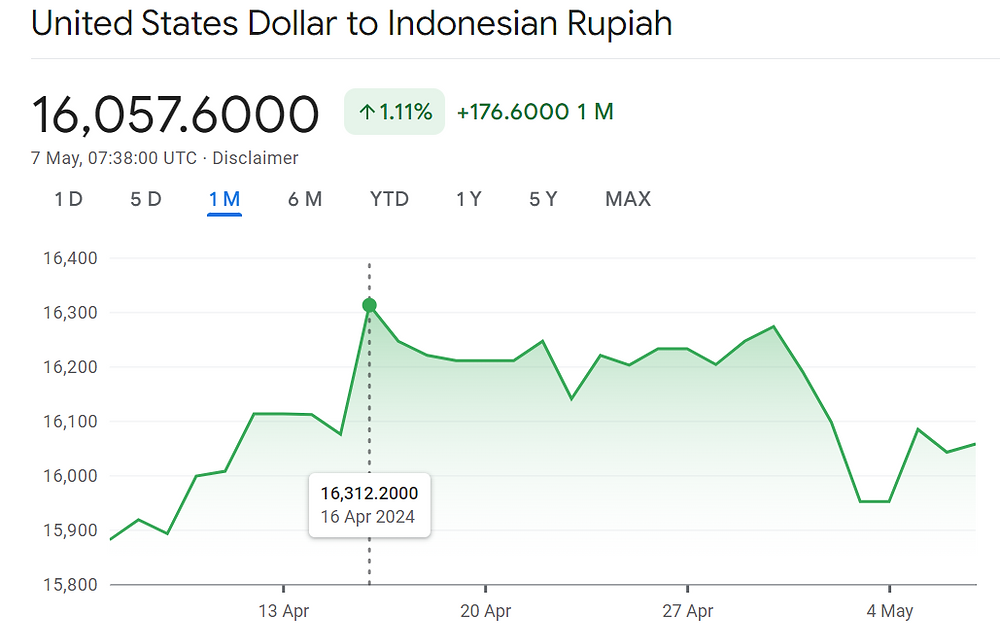
Table of Contents
Understanding the Rupiah Depreciation
Rupiah depreciation refers to a decrease in the value of the Indonesian Rupiah relative to other currencies. Simply put, it means you need more Rupiah to buy the same amount of foreign currency. This weakening occurs due to a complex interplay of factors. Recently, the Rupiah has faced significant pressure from:
- Global economic uncertainty: Global economic slowdowns, geopolitical tensions, and uncertainties in the global financial markets often lead to capital flight from emerging markets like Indonesia, putting downward pressure on the Rupiah.
- Inflationary pressures: Higher inflation rates in Indonesia compared to other countries can make the Rupiah less attractive to investors, leading to depreciation. Increased import costs, fueled by global inflation, further exacerbate this issue.
- Interest rate differentials: If interest rates in other countries are higher than in Indonesia, investors may move their funds elsewhere, reducing demand for the Rupiah and causing depreciation.
- Trade balance fluctuations: A persistent trade deficit (importing more than exporting) weakens the demand for the Rupiah, as the country needs to buy more foreign currency to pay for imports.
- Political and geopolitical risks: Political instability or escalating geopolitical tensions within Indonesia or in the broader region can trigger capital flight and put pressure on the Rupiah.
A weaker Rupiah increases import costs, as Indonesian businesses need to spend more Rupiah to purchase foreign goods. This leads to higher prices for consumers and contributes to inflationary pressures within the country.
The Link Between Rupiah Depreciation and Foreign Exchange Reserves
A depreciating Rupiah directly impacts Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves. When the Rupiah falls, the Indonesian government and Bank Indonesia (BI) may need to intervene in the foreign exchange market to buy Rupiah and support its value. This intervention requires using the country's foreign exchange reserves, leading to their depletion.
Bank Indonesia plays a crucial role in managing these reserves and stabilizing the Rupiah. To counter Rupiah depreciation, BI might employ several strategies:
- Interest rate hikes: Raising interest rates makes it more attractive for investors to hold Rupiah-denominated assets, increasing demand and supporting the currency.
- Foreign exchange interventions: BI can sell its US dollar reserves to buy Rupiah, directly increasing demand and supporting the exchange rate.
- Capital controls (if applicable): In extreme cases, the government might implement capital controls to limit the outflow of capital from the country.
- Macroprudential policies: These policies aim to strengthen the financial system's resilience against external shocks and can indirectly help manage exchange rate fluctuations.
The effectiveness of these strategies depends on various factors, including the severity of the pressure on the Rupiah and the overall global economic environment.
Economic Consequences of Declining Reserves
Declining foreign exchange reserves have several serious economic consequences for Indonesia. A weakening Rupiah and reduced reserves can significantly impact:
- Investor confidence: A depreciating currency and falling reserves can signal economic instability, leading to reduced foreign investment and potentially capital flight.
- Credit rating and borrowing costs: Lower reserves can negatively affect Indonesia's credit rating, making it more expensive for the government to borrow money internationally.
- Various sectors of the Indonesian economy: The impact spreads across various sectors:
- Increased import costs for businesses and consumers.
- Higher inflation, eroding purchasing power.
- Reduced competitiveness for Indonesian exports.
- Potential for economic slowdown and job losses.
Maintaining adequate foreign exchange reserves is crucial for Indonesia's economic stability and its ability to withstand external shocks.
Government Policies and Mitigation Strategies
The Indonesian government has implemented various measures to address the Rupiah depreciation and dwindling reserves. These include fiscal reforms aimed at improving the budget balance, structural reforms to boost economic competitiveness, and efforts to diversify export markets to reduce reliance on specific commodities. Long-term strategies involve:
- Fiscal reforms: Improving government revenue collection and controlling expenditure can strengthen the economy's fundamentals.
- Structural reforms: Improving ease of doing business, enhancing infrastructure, and promoting human capital development can attract foreign investment and improve long-term economic growth.
- Diversification of export markets: Reducing reliance on a few key export markets can make the Indonesian economy less vulnerable to external shocks.
- Promoting foreign investment: Attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) can increase foreign currency inflows and strengthen the Rupiah.
The effectiveness of these policies will depend on their implementation and the evolving global economic landscape.
Conclusion
The sharp decline in Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves is strongly linked to the ongoing Rupiah depreciation. This weakening of the currency has significant economic consequences, impacting investor confidence, inflation, and various sectors of the Indonesian economy. Close monitoring of the situation is crucial. The government's response, including fiscal and structural reforms, will play a vital role in mitigating these challenges and building more resilient reserves. Stay updated on the latest developments regarding Rupiah depreciation by following reputable financial news sources and consulting with economic experts. Understanding the dynamics of IDR depreciation is essential for navigating the complexities of the Indonesian economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Donner Ses Cheveux A Dijon Guide Pratique Pour Une Bonne Cause
May 10, 2025
Donner Ses Cheveux A Dijon Guide Pratique Pour Une Bonne Cause
May 10, 2025 -
 Will Hertl Play Golden Knights Game Against Lightning In Jeopardy
May 10, 2025
Will Hertl Play Golden Knights Game Against Lightning In Jeopardy
May 10, 2025 -
 Adani Ports Jumps 4 Market Rebound Detailed Stock Market Analysis
May 10, 2025
Adani Ports Jumps 4 Market Rebound Detailed Stock Market Analysis
May 10, 2025 -
 Indian Stock Market Update Sensex And Nifty Record Significant Gains
May 10, 2025
Indian Stock Market Update Sensex And Nifty Record Significant Gains
May 10, 2025 -
 The Billionaire Without Berkshire Shares Canadas Potential For Leadership In Investing
May 10, 2025
The Billionaire Without Berkshire Shares Canadas Potential For Leadership In Investing
May 10, 2025
